Google's omnipresence in our daily lives is undeniable. Recent statistics reveal that Google has over 91 percent of the search engine market share. Every click, search, and interaction feeds into an extensive data collection matrix, painting a detailed portrait of your online persona and general habits.
Yet what exactly does Google know about you? The answer may startle you. Google meticulously tracks your search history, location, app usage, and even voice commands. This data, while enhancing the user experience (mostly), raises significant privacy concerns. Understanding Google's data practices is crucial in navigating the digital world in an informed way.
Google's Data Collection Mechanisms
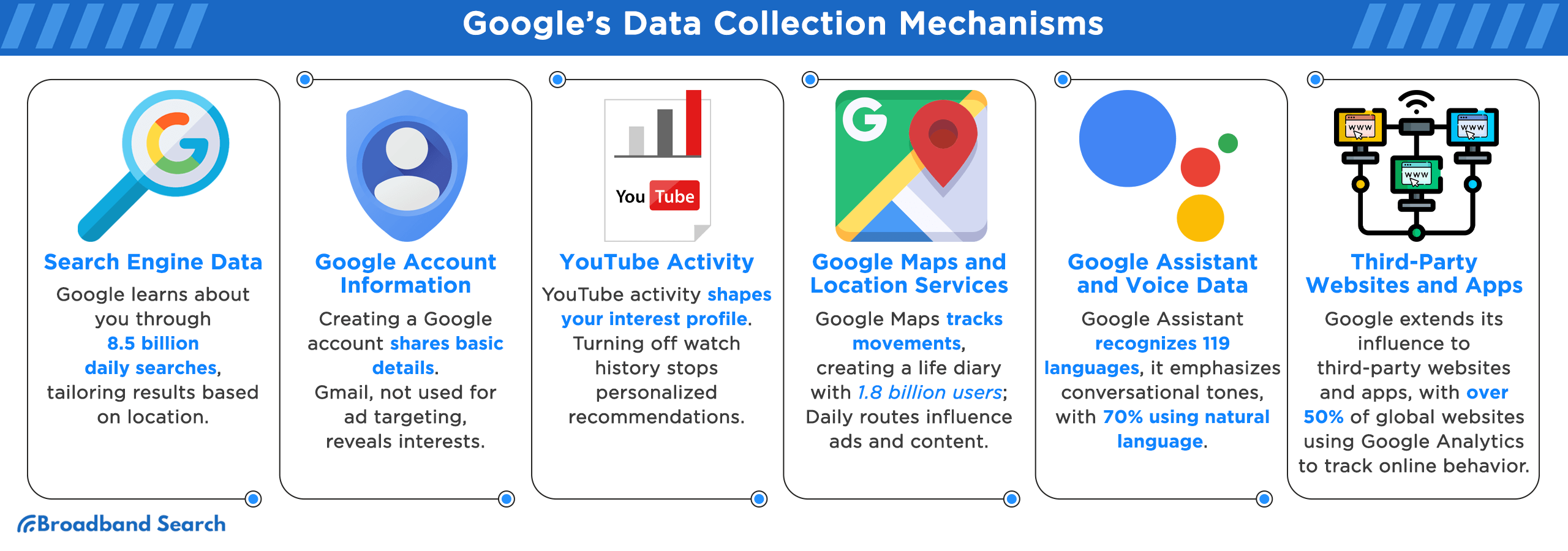
Search Engine Data
Google knows you mostly through the lens of your searches. Each query, from the mundane to the personal, answers your questions. Yet it also tells Google about your interests, concerns, and curiosities. One piece of research shows that Google processes over 8.5 billion searches daily. Each search makes Google just a bit more confident about what people are looking for.
Google tailors your search results based on location, making them more relevant. Yet to do so, they need to pinpoint your whereabouts. Google can map your movements and preferences regarding places you stay and visit, offering Google a vivid picture of your lifestyle and routines. It's not just about finding the nearest coffee shop but understanding your daily patterns.
Google Account Information
When you create a Google account, you hand over key personal details - your name, age, and gender (if you want to share). This basic information sets the foundation of what Google knows about you.
Yet there's more. If you use Gmail, Google has potential access to a wealth of information. Your emails can reveal your interests, habits, and even your social connections. But let's clarify one thing right away—Google states that it doesn't scan or read your Gmail messages to target ads.
While Gmail may not be used for ad targeting, Google doesn't shy away from collecting data. Consider this: Google blocks over 100 million emails daily for malware and phishing. While it's for security reasons, it highlights the vast amount of data Google handles daily. Your email content, although not for ads, is very much part of this statistic.
YouTube Activity
Your YouTube activity is a goldmine for Google. Every video you watch and every preference you express adds to a detailed profile of your interests and tastes. When YouTube watch history is deleted or turned off, YouTube no longer personalizes their experience with video recommendations. The updated interface shows only a search bar and a basic menu, not a feed of suggested videos.
However, Google retains this deleted history in the user's Google account settings under "My Activity." Google's data retention policy allows for some data to be kept for a period even after a user deletes it, including account information for about a month after deletion. Additionally, YouTube comments and interactions aren't affected by deleting watch history
Google Maps and Location Services
Google Maps and Location Services are like a digital compass, guiding you and tracking your movements. Each place you visit, whether frequently or occasionally, is logged. Google's location tracking can create a detailed map of your life, from your favorite cafe to your workplace. With 1.8 billion monthly users, Google Maps is more than a navigation tool; it's a diary of your whereabouts.
This data isn't just about where you've been; it also shapes where Google thinks you might want to go next. According to their privacy policy, location-based recommendations help in improving their services, including making ads more relevant. This means your daily routes influence the ads and content you see online. Recognizing this link between your movements and digital content enriches your understanding of how deeply integrated Google's data collection is in everyday life.
Google Assistant and Voice Data
Google Assistant learns about you through your voice commands and queries. Every "Hey Google" moment is a data point, from setting alarms to asking random questions. In the U.S., 41 percent of adults use voice search daily, and the global count of voice assistants is expected to reach over 8.4 billion by 2024. The assistant recognizes an impressive 119 languages, indicating its broad scope.
The use of natural language in almost 70 percent of Google Assistant requests marks a shift from traditional keyword searches to more conversational tones. Additionally, the Read Aloud feature's adaptation to various accents like British, Indian, and Australian English underscores Google's advanced voice data analysis capabilities.
Third-Party Websites and Apps
Google's reach extends beyond its own services to third-party websites and apps. Many sites use Google Analytics, which tracks and analyzes your online behavior. Shockingly, over 50% of all websites globally use this service, allowing Google to see your browsing patterns.
Moreover, third-party apps play a significant role in Google's data collection. An analysis by cloud storage company pCloud found that 52 percent of apps share user data with third-parties, with 80 percent of these apps using the data to market their products within the app and deliver ads on other platforms. This indicates a significant amount of data exchange between Google and various apps, contributing to a comprehensive profile of user behavior and preferences.
Data Analysis and Profiling
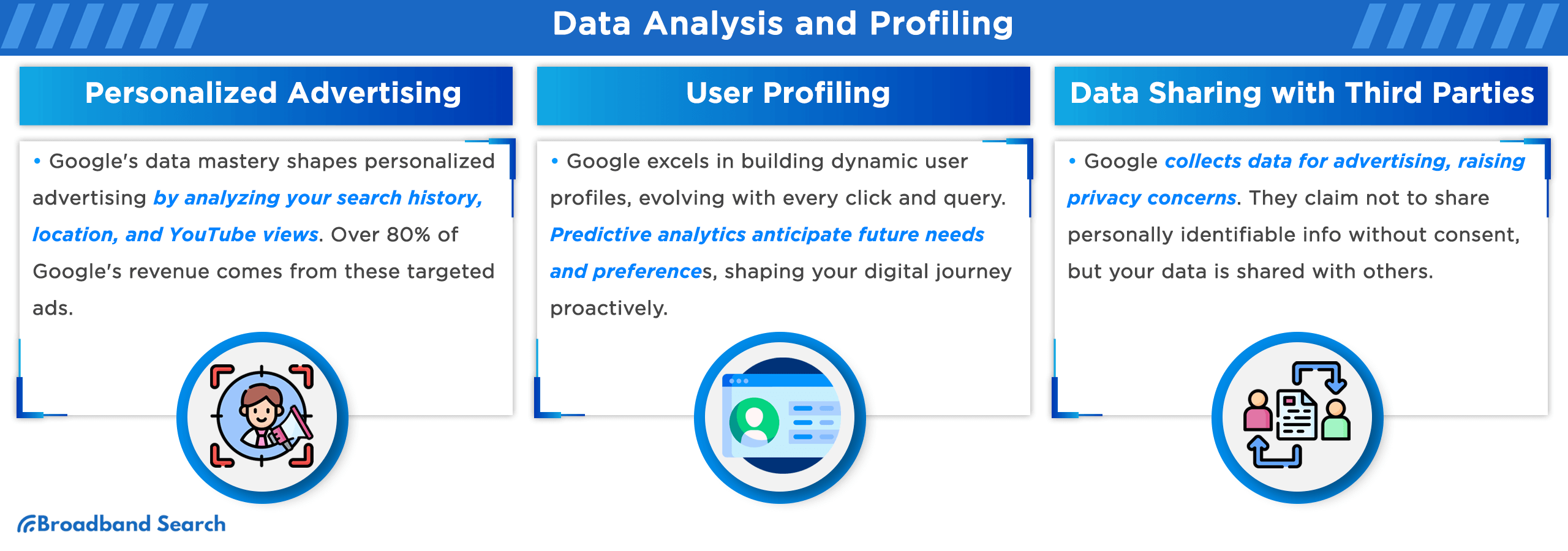
Personalized Advertising
Google's mastery of data most often translates into personalized advertising, a powerful tool that shapes your online experience. By analyzing your search history, location, and even YouTube views, Google crafts targeted ads designed to resonate with your interests. Over 80 percent of Google's revenue comes from advertising, a testament to the effectiveness of their data-driven approach.
This personalized advertising doesn't just catch your eye; it can alter your consumer behavior. Studies show that tailored ads significantly increase the likelihood of purchases. The ads you see are not random; they are reflections of your digital footprint, subtly influencing your shopping choices and preferences.
User Profiling
Google excels in building comprehensive user profiles. By aggregating data from your searches, location history, and even YouTube habits, Google constructs comprehensive user profiles. These profiles, detailed and nuanced, aren't just static; they're dynamic, evolving with every click and query.
Leveraging this data, Google employs predictive analytics to forecast your future needs and preferences. For instance, a survey found that 63 percent of people have clicked on Google ads. Google's predictive algorithms aren't just reactive to your past; they're proactive, shaping your digital journey by anticipating your next move, often before you even make it.
Data Sharing with Third Parties
Google's extensive knowledge about you might surprise you. They collect data like average visit frequency or common query words. Why does Google do this? Primarily, it's to tailor advertising and content, but there's more. Your data helps improve their services, making predictions and recommendations more accurate. However, this raises privacy concerns. How comfortable are you knowing Google has this much information about you?
The sharing of your data with advertisers, partners, sponsors, and third parties is a critical aspect. Google asserts that they share data but doesn't share personally identifiable info without your consent. Specific personal info may be disclosed to comply with legal processes, like search warrants, subpoenas or court orders. In 2022, reports indicated that Google tops at data logging due to its data-centric business model. The implications for privacy are significant. Your data, once shared, can be used in ways you never intended, potentially affecting your online experience and even your offline life.
Privacy Concerns and User Rights
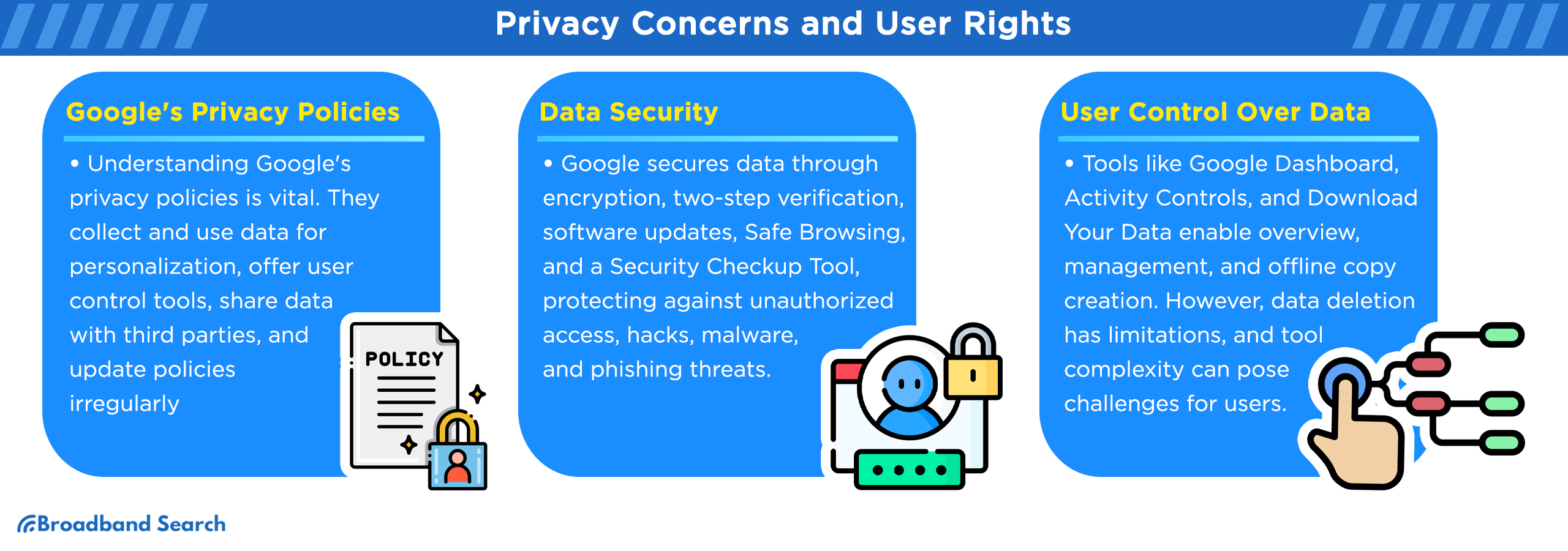
Google's Privacy Policies
Reading and understanding Google's privacy policies are crucial in understanding how your data is managed. Here are five key aspects:
- Data Collection: Google collects data from your interactions with its services. This includes search queries, location history, and device information.
- Data Usage: The collected data is used to personalize your experience, from search results to ads.
- User Control: Google provides tools to view and manage your data. You can check your activity, delete history, or adjust privacy settings, though navigating these options can be complex.
- Data Sharing: Google shares data with third parties under certain conditions, such as advertising or improving services. The specifics of these conditions and the extent of sharing are often points of contention.
- Policy Updates: Google updates its privacy policy on an irregular basis, with the most recent update being on October 4, 2023. The company does not provide a specific schedule for updates, but it typically updates its policy when significant changes are made to its data collection practices or when new laws or regulations come into effect.
Google tries to maintain between utility and privacy, a balancing act that is constantly evolving and subject to public and regulatory scrutiny.
Data Security
Google takes several measures to protect user data:
- Encryption: All data stored and transmitted by Google is encrypted. This means your information is coded to prevent unauthorized access.
- Two-Step Verification: This adds an extra layer of security, requiring both a password and a secondary verification, often through a mobile device.
- Regular Software Updates: Google constantly updates its software to patch security vulnerabilities, protecting against potential hacks and malware attacks.
- Safe Browsing: Google’s Safe Browsing alerts users about potential security threats on websites, protecting against malware and phishing attacks.
- Security Checkup Tool: Google offers a tool for users to review and strengthen their account security settings, helping identify potential vulnerabilities.
Despite these measures, there have been notable incidents:
- Google+ Data Breach (2018): A bug in the Google+ API exposed the personal data of up to 500,000 users, leading (in part) to the platform's eventual shutdown.
- YouTube Children's Privacy Violation (2019): Google and YouTube paid a record $170 million to settle allegations of illegally collecting personal information from children without parental consent.
- G Suite Credential Phishing (2020): Attackers targeted G Suite users in a phishing campaign, compromising user accounts.
- Android Location Data Leak (2020): A flaw in Android’s system exposed users' location data, even when settings were adjusted to protect this information, affecting millions of users globally.
- Chrome Zero-Day Exploits (2021): Zero-day vulnerabilities in the Chrome browser were exploited by malicious actors, posing a security risk.
User Control Over Data
User control over your data on Google is crucial for digital privacy. The following are the top three tools provided by Google for data management:
- Google Dashboard: This dashboard gives you an overview of your data across various Google services. It allows you to review and delete your search history, location data, and more.
- Activity Controls: With Activity Controls, you can choose what types of activity data are saved in your Google Account. You can enable or disable data collection for specific things like Web & App Activity and Location History.
- Download Your Data: Google provides an option to download your data, allowing you to create an offline copy of your information, from emails to photos.
However, there are limitations in user control and data deletion. While you can delete certain data, some logs and records may be retained for legal or operational purposes. Additionally, the complexity of these tools can make it challenging for users to navigate and manage their data effectively.
Real-life Implications of Google's Data Practices
Social and Psychological Impact
Google's data practices have far-reaching effects on our lives, shaping not just what we see online, but also how we think and act. Here are four examples of their impact on public opinion and behavior:
- Democracy Perception: A Pew Research Center study found that 57 percent of people across 19 countries believe social media is good for democracy. However, this belief varies significantly by country, with high support in Singapore (around 76 percent) and lower in the U.S. (about 34 percent).
- Consumer Behavior: Tailored ads influence purchasing decisions. A significant 81 percent of Generation Z prefers personalized ads, a preference that might not directly imply changes in buying habits but indicates a strong inclination towards targeted advertising.
- Filter Bubble Effect: Google's personalized search results can create a "filter bubble", where users are exposed to information that aligns with their existing beliefs. This reinforces preconceptions and limits exposure to diverse perspectives, potentially polarizing public opinion.
Legal and Regulatory Response
Google's data practices have not gone unnoticed by regulators and lawmakers. One significant legal framework that has impacted Google is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
This European Union regulation, implemented in 2018, has impacted how Google and other tech giants handle user data. It places strict requirements on data protection, consent, and user rights. For instance, under GDPR, users have the right to access their data, request its deletion, and opt out of targeted advertising.
However, legal challenges and debates surrounding Google's data practices continue. Below are three prominent ongoing issues:
- Antitrust Investigations: Google faces antitrust scrutiny in various countries, including the United States and the European Union. Allegations of monopolistic behavior and anti-competitive practices are at the center of these investigations.
- Data Privacy Lawsuits: Google has been involved in numerous privacy-related lawsuits, with users and advocacy groups raising concerns about data collection and privacy violations.
- Transparency and Accountability: There is an ongoing debate about the need for more transparency and accountability in tech companies' data practices. Many argue for stricter regulations and oversight to ensure user rights are protected.
Future Prospects
The future holds both promise and challenges in the realm of Google's data practices. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things are poised to usher in a new era of data collection. AI can analyze vast datasets with unprecedented accuracy, while IoT devices constantly feed data into the digital ecosystem. These developments raise questions about the extent of data collection and its implications for privacy.
Balancing innovation with privacy rights will be crucial. As technology evolves, finding the equilibrium between harnessing data for innovation and safeguarding user privacy is complex. Whether or not the balance is found will define the future landscape of data practices, with implications not only for Google but for the entire digital ecosystem.
The Takeaway
Google's knowledge about us is extensive. This wealth of data fuels the convenience we enjoy online, from personalized recommendations to targeted ads. However, it also raises critical questions about privacy and data security.
As users, we must prioritize digital literacy and take active steps to protect our data. Ultimately, the balance between reaping the benefits of Google's services and safeguarding our personal information lies in our hands.
FAQ
How does Google track my online activities when I'm not using their services?
On websites and apps, Google employs various tracking technologies, like cookies and web beacons. With these tools, they can potentially monitor your online behavior even when you're not directly using their services.
How does Google's incognito mode protect my privacy?
Incognito mode prevents your browsing history from being saved locally, but your activities are still visible to websites and your internet service provider. It does not protect perfect anonymity or privacy.
Can Google access the content of my Google Drive files and Google Docs?
Yes, Google can access these files to provide services like syncing and sharing. However, they claim not to use this data for advertising and to not read over or scan files save for very select circumstances.
What information does Google collect when I use an Android device?
Google collects location data, device information, and app usage to improve services. You can adjust settings to limit data collection.
What happens to my personal data if I delete my Google account?
If you delete your Google account, it erases your data from Google services, but Google may retain anonymized data for analysis.

