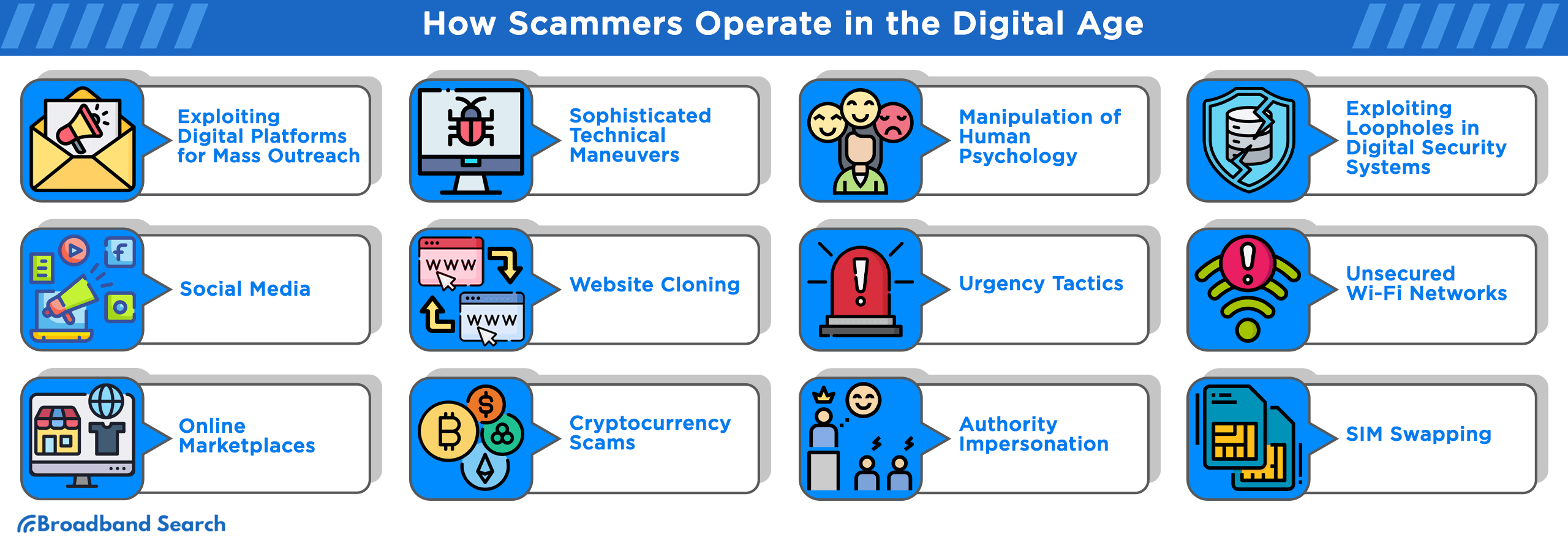
Online scams cost Americans over $16.6 billion in 2024 alone, according to FBI reports. More than 70% of U.S. adults have experienced some kind of online scam or attack, regardless of their age, according to Pew Research. With scammers becoming more sophisticated and the internet playing a central role in our daily lives, it's essential to recognize these threats before they hit your wallet. BroadbandSearch has put together an easy-to-read guide on 17 of the most common online scams, breaking down how they work, how to detect them, and how to protect yourself.
1. Phishing Scams

What it is: Fake emails, texts, or sites posing as trusted sources to steal logins or financial info.
Watch for:
- Generic greetings like "Dear Customer" instead of your name.
- Spelling errors and grammatical mistakes.
- Mismatched email domains or suspicious URLs.
- Urgent threats about account suspension or security breaches.
- Requests for personal information via email.
Protect Yourself: Never click unknown links; verify sender domains.
2. Nigerian Prince / Advance-Fee Fraud

What it is: Offers of inheritance, prize money, or foreign transfers that require upfront fees.
Watch for:
- Unexpected inheritance or windfall notifications.
- Requests for personal information to "verify identity.”
- Demands for upfront payments before receiving funds.
- Stories that sound too good to be true.
Protect Yourself: If it sounds too good to be true — it is.
3. Lottery & Sweepstakes Scams

What it is: Fake prize notifications requiring "taxes" or fees before payout.
Watch for:
- Notifications about winning when you didn't enter.
- Demands for upfront fees before claiming prizes.
- Pressure to act quickly or lose the prize.
- Requests for banking information.
Protect Yourself: Legitimate lotteries never charge winners upfront.
4. Online Shopping Fraud

What it is: Fake websites or sellers offering counterfeit or non-existent products.
Watch for:
- Deals that seem too good to be true.
- Websites with poor design or security.
- Fake or overly positive reviews.
- Non-delivery after payment.
- Requests for unusual payment methods.
Protect Yourself: Shop only on reputable platforms; check reviews and secure payment options.
5. Tech Support Scams
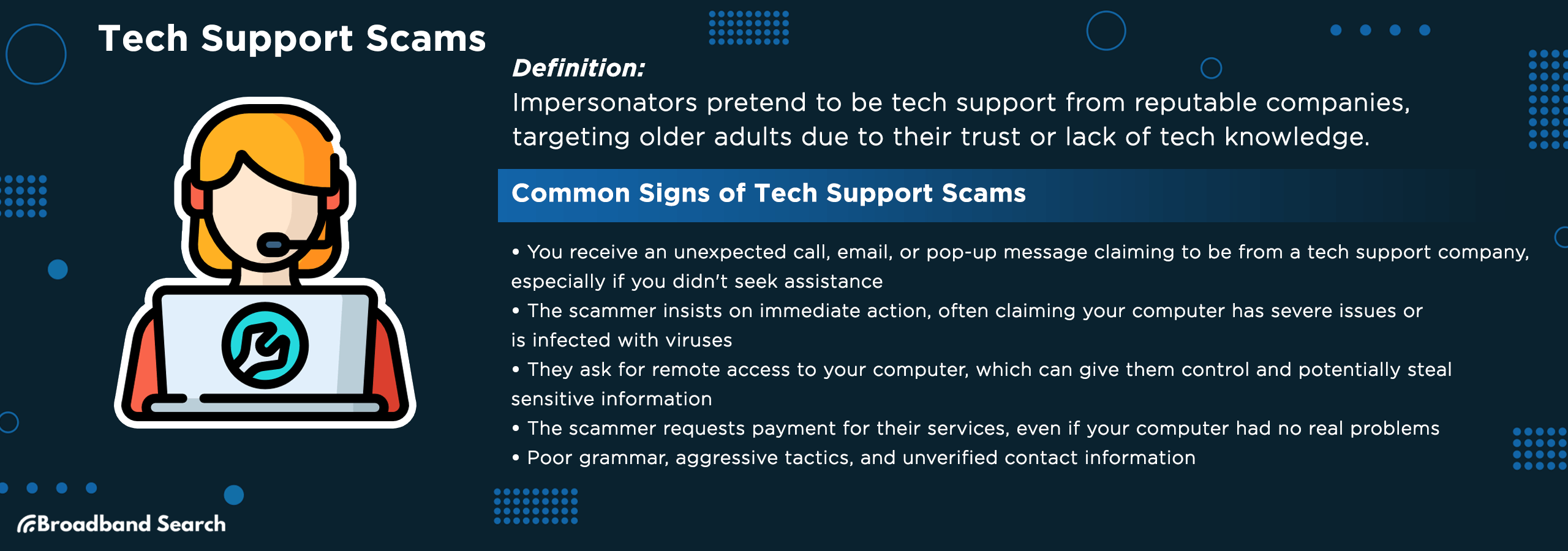
What it is: Calls, pop-ups, or emails claiming your device is infected.
Watch for:
- Pop-up warnings about computer infections.
- Unsolicited calls about tech problems.
- Requests for remote access to your device.
- Demands for immediate payment to fix issues.
Protect Yourself: Ignore random pop-ups/calls; contact tech support directly.
6. Fake Antivirus (Scareware)
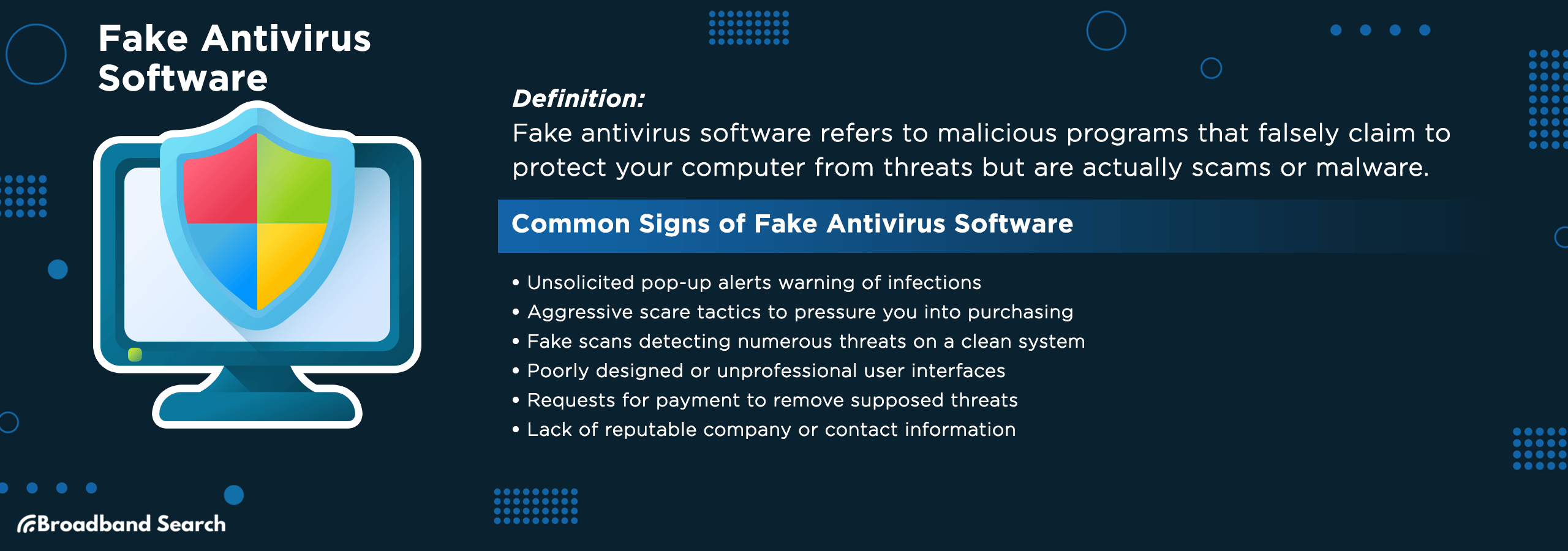
What it is: Rogue software that mimics antivirus tools, demanding payment.
Watch for:
- Alarming pop-ups about system infections.
- Software that appears without installation.
- Demands for immediate payment to remove threats.
- Warnings that seem overly urgent or frightening.
Protect Yourself: Download security software only from official providers.
7. Romance & Dating Scams
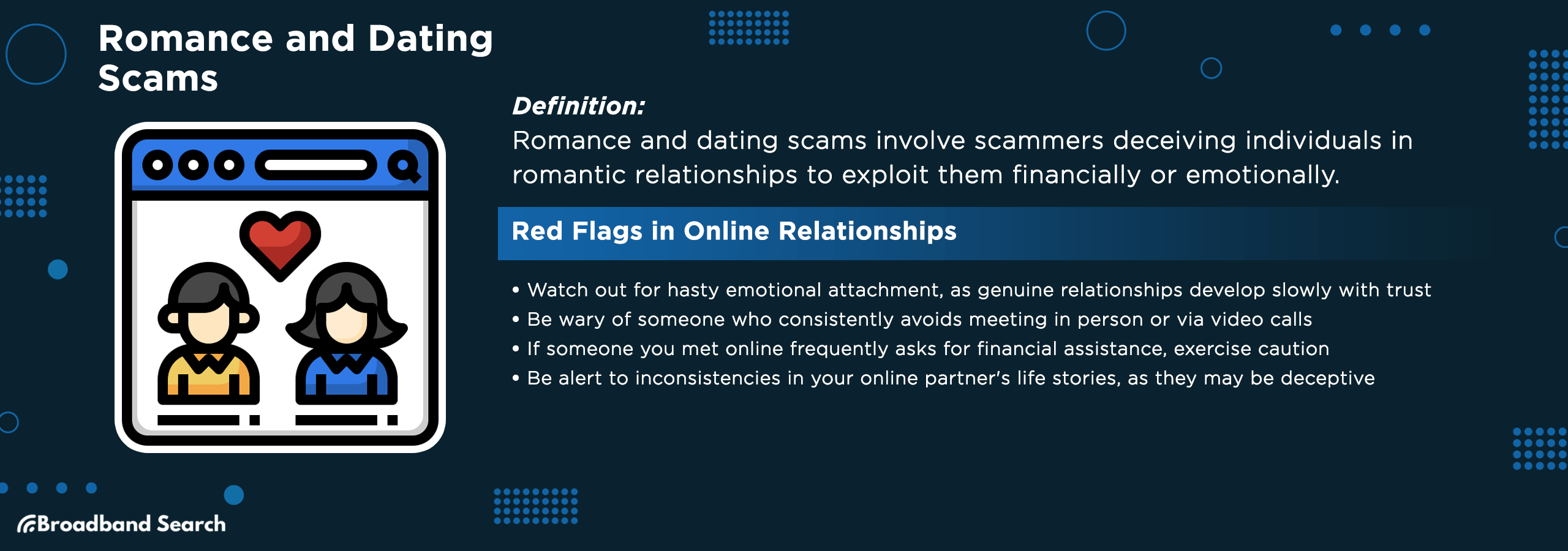
What it is: Fraudsters feign romantic interest to steal money or personal details.
Watch for:
- Rapidly escalating emotional intensity.
- Constant excuses to avoid meeting in person.
- Frequent financial emergencies requiring help.
- Inconsistent personal details or stories.
Protect Yourself: Be cautious with online relationships; never send money to someone you haven't met.
8. Investment Scams
What it is: Ponzi schemes, fake advisors, or sham opportunities promising high returns.
Watch for:
- Promises guaranteed high returns with no risk.
- Pressure to invest immediately.
- Vague or missing information about operations.
- Unusual payment methods required.
Protect Yourself: Research thoroughly; no legitimate investment is risk-free.
9. Fake Job Offers

What it is: Scammers posing as employers to steal fees or personal info.
Watch for:
- Job offers requiring upfront payments.
- Requests for banking details before hiring.
- Communication only through chat apps.
- Pushy or unprofessional recruiter behavior.
- Companies with no verifiable online presence.
Protect Yourself: Verify the company; legitimate jobs don't ask for money.
10. Rental & Real Estate Scams

What it is: Fraudulent listings for properties that don't exist or aren't owned by the scammer.
Watch for:
- Properties listed at below-market rates.
- Landlords who refuse in-person meetings.
- Requests for deposits before viewing.
- Use of stolen property photos.
Protect Yourself: Visit properties in person; use licensed agents.
11. IRS & Tax Scams
What it is: Imposters posing as tax authorities demanding payment or personal info.
Watch for:
- Phone calls about immediate tax payments due.
- Threats of arrest or legal action.
- Demands for payment via gift cards or wire transfers.
- Aggressive or threatening communication style.
Protect Yourself: The IRS never contacts by phone for immediate payments.
12. Social Media Scams
What it is: Fake profiles, promotions, or phishing links on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, TikTok.
Watch for:
- Too-good-to-be-true giveaways or contests.
- Fake celebrity or friend profiles.
- Suspicious links in direct messages.
- Requests for personal information.
Protect Yourself: Verify profiles; avoid clicking suspicious ads or messages.
13. Cryptocurrency Scams

What it is: Fake exchanges, pump-and-dumps, or Ponzi schemes involving digital currencies.
Watch for:
- Promises guaranteed profits in volatile markets.
- Pressure to invest immediately.
- Lack of transparent information about operations.
- Unusual payment methods required.
Protect Yourself: Research platforms and wallets; stick to trusted exchanges.
14. Charity Scams
What it is: Fake charities exploiting crises or disasters.
Watch for:
- Urgent requests for donations following disasters.
- Lack of verifiable registration information.
- High-pressure tactics or emotional manipulation.
- Requests for cash or gift card donations.
Protect Yourself: Verify with sites like Charity Navigator or BBB.
15. Ticket Scams

What it is: Counterfeit or duplicate tickets sold online.
Watch for:
- Prices significantly below market value.
- Sellers requesting payment through peer-to-peer apps.
- Tickets for sold-out events at suspicious prices.
- Sellers who avoid providing detailed ticket information.
Protect Yourself: Buy from official sellers or verified resellers.
16. Gift Card Scams

What it is: Scammers ask victims to buy and share gift card codes for payments.
Watch for:
- Requests to pay bills or taxes with gift cards.
- Claims of emergencies requiring gift card payments.
- Government agencies asking for gift card payments.
- Urgent deadlines for gift card purchases.
Protect Yourself: No government or company accepts gift cards as payment.
17. Malware & Ransomware Attacks
What it is: Malicious software that steals, encrypts, or locks data until ransom is paid.
Watch for:
- Unexpected software installations or pop-ups.
- Sudden computer performance issues.
- Files becoming inaccessible or encrypted.
- Demands for payment to restore access.
Protect Yourself: Keep software updated, avoid unverified links, back up data regularly.
Key Takeaways
- Scams are on the rise: Americans lost over $16.6 billion to online scams last year, showing how widespread and costly they've become.
- Awareness is your best defense: From phishing emails to fake job offers, most scams rely on urgency, fear, or "too-good-to-be-true" promises.
- Red flags are consistent: Watch out for generic greetings, spelling errors, requests for upfront payments, and suspicious links or domains.
- Prevention is simple but powerful: Verify sources, use strong passwords, keep software updated, and avoid sharing personal info with unverified contacts.
- Community matters: Talking openly about scams with friends, family, and coworkers helps spread awareness and makes everyone more vigilant.
FAQ
Are there specific age groups more targeted by online scammers?
Yes, certain age groups can be more vulnerable depending on the type of scam. For instance, older adults might be targeted for pension-related scams, while younger individuals might be more susceptible to social media or job-related scams.
Are there online scams related to COVID-19?
Absolutely. Scammers often exploit current events, and the COVID-19 pandemic has seen a rise in related scams. These can range from fake health products, counterfeit masks, to phishing emails pretending to be from health organizations.
Are mobile apps safe from online scams?
While many mobile apps, especially those on official stores like the App Store or Google Play, undergo security checks, no platform is entirely immune. It's essential to download apps from reputable sources, check reviews, and be wary of apps requesting unnecessary permissions.
How can I report an online scam?
Reporting mechanisms vary by country. Typically, you can report online scams to local law enforcement agencies, dedicated cybercrime units, or consumer protection agencies. Additionally, online platforms often have reporting tools for suspicious activity.
How prevalent are online scams during holiday seasons?
Online scams tend to surge during holiday seasons due to increased online shopping and charitable giving. Scammers take advantage of the festive spirit, offering fake deals, counterfeit products, or posing as charitable organizations. It's crucial to be extra cautious during these times.

