1. Introduction: Why Internet Costs Vary Across States
The internet has become an essential utility in modern life, akin to electricity and water. It’s a gateway to education, job opportunities, and staying connected with the world. However, not all states in the U.S. have equal access to affordable, high-quality internet. Some states enjoy low costs and high speeds, while others face higher bills and limited service.
This disparity influences how communities learn, work, and live. This guide will examine the factors affecting internet pricing, state-by-state rankings, and the societal impact of these cost differences. The guide will also highlight resources like BroadbandSearch, which empowers consumers to find affordable, high-speed internet.
2. What Drives Internet Costs in Each State?
The cost of internet in each state is shaped by factors like infrastructure quality (e.g., fiber-optic networks), population density, competition among providers, and government policies or subsidies. Rural areas often face higher costs due to the challenges of expanding infrastructure, while urban areas benefit from more competitive pricing with multiple providers. Let's take a look at each of the factors below.
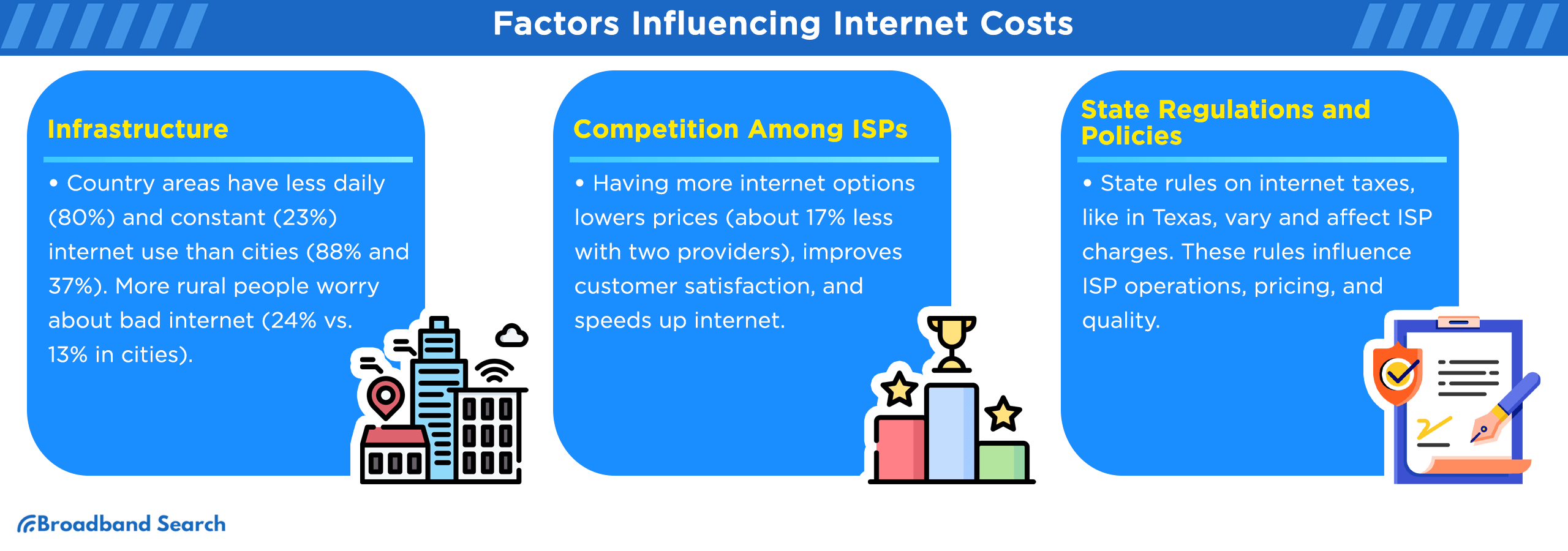
A. Infrastructure Differences
Urban and rural areas face vastly different internet access challenges:
- Urban areas: 88% of people access the internet daily, with fewer connectivity concerns.
- Rural areas: 80% of residents use the internet daily, but access gaps still exist. About 24% of rural dwellers report issues with internet availability compared to only 13% in cities.
Investments in infrastructure also vary. Cities typically receive larger-scale projects, while rural areas face higher setup costs due to sparse populations and challenging terrain.
B. The "Last Mile" Cost Burden
The "last mile" is the final stretch connecting internet service from main infrastructure to individual homes. While it accounts for only 20% of the network, it can make up 80% of the total cost. Rural areas are disproportionately affected, leading to higher internet costs and service concerns.
C. Connection Type Breakdown
The type of internet connection plays a significant role in costs:
- Fiber-optic (fastest, most expensive):
Rhode Island leads the nation in fiber-optic accessibility, with average monthly costs ranging from $40 to $120. Areas with less fiber-optic infrastructure may face higher costs.
- DSL (affordable, moderate speed):
Oregon residents, where DSL is prevalent, pay about $55 on average for this practical option.
- Cable (balanced option):
States like Hawaii see widespread use of cable internet, with prices ranging from $30 to $90 per month.
D. Competition Among ISPs
The number of internet service providers (ISPs) significantly impacts pricing:
- Areas with multiple ISPs see prices drop by roughly 17%.
- Customer satisfaction and internet speeds tend to increase when there’s healthy competition.
Conversely, states with limited ISP options often face higher costs and slower speeds.
E. Municipal Broadband as a Cost-Leveling Tool
Cities like Wadsworth, Ohio, demonstrate how municipal broadband can lower costs through public ISPs. Wadsworth residents enjoy plans starting at $25/month, creating competition that benefits customers.
F. State Taxes and Regulatory Policies
Taxes and regulations further influence internet costs:
- States like Texas impose taxes on internet charges over $25/month.
- Net neutrality laws, such as those in California, promote fair access to internet services but may also impact operational costs.
3. Internet Cost Rankings by State
A. Top 5 States with the Lowest Internet Costs
- Connecticut – $0.61 per Mbps
- North Dakota – $0.64 per Mbps
- South Carolina – $0.67 per Mbps
- South Dakota – $0.69 per Mbps
- Hawaii – $0.69 per Mbps
Factors lowering costs in these states include robust competition, infrastructure investment, and— in most cases—supportive state or federal broadband programs, such as Connecticut’s ConneCTed Communities Grant Program, Broadband North Dakota (Capital Projects Fund) in North Dakota and ConnectSD Program in South Dakota, state grants from South Carolina’s SC Broadband Office, and Hawaii’s Broadband and Digital Equity Office.
B. Top 5 States with the Highest Internet Costs
- Alaska – $2.92 per Mbps
- Montana – $2.63 per Mbps
- West Virginia – $1.88 per Mbps
- District of Columbia (D.C.) – $1.72 per Mbps
- Vermont – $1.36 per Mbps
Limited ISP competition, restrictive laws, and rural geography contribute to higher costs in these states.
C. Average Internet Costs by State
Below is a comprehensive list of all 50 states and their average cost per Mbps:
- Alabama - $1.02 per Mbps
- Alaska - $2.92 per Mbps
- Arizona - $0.91 per Mbps
- Arkansas - $1.27 per Mbps
- California - $0.84 per Mbps
- Colorado - $0.81 per Mbps
- Connecticut - $0.61 per Mbps
- Delaware - $0.93 per Mbps
- District of Columbia - $1.72 per Mbps
- Florida - $0.82 per Mbps
- Georgia - $0.87 per Mbps
- Hawaii - $0.69 per Mbps
- Idaho - $1.27 per Mbps
- Illinois - $0.85 per Mbps
- Indiana - $0.88 per Mbps
- Iowa - $1.22 per Mbps
- Kansas - $1.01 per Mbps
- Kentucky - $0.92 per Mbps
- Louisiana - $1.15 per Mbps
- Maine - $1.21 per Mbps
- Maryland - $0.76 per Mbps
- Massachusetts - $0.85 per Mbps
- Michigan - $0.87 per Mbps
- Minnesota - $0.79 per Mbps
- Mississippi - $0.98 per Mbps
- Missouri - $0.92 per Mbps
- Montana - $2.63 per Mbps
- Nebraska - $1.01 per Mbps
- Nevada - $0.96 per Mbps
- New Hampshire - $1.08 per Mbps
- New Jersey - $0.77 per Mbps
- New Mexico - $1.04 per Mbps
- New York - $0.81 per Mbps
- North Carolina - $0.87 per Mbps
- North Dakota - $0.64 per Mbps
- Ohio - $0.89 per Mbps
- Oklahoma - $0.91 per Mbps
- Oregon - $0.85 per Mbps
- Pennsylvania - $0.87 per Mbps
- Rhode Island - $0.78 per Mbps
- South Carolina - $0.67 per Mbps
- South Dakota - $0.69 per Mbps
- Tennessee - $0.84 per Mbps
- Texas - $0.90 per Mbps
- Utah - $0.72 per Mbps
- Vermont - $1.36 per Mbps
- Virginia - $0.81 per Mbps
- Washington - $0.77 per Mbps
- West Virginia - $1.88 per Mbps
- Wisconsin - $0.92 per Mbps
- Wyoming - $0.96 per Mbps
4. Regional Variations Within States
Even within a state, internet costs vary:
- Urban vs. rural areas: Cities typically offer better and cheaper internet connectivity.
- Income disparities: Lower-income regions may rely on less costly, lower-quality plans.
- Geographic challenges: Mountainous or remote areas drive up infrastructure costs, limiting affordable access.
5. How Internet Costs Affect Communities
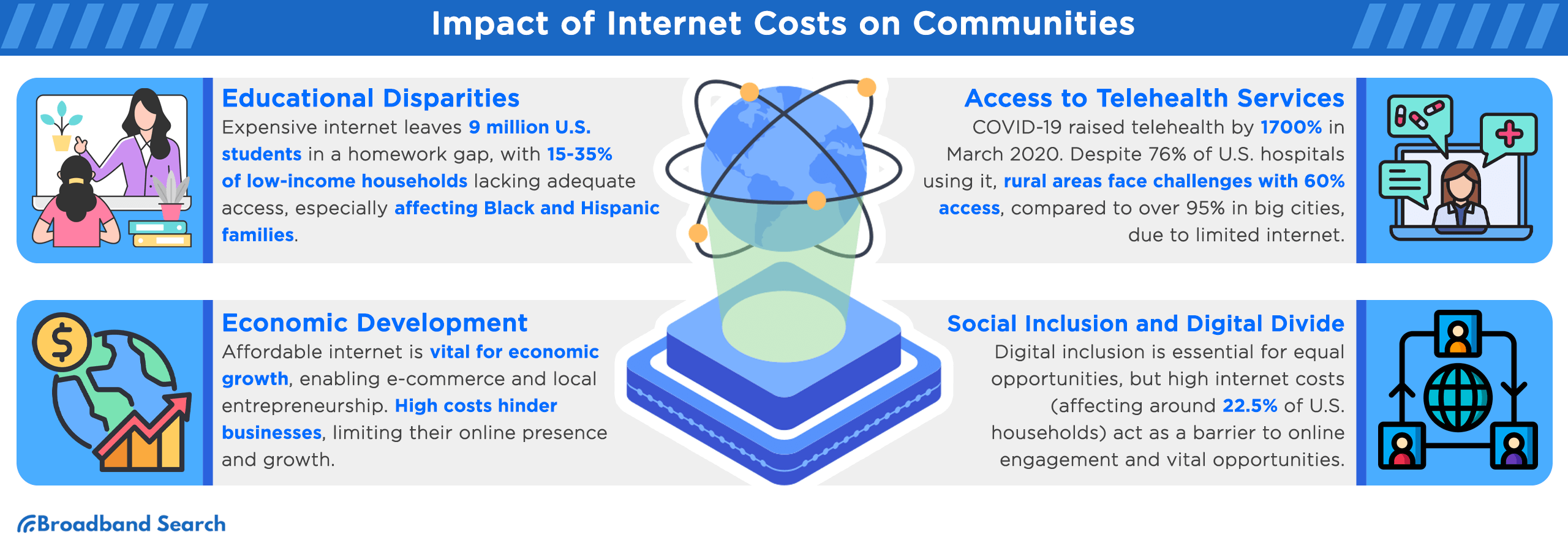
A. Education Access
High internet costs exacerbate the "homework gap," where students lack reliable home internet for education. Pew Research highlights that 35% of low-income households with school-age children face connectivity challenges, disproportionately impacting Black and Hispanic families.
B. Economic Development
Affordable internet fosters small business growth and e-commerce, which generated $791 billion in U.S. sales in 2022. Businesses in high-cost states face hurdles in reaching customers and scaling operations.
C. Access to Healthcare (Telehealth)
Telehealth services surged during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet many rural areas still lack sufficient internet for effective video consultations. Expanding rural internet access can significantly improve healthcare outcomes in underserved regions.
D. Social Inclusion and Digital Divide
High internet costs leave 22.5% of U.S. households disconnected, perpetuating the digital divide. Without affordable options, many communities miss out on online opportunities for education, employment, and societal participation.
6. Conclusion: Bridging the Digital Divide
Disparities in internet costs stem from infrastructure limitations, competition levels, and regulatory environments. Addressing these gaps requires state-specific strategies, including fostering ISP competition and supporting municipal broadband.
Finding affordable internet is essential for inclusion, education, and economic growth. With tools like BroadbandSearch, you can compare costs, connection types, and providers to make informed decisions and secure high-speed internet tailored to your location.
FAQ
How does affordable internet relate to economic growth?
Affordable internet drives e-commerce and entrepreneurship, benefiting businesses and communities alike.
Why is internet cost a big issue in the U.S.?
High internet costs limit education, economic opportunities, healthcare access, and social inclusion.
What is digital inclusion, and why is it important?
Digital inclusion ensures equal access to the internet and its opportunities, bridging societal gaps.
How can individuals help bridge the digital divide?
By advocating for affordable internet, supporting community initiatives, and donating to organizations expanding access.
How can businesses close the internet cost gap?
By promoting affordable rural internet solutions and funding digital literacy programs.