Key Takeaways
- Small businesses experienced a 46% cyberattack rate in 2025, with incidents occurring every 11 seconds. Globally, organizations faced an average of 1,876 attacks per quarter in 2024.
- Businesses with fewer than 100 employees are 2.5 times more likely to be targeted than larger enterprises.
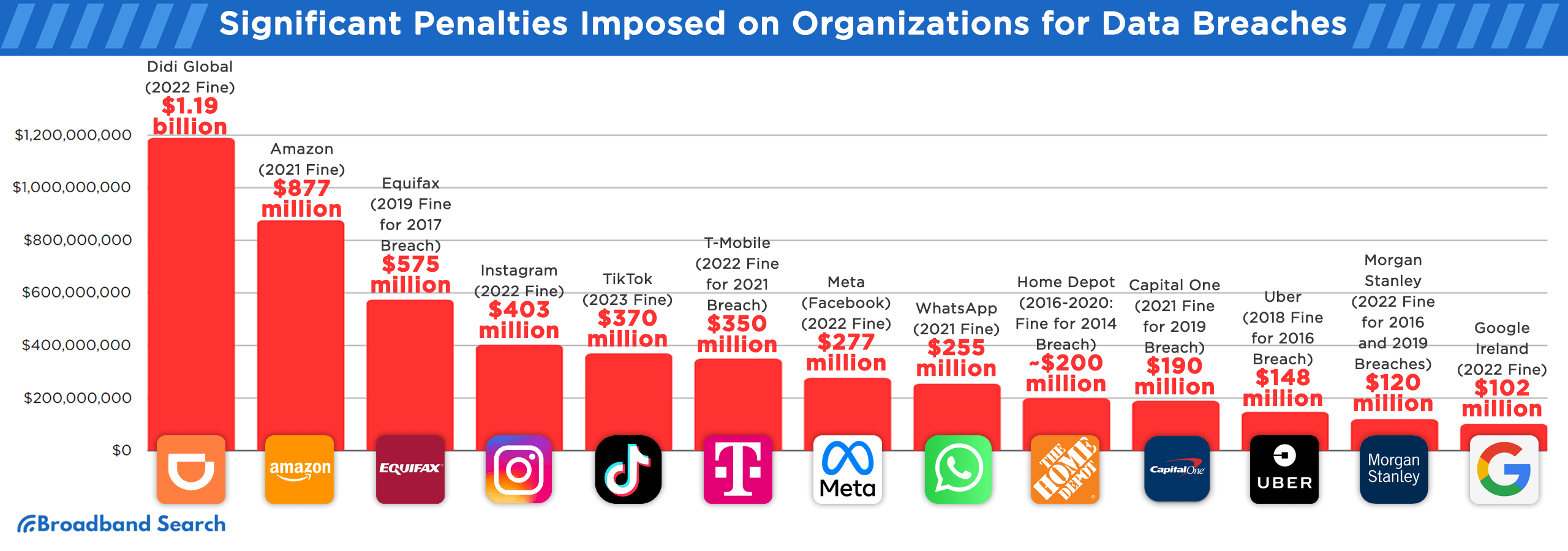
- The global average cost of a data breach was $4.44 million in 2025, but this figure reached a record $10.22 million in the U.S. due to regulatory fines.
- Ransomware accounted for nearly half of all security incidents in 2025. Ransomware attacks alone impacted 37% of all small businesses in 2025.
- Healthcare remains the most expensive industry for breaches, with average costs around $7.42 million globally in 2025. Manufacturing is one of the most targeted industries, seeing a 61% increase in ransomware attacks in 2025. Financial Services faces an average breach cost of $6.08 million, often targeted by social engineering and malware.
Why Is Cybersecurity So Important for Business Owners in 2025?
Cybersecurity isn't optional — it's an operational necessity. Whether you manage a small local business or a national enterprise, your data and systems are targets.
- Small U.S. businesses are prime targets for cybercriminals, with 61% reporting at least one successful cyberattack in 2025 alone.
- The economic impact of cybercrime is projected to cost the global economy up to $10.5 trillion per year by the end of 2025.
- Executives rank cybersecurity among the top three organizational risks.
What Does the Cyber Threat Landscape Look Like for Businesses in 2025?
AI-powered tools, including sophisticated ransomware and multifaceted extortion schemes, will increase the number of cyberattacks per year.
How Many Cyberattacks Happen Each Year?
- Global cybercrime grew by nearly 15% year-over-year, with hundreds of thousands of incidents reported worldwide.
- The U.S. accounts for roughly half of all ransomware attacks globally — up 146% from 2024.
- The average global cost of a data breach is now $4.44 million.
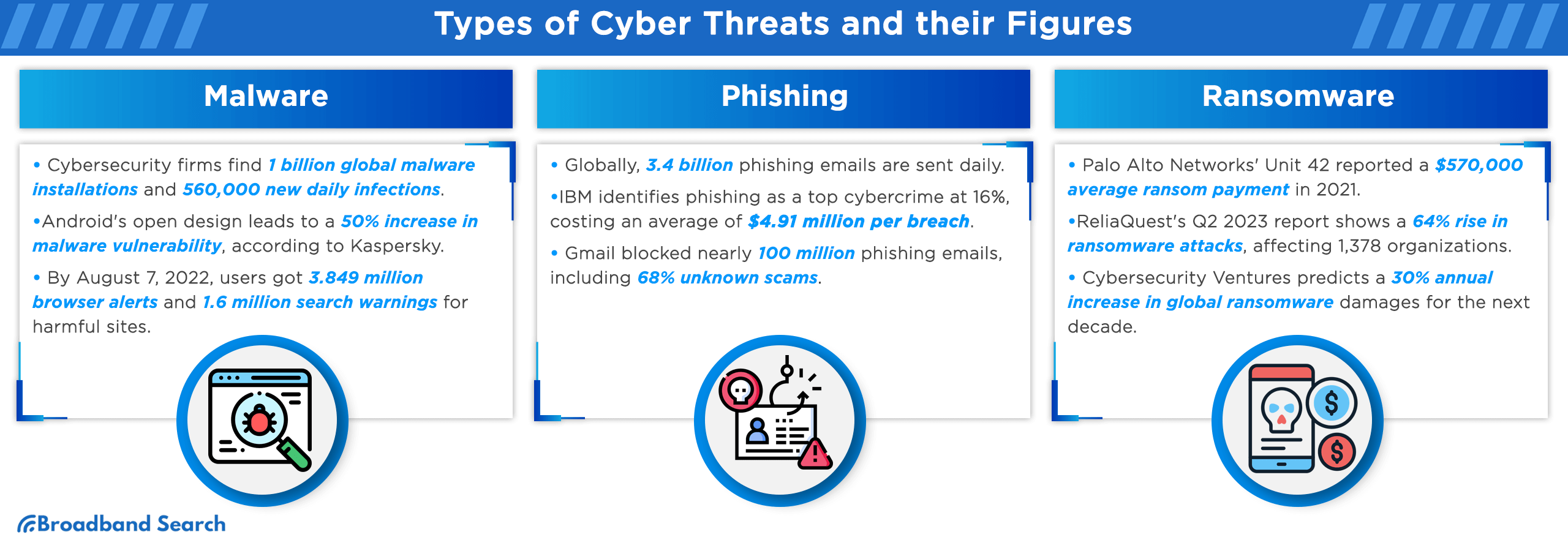
What Are the Most Common Cyberattacks in 2025?
- Credential theft surged by 160%, accounting for about 20% of all breaches.
- Over 30,000 new vulnerabilities were disclosed — a 17 % increase from 2024.
- A supply-chain compromise is a cyberattack where a threat actor infiltrates an organization's systems by exploiting vulnerabilities in a trusted third-party vendor or software. Supply-chain compromise attacks are now responsible for 15% of small-business hacker statistics.
How Do Cyberattacks Affect Small Businesses?
- Nearly 46% of breaches affect companies with fewer than 1,000 employees, according to small business data breach statistics.
- One in five small businesses has suffered a ransomware attack.
- Average breach costs range from $120K to $1.24M for U.S. SMBs.
- 42% of small businesses still don't back up critical data.
Which Industries Are Most Vulnerable to Cyberattacks?
- Financial Services: With the highest average breach costs at $6.08 million per incident, the industry is under pressure due to the high value and sensitivity of its data.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations have unique and severe consequences of breaches. They can disrupt critical operations, endanger patient safety, and lead to significant financial losses.
- Retail & E-Commerce: The retail and e-commerce sector faces increasing risks from fraud and identity theft, with malicious bots and account takeovers targeting businesses and consumers.
- Manufacturing & Critical Infrastructure: According to cybersecurity statistics, the manufacturing sector remains the most targeted industry globally, accounting for over 26% of all cyberattacks.

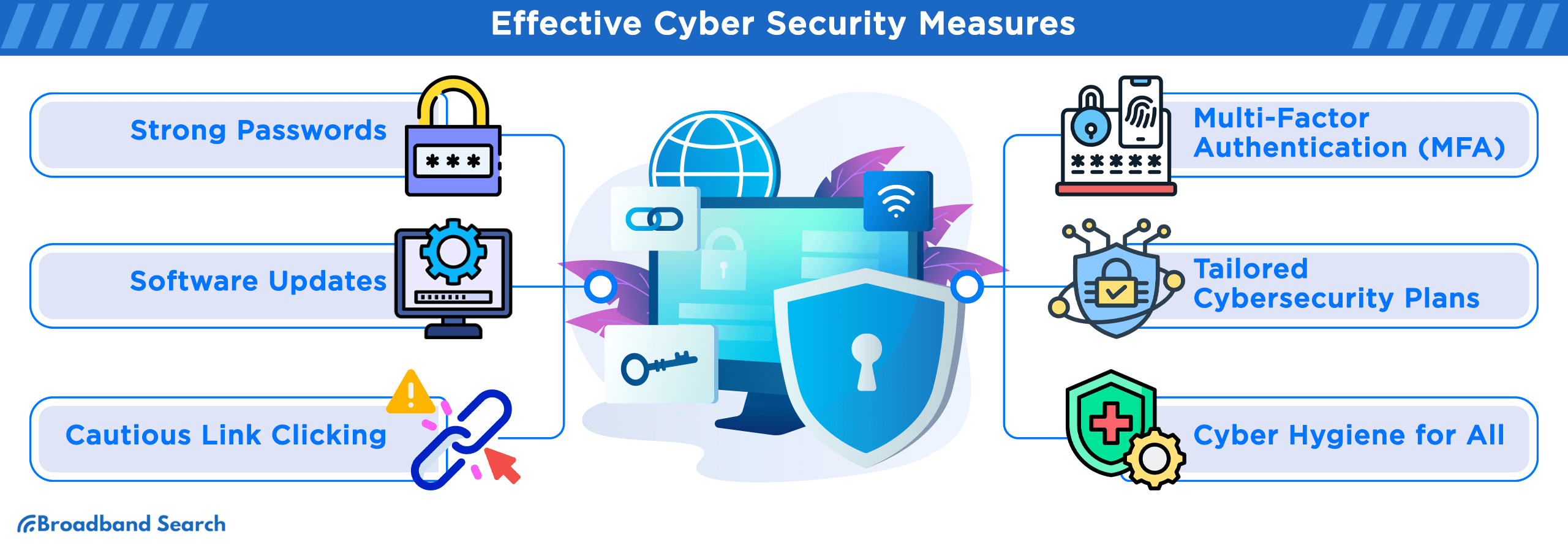
What Are the Best Cybersecurity Practices for Business Owners?
The best cybersecurity practices for business owners involve a multi-layered approach, including implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), regularly backing up data, keeping all software up to date, and training employees to recognize threats.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a critical security measure that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource such as an application, online account, or VPN, thereby significantly hardening your access points and strengthening authentication beyond just strong passwords.
How Can Strong Passwords and MFA Protect My Business?
- Harden Your Access Points: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible and require unique, complex passwords for all user accounts.
Why Are Software Updates and Patching So Critical?
- Patch Vulnerabilities Promptly: Timely updates are crucial to prevent attackers from exploiting them. Ensure all systems are updated immediately. Prompt patching of new vulnerabilities is your best defense against exploitation.
What Role Does Employee Training Play?
Most security incidents involve a human element. By implementing a comprehensive security awareness program that includes regular, targeted phishing simulations, you can reduce the likelihood of a successful attack by up to 70%.
What Is a Zero-Trust Security Model?
A zero-trust security model is a modern framework that assumes no user or device is trustworthy by default. It operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," meaning every user and device is continuously authenticated and authorized, regardless of their location. It is particularly vital for hybrid and remote workers.
Should Businesses Invest in Cyber Insurance?
While insurance is not a substitute for strong technical security controls, a dedicated cyber insurance policy is a crucial component of risk management. It provides essential financial mitigation for losses and recovery costs following a breach.
How Can Business Leaders Strengthen Cyber Resilience?
Business leaders can strengthen cyber resilience by fostering a security-first culture through training and leading by example, and by implementing a comprehensive technical strategy.
What's the Role of Leadership in Cybersecurity?
Executive leadership is crucial for fostering a strong security culture. Leaders must not only allocate the necessary budget for a strong defense but also consistently model good security behavior.
A 2024 CyberArk survey of over 14,000 employees found that 65% admit to bypassing cybersecurity measures, typically for convenience or to increase productivity. 42% of employees admitted to being bombarded with so many authentication requests that they click "accept" without properly verifying them.
What Are the Legal and Compliance Implications?
U.S. businesses must navigate a constantly changing landscape of federal and state data privacy laws.
Compliance obligations extend beyond a single law, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), to include many other state-specific regulations that are already in effect or coming soon.
Non-compliance with any applicable law risks heavy fines and significant reputational damage.
How Does Cybersecurity Impact Customer Trust?
Customer loyalty is heavily dependent on data security. A staggering 85% of consumers report they would stop doing business with a company following a data mishandling incident.
While prevention is key, a swift, transparent, and empathetic breach response is essential for preserving credibility and rebuilding trust.
What Are the Key Cybersecurity Trends to Watch in 2025?
- AI in cybercrime: Attackers exploit AI for advanced phishing and deepfakes. At the same time, cybersecurity professionals use AI to enhance threat detection and automate responses. Businesses need to leverage AI defensively to keep pace with increasing hacker statistics.
- Cyber insurance boom: As cyberattacks against small and medium-sized businesses rise, more companies are investing in cyber insurance policies to manage financial risk and accelerate recovery.
- Monitor Key Emerging Threats: Organizations face growing concerns about identity-based attacks (which target credentials) and "zero-day" exploits (which exploit unknown vulnerabilities).
- Critical Workforce Shortage: The cybersecurity industry faces a severe global talent gap, with an unmet demand for approximately 3.5 million professionals required to defend systems globally.
What Can Business Owners Do Right Now to Improve Cybersecurity?
- Assess risks. Conduct a risk assessment to pinpoint vulnerabilities and clearly identify which critical assets must be protected first.
- Update company policies. Update internal documentation to clearly define standards for password management, mandatory MFA, patch management schedules, and secure remote access controls.
- Train employees regularly. Implement regular security training sessions to educate employees on recognizing phishing attacks, avoiding social engineering, and maintaining safe online behavior.
- Develop an incident response plan. Develop an incident response strategy today and conduct frequent tests of your data backups to guarantee business continuity.
- Vet vendors. Assess all third-party vendors for sound security practices and implement specific cybersecurity and data privacy clauses into all service agreements to mitigate external risk.
- Track metrics. Track key performance metrics to continuously measure the effectiveness of your security program and find areas for improvement.
- Communicate proactively. Clearly communicate your cybersecurity policies to customers and stakeholders. Transparency is key to managing expectations and maintaining credibility and trust.
Cybersecurity Is Now a Leadership Decision
Cyber threats are faster, smarter, and more expensive than ever, but so are the tools to combat them. Cybersecurity is no longer just an IT concern—it's a critical leadership priority.
Invest in the right practices today to protect your company's data, reputation, and long-term viability.
FAQ
What are the first steps a small business should take to improve its cyber security posture?
Small businesses should start with a cybersecurity audit. From there, they should implement multi-factor authentication, regularly update software, train employees on cybersecurity best practices, and establish basic firewall and antivirus protections.
How does remote work or a distributed workforce impact a business’s cyber security strategy?
Remote work necessitates additional security measures like secure VPNs, stronger endpoint protections, enhanced data encryption, and specific policies for remote workers to address the vulnerabilities of home networks and personal devices.
What are some common signs that a business may have been compromised by a cyber attack?
Common indicators that a business may have been compromised include unusual network activity, unexpected access to files or systems, frequent system crashes, ransomware messages, and suspicious outbound data transfers.
Can small businesses afford cyber security measures, and are there cost-effective strategies they can implement?
Yes, small businesses can afford cybersecurity through cost-effective strategies like using reputable open-source security tools, prioritizing key assets for protection, and leveraging cloud-based security services.
How can businesses stay informed about the latest cyber security threats and trends?
Businesses can stay informed by subscribing to cybersecurity newsletters, attending industry webinars and conferences, and following reputable cybersecurity experts and organizations on social media.