Internet speed plays a crucial role in our daily lives, impacting activities like streaming, gaming, remote work, and communication. Slow internet connections can be a source of frustration and hinder productivity.
To overcome these limitations, there are devices you can use that are designed to enhance internet speed and optimize connectivity.
This article explains the functions, benefits, and considerations of the seven top devices and methods used to increase internet speed.
Key Takeaways
- Fastest single upgrade: Mesh Wi-Fi or a modern Wi-Fi 6/6E/7 router for Wi-Fi bottlenecks; Cat6a Ethernet for stationary devices.
- If your plan is the cap: Upgrading devices won't exceed your ISP plan; verify your provisioned speed first.
- Wi-Fi dead zones: Prefer mesh over basic extenders/repeaters.
- Old cables: Use Cat6a for 10 Gbps-ready links.
Common Speed Bottlenecks: What's Slowing You Down?
- Before investing in new devices, it helps to understand where your speed issues might be coming from:
- Outdated router or modem: Older hardware may not support your current internet plan speeds or the latest Wi-Fi standards.
- Weak Wi-Fi signal: Distance from the router, walls, and interference from other devices can weaken your wireless connection.
- Old Ethernet cables: Cat5 or damaged cables can limit wired speeds, even if your plan supports faster speeds.
- ISP plan limitations: Sometimes the issue isn't your equipment—it's the speed tier you're paying for.
- Network congestion: Too many devices connected simultaneously can overwhelm your network, especially during peak usage times.
Identifying the bottleneck helps you choose the right solution. Now, let's explore the devices that can help.
1. Modem and Router Upgrades
What it is
A modem connects your network to your Internet Service Provider (ISP), while a router distributes that connection to multiple devices. Upgrading to newer hardware can unlock faster speeds and improved performance.
When to use it
- Your modem or router is more than 3-5 years old.
- You've upgraded your internet plan but aren't seeing faster speeds.
- You experience frequent dropouts, buffering, or slow Wi-Fi in multiple rooms.
Potential speed impact
Upgrading from an outdated router to a Wi-Fi 6 model can deliver speeds up to 10 Gbps (depending on your plan). Expect real-world improvements of 20-50% in coverage and speed for most households.
Cost range
- Budget routers: $50–$100
- Mid-range Wi-Fi 6 routers: $100–$250
- High-end Wi-Fi 6E/7 routers: $250–$600+
- ISP-provided modem rental: $10–$15/month (purchasing your own pays for itself within 1-2 years)
Setup tips
- Ask your ISP for a new modem or gateway, or purchase your own compatible model.
- Place your router in a central location, elevated and away from walls or metal objects for optimal signal distribution.
Caveats
- Your internet speed is still limited by your ISP plan—a new router won't magically exceed what you're paying for.
- Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 require compatible devices to take full advantage of the faster speeds.
2. High-Speed Ethernet Cables
What it is
Ethernet cables provide a direct wired connection between your device and router, offering faster and more stable speeds than Wi-Fi.
When to use it
- You're a gamer, streamer, or work from home and need a reliable, low-latency connection.
- Your device is stationary (desktop computer, gaming console, smart TV).
- You want to eliminate Wi-Fi interference and signal drops.
Potential speed impact
- Cat5e: Up to 1 Gbps (sufficient for most home users)
- Cat6: Up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances (ideal for gaming/streaming)
- Cat6a/Cat7: Up to 10 Gbps over longer distances with superior shielding
Cost range
- Cat5e cables: $5–$15
- Cat6 cables: $10–$25
- Cat6a/Cat7 cables: $15–$40+
Setup tips
- Run cables along walls or use cable management clips to keep them organized and out of the way.
- For runs longer than 50 feet, opt for Cat6a or Cat7 to maintain maximum speeds.
Caveats
- Physical installation may not be practical in all spaces, especially if devices are far from the router.
- Damaged or kinked cables can reduce performance—inspect cables regularly.
3. Powerline Adapters
What it is
Powerline adapters extend your internet connection by transmitting data through your home's existing electrical wiring.
When to use it
- You have rooms with weak Wi-Fi that are too far from the router for Ethernet cables.
- Running new cables isn't practical or desirable.
- You need a wired connection in a location where Wi-Fi is unreliable.
Potential speed impact
Powerline adapters typically deliver speeds between 200 Mbps to 2 Gbps, depending on the model and your home's electrical wiring quality. Expect real-world speeds of 50-70% of the rated maximum.
Cost range
- Basic adapters: $40–$70
- High-speed adapters (1 Gbps+): $70–$150
Setup tips
- Plug adapters directly into wall outlets (not power strips) for best performance.
- Use adapters on the same electrical circuit for optimal speeds.
Caveats
- Performance depends heavily on the age and quality of your home's electrical wiring.
- Distance between adapters and interference from large appliances (refrigerators, air conditioners) can reduce speeds.
4. Wi-Fi Extender and Booster
What it is
Wi-Fi extenders (also called boosters) expand your Wi-Fi coverage by capturing and rebroadcasting your router's signal to eliminate dead zones.
When to use it
- You have specific rooms or areas with weak or no Wi-Fi signal.
- You live in a large home or multi-story building.
- You want to improve signal strength in outdoor spaces like a patio or garage.
Potential speed impact
Extenders typically provide 50-75% of your router's original speed in extended areas. A dual-band extender is more effective than a single-band model.
Cost range
- Basic extenders: $20–$50
- Dual-band extenders: $50–$100
- Tri-band or mesh extenders: $100–$200+
Setup tips
- Place the extender midway between your router and the dead zone for optimal signal relay.
- Choose a model with an Ethernet port if you need a wired connection in the extended area.
Caveats
- Extenders can introduce latency and reduce overall speed compared to a direct router connection.
- Basic extenders create a separate network name (SSID), requiring manual switching between networks as you move around.
5. Signal Repeater
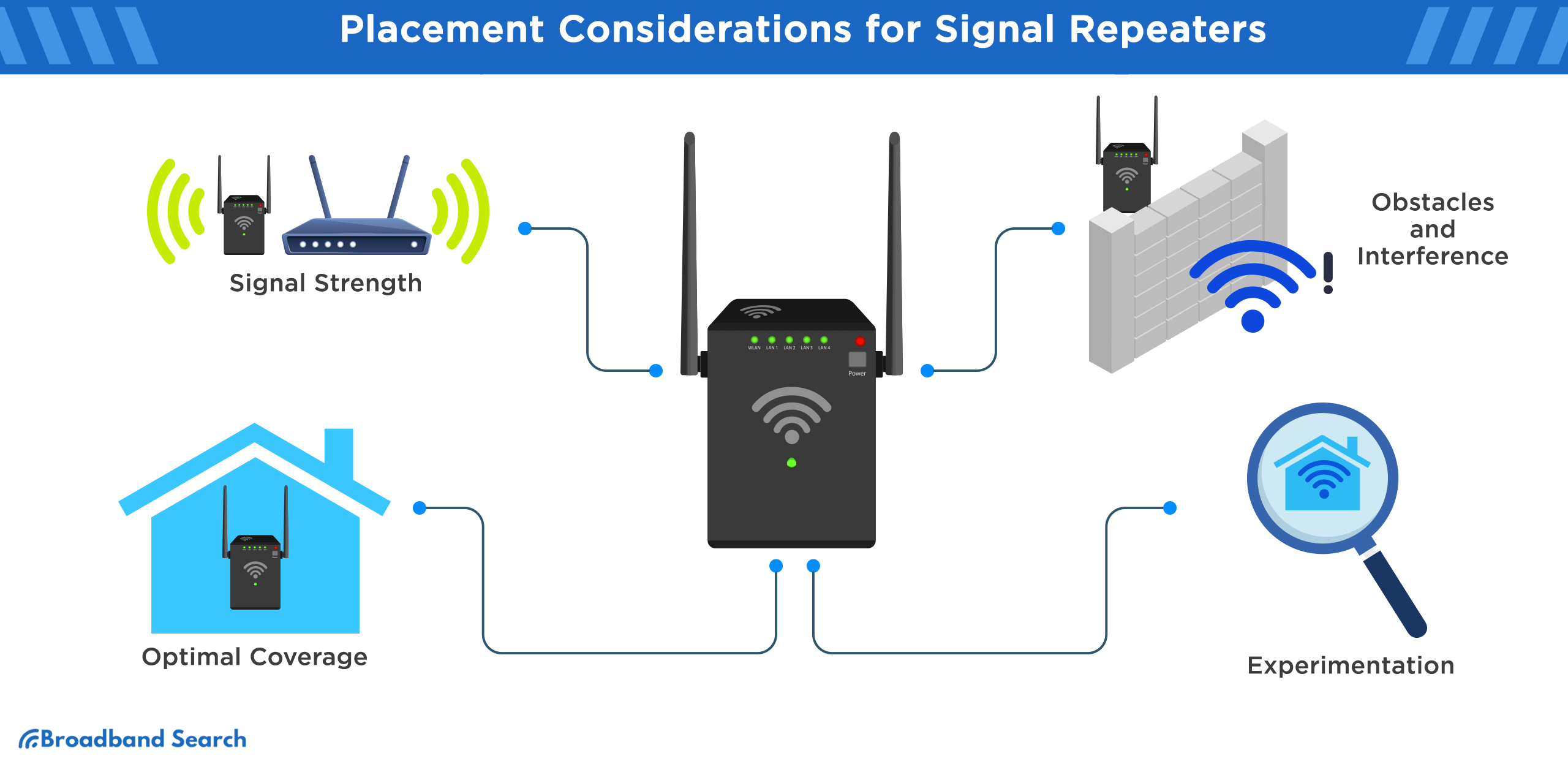
What it is
Signal repeaters are similar to extenders but rebroadcast the Wi-Fi signal to extend its range even farther.
When to use it
- You need to extend Wi-Fi coverage over a very large area (300+ feet).
- You have multiple dead zones throughout your home or office.
- You're looking for a budget-friendly alternative to a mesh system.
Potential speed impact
Repeaters can extend range by up to 800 feet or more, but expect speeds to drop by 25-50% compared to the original signal.
Cost range
- Basic repeaters: $25–$60
- Advanced repeaters: $60–$120
Setup tips
- Install the repeater where it can still receive a strong signal from the router—ideally halfway to the dead zone.
- Avoid placing repeaters near physical obstacles like metal objects or thick walls.
Caveats
- Each "hop" the signal takes through a repeater reduces overall speed.
- Repeaters can introduce additional latency, which may affect real-time activities like gaming or video calls.
6. Optimize Your DNS Settings
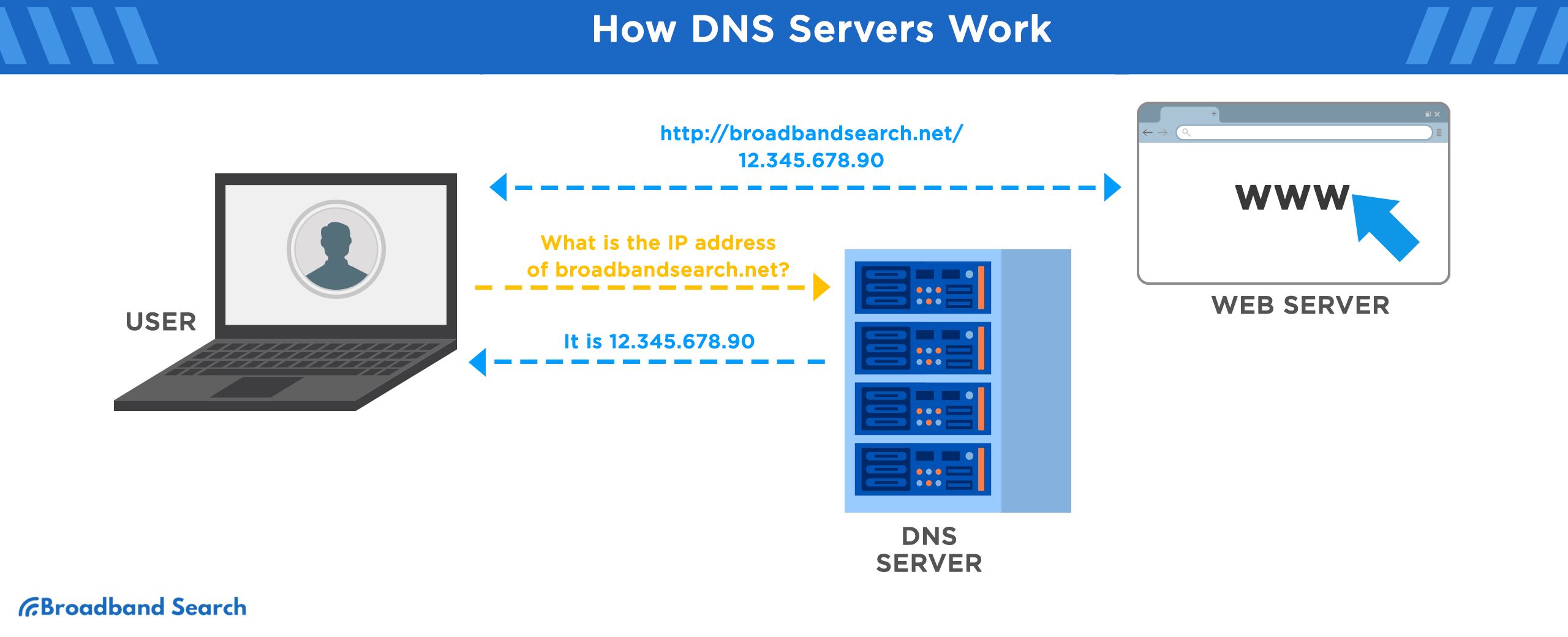
What it is
DNS (Domain Name System) servers translate website names into IP addresses. Using faster DNS servers can reduce website loading times.
When to use it
- Websites are loading slowly even though your connection speed is fine.
- You want to improve browsing responsiveness and reduce latency.
- You're experiencing frequent DNS errors or timeouts.
Potential speed impact
Switching to a faster DNS provider can reduce latency by 20-120 milliseconds, making web pages load noticeably faster.
Cost range
Free (most public DNS services are free to use)
Setup tips
- Change DNS settings in your router to apply them network-wide, or adjust them on individual devices.
- Popular DNS providers include Google DNS (8.8.8.8), Cloudflare (1.1.1.1), and OpenDNS.
Caveats
- DNS optimization won't increase your actual download/upload speeds—it only improves how quickly domain names are resolved.
- Some ISPs block third-party DNS servers; check if your provider allows custom DNS settings.
7. Firewall Optimization for Speed and Security
What it is
Firewalls monitor and control network traffic. Properly configuring your firewall can reduce congestion and free up bandwidth without compromising security.
When to use it
- Your network feels sluggish despite having adequate internet speed.
- You want to prioritize bandwidth for specific activities (gaming, video calls, streaming).
- You're experiencing lag during peak usage times.
Potential speed impact
Optimizing firewall settings can improve network efficiency by 10-30%, particularly for households with multiple connected devices.
Cost range
Free (configuration-only; no additional hardware required)
Setup tips
- Use Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize bandwidth for essential applications like video conferencing or gaming.
- Regularly update your router's firmware to ensure optimal performance and security.
Caveats
- Overly restrictive firewall settings can block legitimate traffic and slow down your connection.
- Firewall configuration requires some technical knowledge—consult your router's manual or ISP support if needed.
Your Speed-Boosting Checklist
Here's a quick summary of the seven ways to increase your internet speed:
- Upgrade your modem and router for faster speeds, better stability, and enhanced security.
- Use Ethernet cables for wired connections that are faster and more reliable than Wi-Fi.
- Install powerline adapters to extend your connection via existing electrical wiring.
- Add Wi-Fi extenders or boosters to eliminate dead zones and expand coverage.
- Consider a signal repeater as an alternative to extenders for very large areas.
- Switch to faster DNS servers to reduce website loading times.
- Optimize firewall settings to prioritize bandwidth and improve network efficiency.
Choose the solutions that best match your specific needs, considering factors like coverage area, device compatibility, speed requirements, and budget. Remember, the best results often come from combining multiple strategies—like pairing a modern router with Ethernet cables and a mesh extender.
Regular maintenance and updates are key to sustained performance. Fine-tune your settings over time to adapt to changing demands and ensure your network stays fast and secure.
FAQ
How can I increase internet speed?
Start by testing your current speed using an internet speed test to see if you're getting what you're paying for. If your speed matches your plan, consider upgrading your plan or optimizing your setup with the devices mentioned above—like a new router, Ethernet cables, or Wi-Fi extenders.
What is the easiest way to boost internet speed?
The easiest way is to upgrade your router or modem, especially if your current one is more than 3-5 years old. Switching to a Wi-Fi 6 router can deliver noticeable improvements in speed and coverage with minimal setup required.
Why is my WiFi so slow?
Slow Wi-Fi can result from several factors: outdated equipment, too many connected devices, poor router placement, interference from other electronics, or simply needing a better internet plan. Troubleshooting each of these areas can help identify and fix the issue.
Why am I getting different internet speeds on different devices?
Older devices may not support the full capabilities of your network, especially if you have a gigabit plan. Other possibilities include malware or viruses on specific devices, different Wi-Fi bands.