Choosing the right internet plan often feels like navigating a maze of acronyms and technical jargon. With terms like "Mbps vs Gbps," "fiber optics," and "latency" thrown around, it is easy to get lost. However, understanding these concepts is crucial to avoiding overpaying for speed you don’t need or suffering through buffering during a movie night.
This guide breaks down the key factors of internet speeds, helping you make an informed decision based on your specific online activities.
What is Internet Speed?
At its core, internet speed refers to how fast data travels between the web and your device. It is typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or, for ultra-fast connections, gigabits per second (Gbps). While the terminology can be confusing, the math is simple: 1 Gbps equals 1,000 Mbps.
Most households don't require gigabit speeds, but knowing the difference helps you choose a plan that fits your digital life. There are two main components to consider:
- Download Speed: How fast data is transferred to your device. This affects streaming movies, loading webpages, and downloading large files.
- Upload Speed: How fast data is transferred from your device. This is critical for video calls, posting to social media, and backing up files to the cloud.
Internet plans are measured in megabits (Mb), but file sizes are usually megabytes (MB). 1 byte = 8 bits, so 100 Mbps is about 12.5 MB/s under ideal internet connection conditions.
If you are unsure about the technical details of data transmission, our guide on bits vs bytes explains the fundamental units of digital information.
Bandwidth vs. Speed: What’s the Difference?
These terms are often used interchangeably, but they mean different things.
- Speed refers to how fast data packets move.
- Bandwidth refers to the volume of data that can move at once.
Think of your internet connection like a highway. Speed is the speed limit, while bandwidth is the number of lanes. Even with a high speed limit, a single-lane road will get congested if too many cars (devices) try to use it at once. This congestion is often why ISPs utilize bandwidth throttling during peak usage times.
To dive deeper into this distinction, read our article on bandwidth vs. internet speed.
Internet Speed Comparisons: How Much Speed Do You Actually Need?
The "right" speed depends entirely on your usage habits and household size. A single user browsing the web needs far less power than a family of five streaming Netflix in 4K.
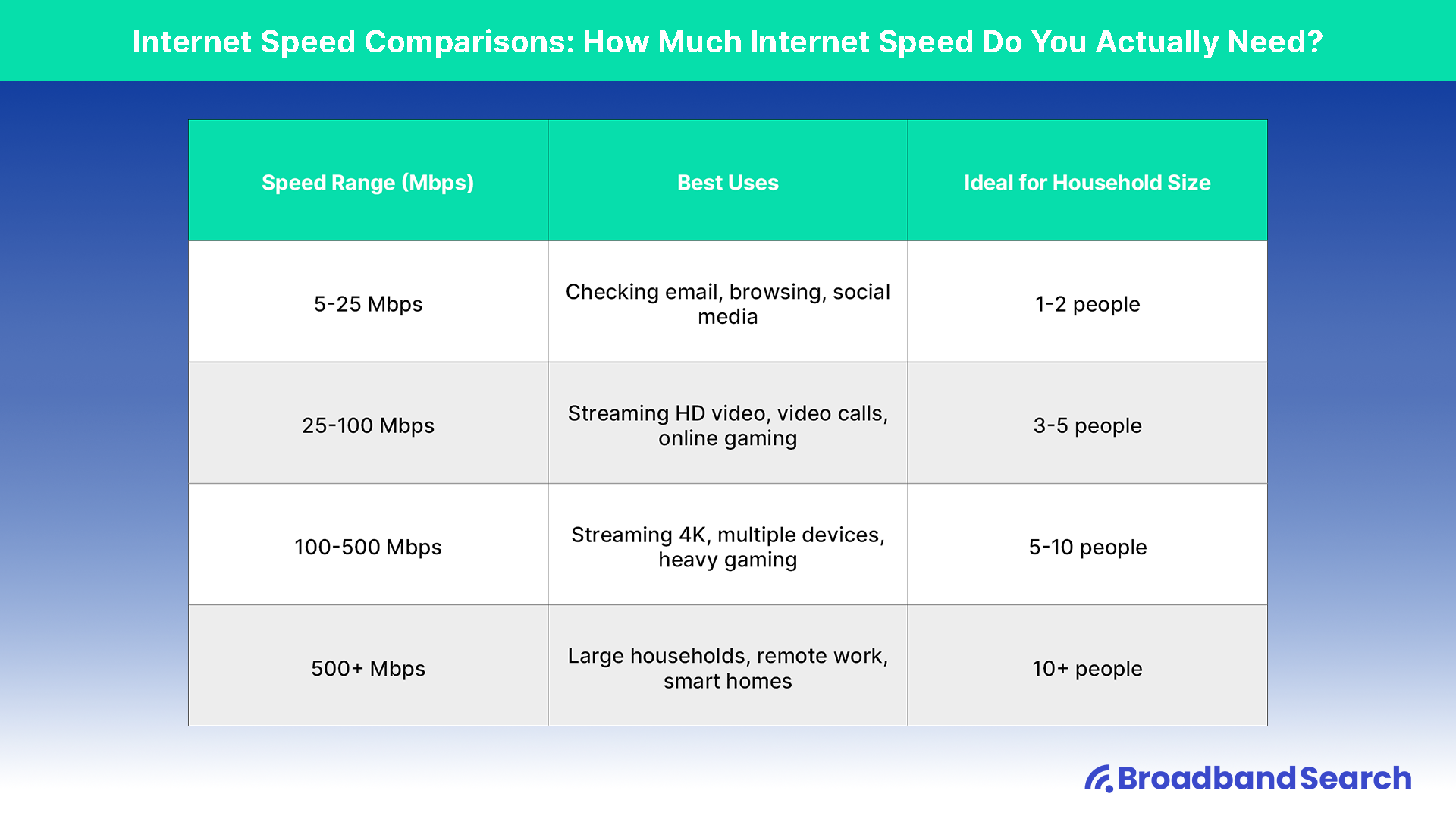
Use this breakdown of speed recommendations based on activities to get an idea of how much internet speed you actually need:
| Speed Range (Mbps) | Best Uses | Ideal for Household Size |
|---|---|---|
| 5-25 Mbps | Checking email, browsing, social media | 1-2 people |
| 25-100 Mbps | Streaming HD video, video conferencing, online gaming | 3-5 people |
| 100-500 Mbps | Streaming 4K, multiple smart devices, heavy gaming | 5-10 people |
| 500+ Mbps | Large households, remote work, smart homes | 10+ people |
If you frequently experience buffering, pixelation, and audio that doesn't sync with the video, or long load times, your current plan might be struggling to keep up. Check out our guide to broadband internet for more details on choosing a provider.
What is a Fast Internet Speed?
While definitions vary, a "fast" internet speed typically starts at 100 Mbps and above. Recently, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) updated its benchmark for high-speed broadband to 100 Mbps download / 20 Mbps upload, reflecting the modern need for robust connectivity.
Some providers in some markets offer fiber internet with speeds up to 10 Gbps. Unless you are running a server farm or a high-tech business from home, this level of speed is likely overkill. However, having a fiber optic connection ensures you are future-proofed against increasing data demands.
Is 100 Mbps Enough?
Yes, for the majority of households, 100 Mbps is considered a good internet speed. On March 14, 2024, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) updated its benchmark for high-speed broadband to 100 Mbps download and 20 Mbps upload. This update reflects the modern necessity for robust connectivity to support work, education, and entertainment.
With 100 Mbps, you can typically:
- Stream 4K video on 2-3 devices at once.
- Participate in Zoom calls without lag.
- Browse the web and use social media seamlessly.
If you have a larger household or download massive files regularly (like modern video games), you may want to look at plans offering 300 Mbps or higher.
Upload Speed vs. Download Speed
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) often advertise download speeds in big, bold numbers because users consume more data than they send. However, upload speeds are often just as important for modern tasks.
Fast upload speeds are essential for:
- Video Conferencing: Apps like Zoom and Teams require stable upload bandwidth for synced audio and video and a smooth experience.
- Cloud Backups: Syncing large files and photos to iCloud or Google Drive.
- Online Gaming: Sending your inputs to the game server instantly.
If upload speed is a priority, consider symmetrical bandwidth, where upload and download speeds are equal—a common feature of fiber optic plans.
Latency and Ping: Why They Matter
Latency, often referred to as ping, is the reaction time of your connection. It measures how long (in milliseconds) it takes for data to travel from your device to a server and back.
Low latency is crucial for real-time activities:
- Ideal for gaming: Under 50 ms (recommended).
- Ideal for video calls: Under 100 ms (recommended).
High latency causes "lag," which can make gaming impossible and video calls choppy, even if your download speed is high. Satellite internet typically has higher latency due to the distance data must travel, though newer LEO satellites like Starlink are improving this.
Types of Internet Connections
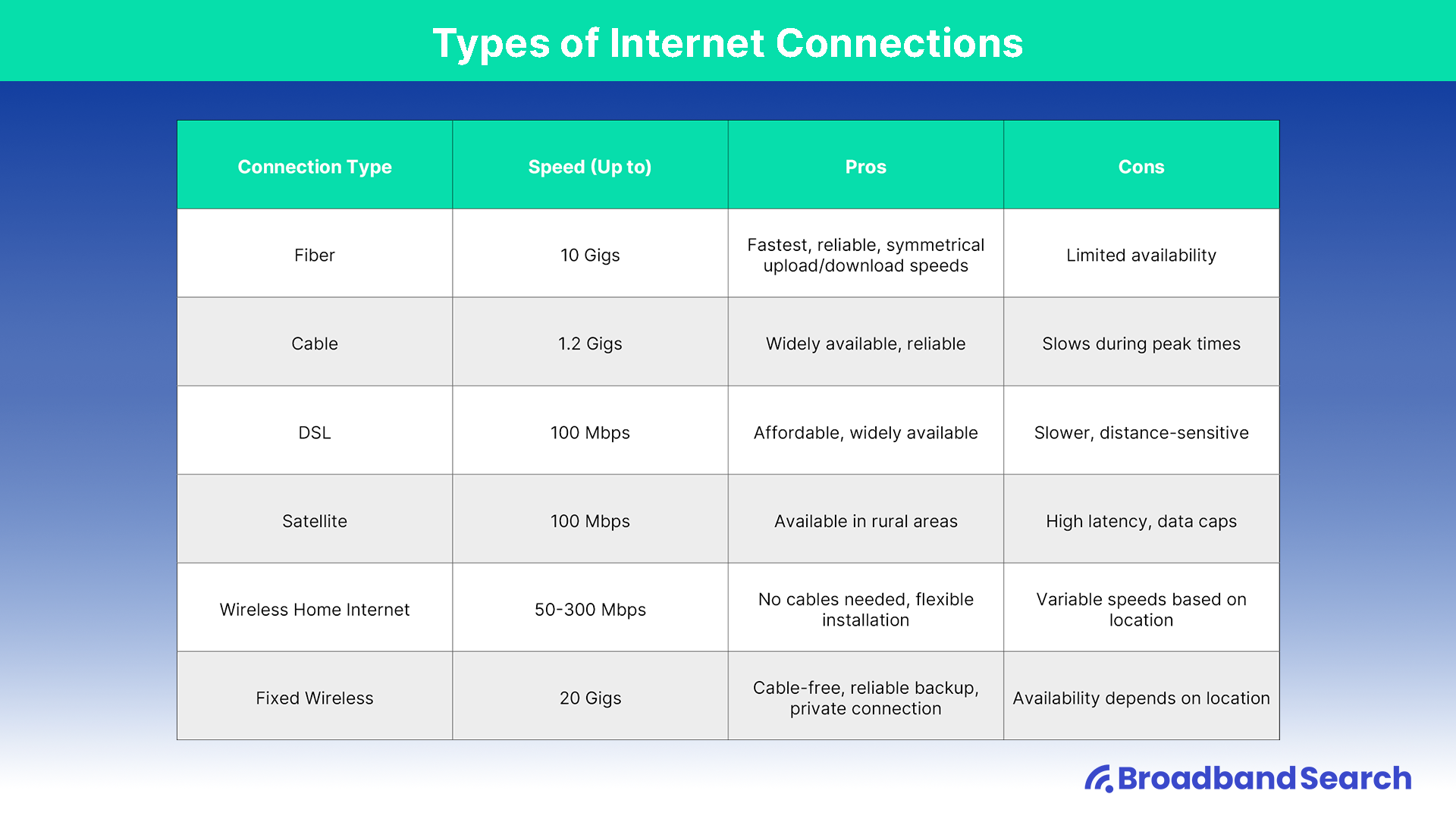
The technology delivering your internet plays a massive role in the speeds you can achieve.
| Connection Type | Speed (Up to) | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber | 10 Gbps | Fastest, reliable, symmetrical speeds | Limited availability |
| Cable | 1.2 Gbps | Widely available, reliable | Slows during peak times |
| DSL | 100 Mbps | Affordable, widely available | Slower, distance-sensitive |
| Satellite | 200 Mbps (depends on provider) | Available in rural areas | High latency, data caps; |
| Fixed Wireless | 1 Gbps | Cable-free, reliable backup | Line-of-sight required |
| 5G Home Internet | 300+ Mbps | Easy setup, no cables | Variable speeds |
Mbps vs. Gbps: Is Gigabit Internet Worth It?
For the average user, Gigabit internet (1 Gbps or 1,000 Mbps) is a luxury rather than a necessity. A plan offering 100-500 Mbps is usually sufficient for streaming 4K and browsing on multiple devices.
However, a Gig plan might be beneficial if:
- You have a large family with 10+ connected devices.
- You frequently download large video games or upload 4K video files.
- You have a smart home ecosystem that requires constant connectivity.
Remember that actual speeds depend on your hardware. Using an outdated router or relying on Wi-Fi instead of Ethernet can bottleneck a Gigabit connection.
What is the Right Internet Speed for Me?
Deciding on a plan doesn’t have to be complicated. Follow these steps to narrow down your options:
- Assess Usage: Count the users and devices that use the internet simultaneously.
- Identify Activities: Do you mostly browse, or do you game and stream 4K?
- Check Availability: Use our internet provider search to see what is available at your address.
- Run a Test: Use TestMySpeed.com to check your current performance.
- Match Needs: Refer to the comparison chart above.
- Future Proof: If you plan to work remotely, consider a plan with higher upload capacity or switching to fiber internet.
How to Test Your Internet Speed
Knowing your theoretical speed is one thing, but verifying it is another. Regular testing ensures you are getting what you pay for and helps identify equipment issues.
Run a Speed Test
Use a tool like TestMySpeed.com to measure your download speed, upload speed, ping, and network jitter (latency variation).
Test Under Normal Conditions
Avoid large downloads or streaming movies while testing to get an accurate reading of your available bandwidth. Background processes can skew results significantly.
Test Multiple Areas (Wi-Fi)
Check speeds in different rooms to ensure your Wi-Fi coverage isn’t limiting your bandwidth. If you find dead zones, you may need a Wi-Fi range extender or a mesh system.
Test Multiple Devices
Identify if specific devices are limiting your available bandwidth. An older laptop might not support the speeds your router is broadcasting.
Repeat Tests
Run tests at different times of the day to account for network congestion and fluctuations in available bandwidth. Cable internet can slow down during "prime time" evening hours.
Record Results
Keep track of your speed test results to monitor consistency. This data is valuable if you need to contact your ISP to troubleshoot internet problems.
Understanding Your Results
- Bandwidth: How much data your connection can handle at once—critical for multiple devices and high-demand activities.
- Download Speed: How quickly your device receives data from the web.
- Upload Speed: How quickly your device sends data to the web.
- Ping/Latency: Time for data to travel to a server and back; important for gaming and video calls.
- Network Jitter: Variation in latency, which can affect the smoothness of streaming, video calls, and real-time apps.
Optimizing Your Bandwidth and Internet Speed
- Use a wired Ethernet connection where possible for more stable bandwidth.
- Place your router centrally and reduce Wi-Fi interference to maximize available bandwidth.
- Close unnecessary background applications that consume bandwidth.
- Update your router firmware regularly to ensure security and performance.
- Consider upgrading your plan or provider if your bandwidth is consistently below expectations.
Testing your bandwidth regularly helps ensure your connection can handle your online activities, prevents slowdowns, and provides a benchmark for troubleshooting issues.
Recommended Speeds for Streaming and Gaming
Different apps have different "appetites" for data. Here are the recommended speeds for popular services based on BroadbandSearch research and official requirements:
- Netflix (HD): 5 Mbps
- Netflix (4K UHD): 15-25 Mbps
- YouTube (4K): 20 Mbps
- Zoom (Group HD Call): 3-5 Mbps (plus stable upload speed)
- Online Gaming: 5 Mbps to 50+ Mbps (Prioritize low latency over raw speed)
For a deeper dive into gaming requirements, check our guide on internet setups for gaming.
Work-From-Home Internet Speeds
Remote work has made having a reliable internet essential. Whether you are attending Zoom meetings or accessing a VPN, stability is key.
Minimum Requirements for WFH
- Email & Browsing: 5-10 Mbps
- Video Calls (Zoom, Teams): 10-25 Mbps
- Large File Uploads: 10-50+ Mbps (upload speed is critical here)
- Multiple Remote Workers: 100+ Mbps
To improve your home office setup, consider using a wired connection and checking for ISP throttling. For more tips, see our article on the best ISPs for remote work.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Internet Speed
Selecting the right internet speed is about matching your bandwidth to your lifestyle. You don't always need the most expensive Gigabit plan; you need a plan that supports your daily habits without interruption.
By understanding your usage, testing your current speeds, and comparing providers, you can find a connection that keeps you online without breaking the bank. Ready to explore your options? Visit our internet service providers page to get started.
FAQ
What is a good internet speed for working from home?
A minimum of 100 Mbps download and 10 Mbps upload is generally sufficient for most remote roles involving video calls and file sharing. However, if multiple people are working from home, BroadbandSearch recommends looking into business internet plans or higher-tier residential plans to prevent bottlenecks.
Why is my internet slow even though I have a high-speed plan?
Slow speeds can be caused by network congestion, outdated hardware, or Wi-Fi interference. Before calling your ISP, try restarting your modem and running an internet speed test near your router.
Is fiber internet worth it?
Yes. Fiber internet offers superior reliability, lower latency, and symmetrical upload speeds compared to cable or DSL. It is the best option for heavy users, gamers, and remote workers.
How can I upgrade my internet speed?
Start by checking your current contract. You can often upgrade your tier by contacting your ISP. Alternatively, use our provider comparison tool to see if a competitor offers better speeds for a lower price in your area.

