In this age of widespread digital integration, internet speed has become the pulse of modern society. From streaming our favorite shows to engaging in global commerce, from remote learning to telehealth, our daily lives are intertwined with the rapid flow of data. The speed of our internet connection isn't just about faster downloads or smoother streaming; it's about unlocking opportunities, bridging distances, and fueling innovation.
In this article, we ranked the fastest and slowest internet to help determine the extent of the digital divide that persists in 2024. By shining a spotlight on the discrepancies in internet speeds, we aim to raise awareness about the challenges faced by some regions and discover the factors that contribute to the success of others. Understanding these factors is crucial in formulating effective strategies to bridge the digital divide and ensure equitable access to high-speed internet for all.
State of Internet Speeds in the U.S.
As of April last year, the United States stands among the leading countries globally in terms of internet connectivity. With an average fixed broadband download speed of 80.12 Mbps and an upload speed of 35.1 Mbps, the nation boasts robust digital infrastructure that enables seamless online experiences for its citizens. While these figures place the U.S. ahead of the global average, efforts continue to bridge the urban-rural divide and ensure equitable access to high-speed internet for all.
Top 10 Fastest Internet Download Speeds by State
With the rapid expansion of internet connectivity options, especially fiber internet, some states now enjoy the privilege of exceptionally fast speeds. As technology continues to advance, certain states have emerged as frontrunners in delivering blazing-fast internet service, especially when it comes to download speeds.
Here are the top 10 states with the fastest average internet download speeds:
- Delaware — 246.95 Mbps
- Maryland — 238.26 Mbps
- New Jersey — 235.67 Mbps
- Connecticut — 233.88 Mbps
- Florida — 232.80 Mbps
- Virginia — 230.49 Mbps
- Rhode Island — 227.10 Mbps
- Texas — 225.74 Mbps
- California — 223.59 Mbps
- Nevada — 220.91 Mbps
Top 10 Slowest Internet Download Speeds by State
On the other hand, not all states are as fortunate when it comes to fast internet speeds or a wide variety of connectivity options. Many continue to face the challenge of slower service. Interestingly, most of the states with the slowest internet speeds are in rural areas, where limited infrastructure and geographical barriers create significant obstacles.
Here are the top 10 states with the slowest average internet download speeds:
- Idaho — 124.57 Mbps
- Alaska — 125.09 Mbps
- Montana — 129.73 Mbps
- Hawaii — 146.07 Mbps
- Wyoming — 147.19 Mbps
- Iowa — 150.74 Mbps
- Minnesota — 164.68 Mbps
- South Dakota — 164.71 Mbps
- West Virginia — 164.85 Mbps
- Vermont — 166.40 Mbps
Factors Affecting Internet Speed
- Bandwidth Availability: The amount of available bandwidth directly impacts internet speed. Higher bandwidth allows for faster data transfer rates, enabling users to download and upload data more quickly. Internet service providers (ISPs) with greater bandwidth capacity can offer faster and more reliable connections.
- Type of Connection: The type of internet connection a user has can significantly affect their internet speed. Common types of connections in the US include DSL, cable, fiber-optic, satellite, and wireless (e.g., 4G/5G). Fiber-optic and cable connections tend to offer higher speeds compared to DSL and satellite connections.
- Network Traffic: The amount of data being transmitted across the network at any given time affects internet speeds. During peak hours, when many users are online and accessing data-intensive services like video streaming, network congestion may occur, leading to slower internet speeds.
- Hardware and Infrastructure: The quality and capabilities of the user's equipment, such as routers, modems, and network cards, can impact internet speeds. Upgrading outdated or inefficient hardware can lead to improved performance. Additionally, the quality of the ISP's infrastructure and data centers also plays a significant role in delivering faster speeds.
- Geographical Factors: Geographical factors, particularly in rural and remote areas, significantly impact internet speeds in the US. Limited physical infrastructure, such as fiber-optic networks, coupled with the challenge of extending high-speed services to sparsely populated regions, contribute to the rural-urban divide in connectivity. These areas often face difficulties in laying down essential infrastructure, leading to slower internet speeds and hindering efforts to bridge the digital divide.
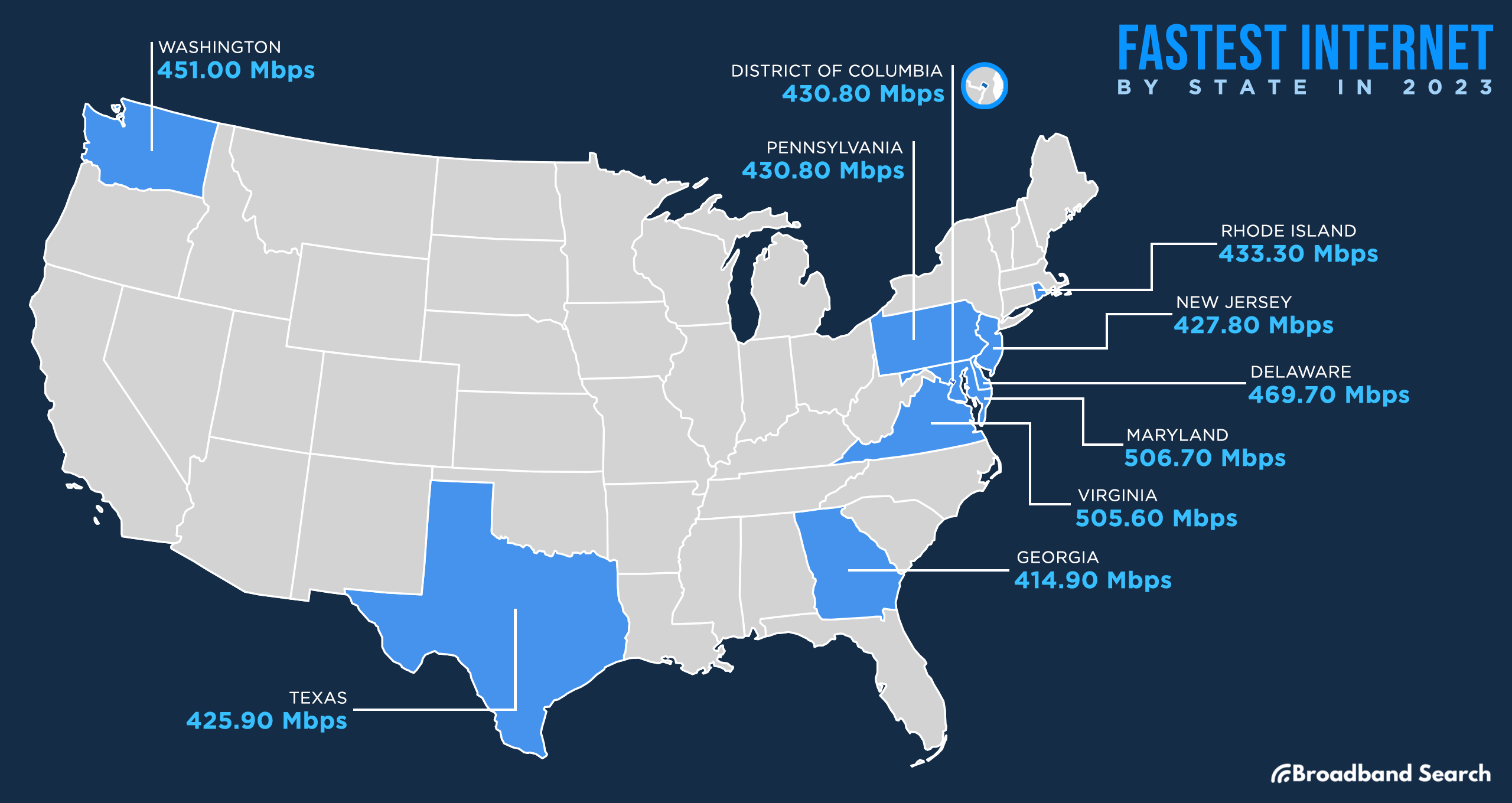
Average Internet Speed in Each State, Ranked from Fastest to Slowest
- Maryland - 506.70
- Virginia - 505.60
- District of Columbia - 473.80
- Delaware - 469.70
- Washington - 451.00
- Rhode Island - 433.30
- Pennsylvania - 430.80
- New Jersey - 427.80
- Texas - 425.90
- Georgia - 414.90
- Vermont - 408.20
- Massachusetts - 401.20
- New York - 397.70
- Arizona - 396.10
- South Carolina - 373.40
- Tennessee - 351.10
- Oklahoma - 351.00
- Colorado - 347.00
- Alabama - 344.60
- Nevada - 334.60
- Michigan - 334.10
- Indiana - 331.00
- Kansas - 325.70
- Illinois - 324.90
- Louisiana - 324.90
- Florida - 322.30
- New Hampshire - 317.90
- Oregon - 316.90
- Connecticut - 314.60
- Utah - 314.10
- North Carolina - 312.50
- Minnesota - 304.20
- Missouri - 293.40
- New Mexico - 288.70
- Alaska - 285.10
- Ohio - 278.30
- Wisconsin - 277.10
- West Virginia - 273.20
- Nebraska - 270.00
- Kentucky - 261.80
- North Dakota - 244.30
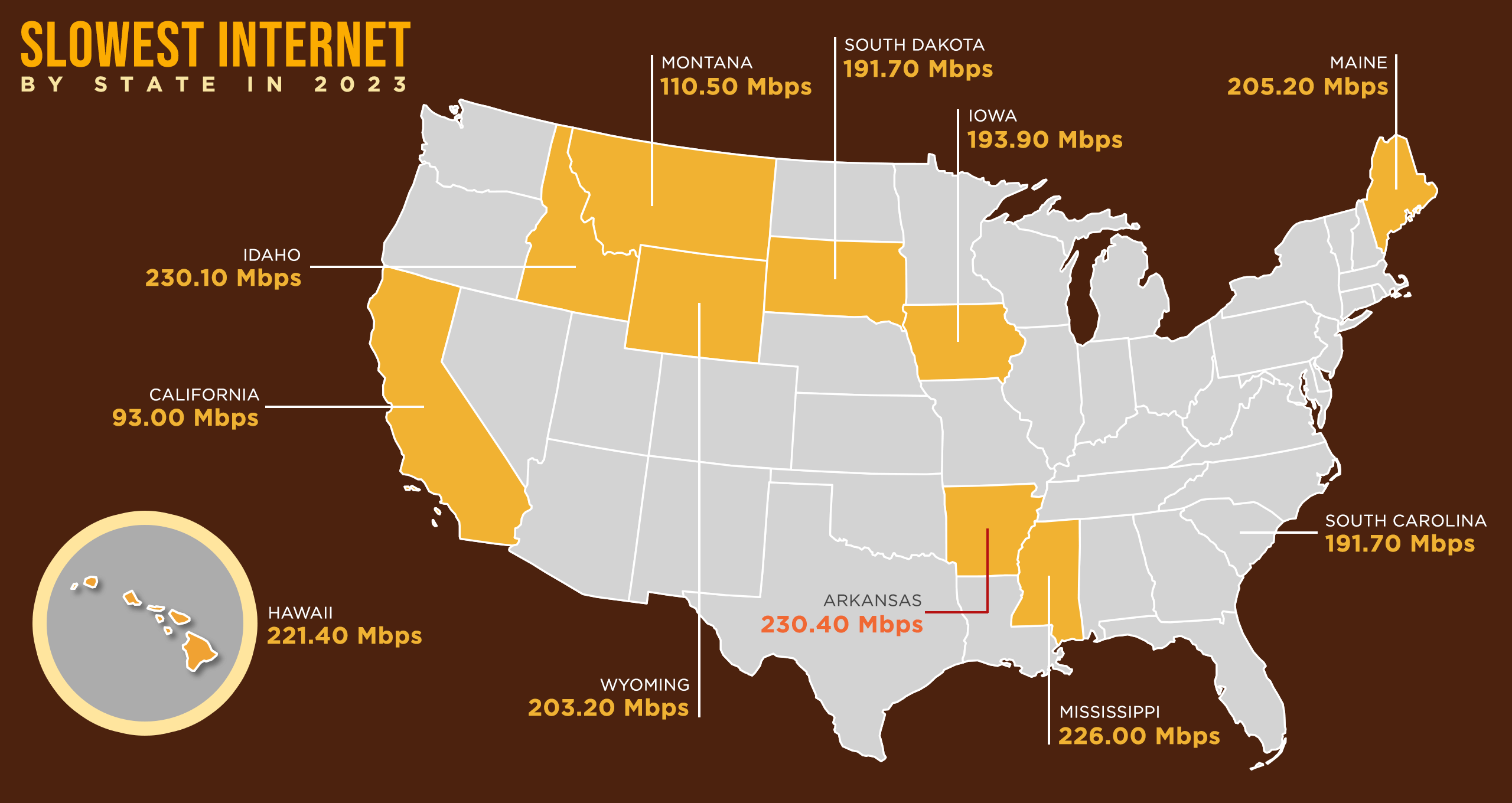
- Arkansas - 230.40
- Idaho - 230.10
- Mississippi - 226.00
- Hawaii - 221.40
- Maine - 205.20
- Wyoming - 203.20
- Iowa - 193.90
- South Dakota - 191.70
- Montana - 110.50
- California - 93.00
Technologies Powering the Fastest Internet
In the ceaseless quest for faster, more reliable Internet, technological innovation continues to push the boundaries of what's possible. From our homes to our mobile devices and even to the most remote corners of the globe, new technologies are revolutionizing how we connect. Here's a closer look at some of the most promising advancements:
- Fiber Optic Technologies: Innovations in fiber optic networks have ushered in a new era, surpassing traditional copper-based systems with an array of benefits and advanced capabilities. Fiber optic technology is now a key player in delivering high-speed internet services to both residential and commercial spaces. Through Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) deployments, users can enjoy symmetrical upload and fast download speed, minimized latency, and unrestricted bandwidth. These features not only enhance the overall user experience but also pave the way for sophisticated applications such as 4K video streaming, immersive online gaming, and seamless cloud services.
- 6G Mobile Networks: 6G, the upcoming sixth-generation mobile system standard, promises to surpass 5G with greater speed and advanced features. Utilizing machine learning and artificial intelligence, 6G aims to enhance wireless communication for connected devices. Its potential impact extends beyond smartphones and mobile networks, fostering innovation in areas such as smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences. The development of 6G marks a significant stride in telecommunications technology.
- Satellite Internet: Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites are transforming satellite Internet by operating at lower altitudes, facilitating faster data transmission with less power required for communication signals. This innovation extends high-speed Internet to remote regions, previously beyond traditional broadband's reach. The benefits encompass various sectors, including communications, business, and government, invigorating industries like mining, oil, and gas. Enhanced connectivity also improves emergency and disaster response, potentially saving lives. LEO satellites like Starlink are unlocking unprecedented opportunities in global communication.
- Quantum Communication: Quantum computing (QC), quantum sensing (QS), and quantum communication (QComm) are emerging technologies with transformative potential. While QC is about a decade away from commercialization, QS and QComm may become available sooner. QC promises to exponentially decrease processing time for complex problems, QS may enhance accuracy and accessibility in measurements, and QComm could fortify encryption for more secure information. Collectively, these technologies hold promise across various markets, such as high-performance computing, navigation, pharmaceuticals, and medical imaging, heralding a new era of innovation.
Average Download Speed in a Global Perspective
Globally, the race for faster connectivity continues, with various countries pushing the boundaries of technology to achieve unprecedented speeds. Within this competitive landscape, the United States holds a notable yet not leading position, ranking 7th in fixed broadband speeds at 202.4 Mbps. Despite the U.S.'s significant advancements in technology and infrastructure, the country's rankings reflect the continuous challenge to keep pace with global innovations in Internet speed. Countries leading in this race have heavily invested in next-generation technologies, infrastructure development, and policy frameworks that promote digital growth.
Fastest Internet Speed in the World
Smaller countries often have an advantage in achieving the world's fastest Internet speeds due to their ability to rapidly upgrade necessary infrastructure. This process becomes more complex and slower in larger nations, where sprawling geography, diverse terrain, and widespread populations present challenges in implementing uniform upgrades.
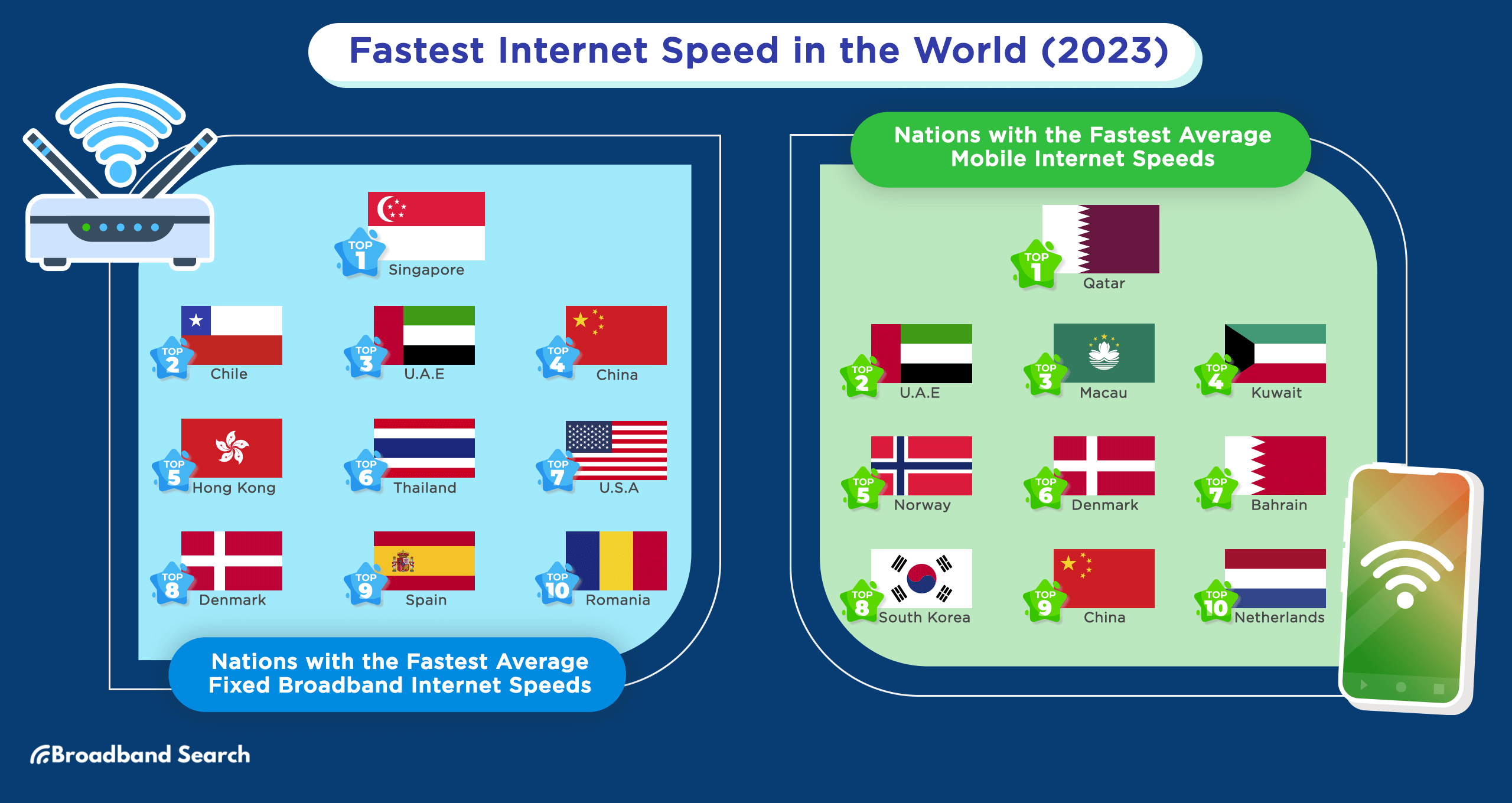
Nations with the Fastest Average Fixed Broadband Internet Speeds
- Singapore - 242.01 Mbps
- Chile - 222.49 Mbps
- United Arab Emirates - 216.78 Mbps
- China - 215.8 Mbps
- Hong Kong (SAR) - 205.19 Mbps
- Thailand - 204. 26 Mbps
- United States - 202.4 Mbps
- Denmark - 199.94 Mbps
- Spain - 175.96 Mbps
- Romania - 174.26 Mbps
Nations with the Fastest Average Mobile Internet Speeds
- Qatar - 189.98 Mbps
- United Arab Emirates - 175.34 Mbps
- Macau (SAR) - 171.73 Mbps
- Kuwait - 139.03 Mbps
- Norway - 131.16 Mbps
- Denmark - 118.83 Mbps
- Bahrain - 115 Mbps
- South Korea - 110.59 Mbps
- China - 110.1Mbps
- Netherlands - 109.13 Mbps
Factors Affecting the Ranking of the World's Internet Speed
The ranking of a country's Internet speed isn't just a matter of technological prowess. It's a complex interplay of several factors, each contributing to the overall performance and availability of internet services.
- Infrastructure and Technology: The quality and advancement of infrastructure and technology play a critical role in determining Internet speed. Countries investing in state-of-the-art technologies like fiber optics and 5G networks are likely to achieve higher speeds. A robust and modern infrastructure facilitates faster and more reliable connections, placing such nations at the forefront of the digital race.
- Economic Factors: Economic strength enables countries to invest in the development and maintenance of high-speed Internet infrastructure. Wealthier nations often have the resources to foster innovation, encourage competition among service providers, and subsidize connectivity in underserved areas. Economic factors, therefore, directly correlate with a country's ability to provide fast and accessible Internet to its citizens.
- Regulatory and Policy Environment: Government regulations and policies can either spur or hinder the growth of Internet speeds. Proactive policies that encourage investment in new technologies, remove bureaucratic barriers, and ensure fair competition can boost a country's highest Internet speed ranking. Conversely, restrictive regulations may limit growth and innovation in this sector.
- Geographical Considerations: A country's geography significantly impacts the ease and cost of deploying Internet infrastructure. Mountainous terrains, remote locations, and vast distances can pose challenges to laying cables and setting up networks. Smaller countries or those with favorable geography often find it easier to implement uniform high-speed Internet across their territories.
- Population: The density and distribution of a population affect Internet speeds as well. Densely populated urban areas might enjoy higher speeds due to economies of scale in infrastructure investment, while sparsely populated regions may face challenges in accessing high-speed Internet. Population factors thus contribute to the overall ranking of a country's Internet speed by influencing demand, accessibility, and investment in connectivity.
Advantages of High-Speed Internet Access
The advantages of high-speed internet extend beyond mere convenience, impacting various facets of daily living and professional endeavors. Here's an exploration of some of the key benefits:
- Efficient Communication: High-speed Internet fosters efficient communication by enabling smooth video conferencing, instant messaging, and rapid file sharing. Whether in a professional setting or personal connections, swift and reliable Internet enhances the way we interact and collaborate, bridging distances and time zones effortlessly.
- Seamless Streaming: With high-speed Internet, users can enjoy seamless streaming of videos, music, and live events. Buffering becomes a thing of the past, allowing for an uninterrupted entertainment experience that caters to modern demands for on-the-go content consumption.
- Improved Productivity: Fast Internet contributes to improved productivity by minimizing delays and enhancing collaboration in the workplace. Quick access to online resources, cloud services, and remote working tools translates into more efficient work processes, boosting overall output.
- Enhanced Online Gaming: Gamers benefit immensely from high-speed Internet, experiencing reduced lag and more responsive gameplay. This ensures an immersive and competitive gaming experience, where split-second decisions and reactions are not hampered by slow connections.
- Support for Multiple Users: High-speed Internet enables smooth connectivity for multiple users within a household or organization. Whether it's simultaneous streaming, gaming, or working, a robust connection supports diverse online activities without compromising speed or quality. This fosters a more flexible and accommodating digital environment, suitable for the multifaceted needs of modern living.
Ways to Boost Your Internet Connection Speed
Boosting your internet connection speed can greatly improve your online experience. Here are some quick tips to achieve that:
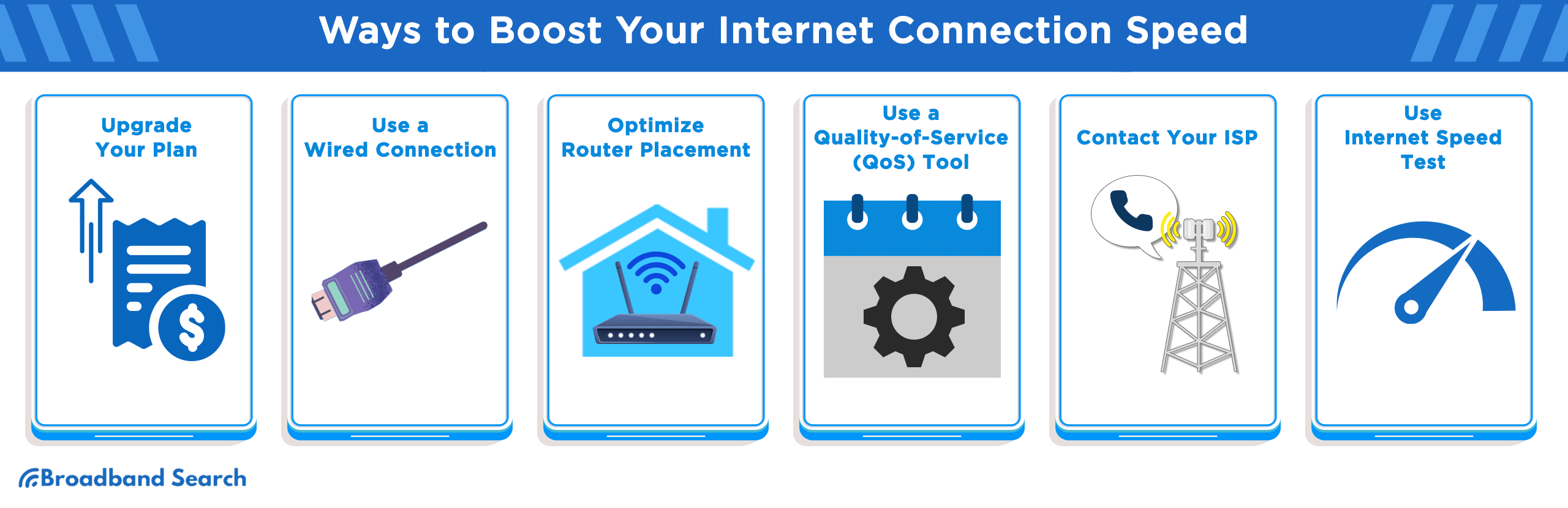
- Upgrade Your Plan: Sometimes, the easiest way to increase Internet speed is by upgrading your current plan with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). If your current plan doesn't meet your needs, a higher-tier plan with more bandwidth can offer the speed you require. It's worth comparing different packages and considering factors like download and upload speeds, monthly cost, and any additional services that might be included.
- Use a Wired Connection: Wi-Fi is convenient, but a wired connection often provides a more stable and faster Internet experience. By using an Ethernet cable to connect directly to the router, you can eliminate potential wireless interference and enjoy a more reliable connection. It's an ideal option for activities that demand high-speed Internet, such as gaming or HD streaming.
- Optimize Router Placement: The placement of your router can significantly impact Wi-Fi speed and signal strength. Positioning the router in a central location, away from physical obstructions and electronic interference, can improve connectivity. Elevating the router and keeping it free from obstacles like walls and large appliances can also enhance performance.
- Use a Quality-of-Service (QoS) Tool: Quality-of-Service (QoS) tools play a vital role in managing and optimizing Internet traffic, especially when multiple applications are competing for bandwidth. For example, if you're working from home and frequently engage in video conferences, QoS settings can be configured to prioritize this activity over others like file downloads or streaming videos. By doing so, you ensure that video conferencing receives sufficient bandwidth, reducing lags or interruptions.
- Contact Your ISP: If you're experiencing persistent slow speeds, it might be time to contact your ISP. They can conduct a diagnostic test, identify potential issues, and provide solutions or even send a technician if needed. Your ISP can be an essential resource in resolving connectivity problems and ensuring you get the speed you're paying for.
- Use Internet Speed Test: Regularly testing your internet connection with speed test tools is a practical approach to monitor and evaluate your connection's performance. These tools measure download and upload speeds, offering valuable insights into whether you're receiving the speeds promised by your ISP. If you consistently notice discrepancies or slowdowns, this information can be instrumental when troubleshooting with your provider.
Final Thoughts
The role of internet speed in modern society is both intricate and essential, reflecting a world where digital connectivity is pivotal. Faster internet is not just a technological advancement but a symbol of progress, embodying the human spirit of innovation and offering opportunities that impact economies, education, culture, and more.
However, the existence of the slowest internet speeds highlights the ongoing digital divide, underscoring the need to address accessibility and efficiency across geographical and socio-economic lines. The future demands not just a pursuit of speed but a concerted effort to ensure that internet connectivity is an inclusive right rather than a privilege. It's a complex issue that touches us all, no matter where we live or what we do.
FAQ
Is the fastest internet speed accessible in rural areas?
The accessibility of the fastest internet speeds in rural areas can vary greatly depending on the country, infrastructure, and local policies. While advancements have been made, rural areas might still experience challenges in accessing the fastest internet speeds compared to urban areas.
Can I get the fastest internet speeds over Wi-Fi?
Yes, it is possible to achieve fast internet speeds over Wi-Fi, but it might not always match the fastest wired connections. The speed over Wi-Fi can be affected by factors like router quality, interference from other devices, distance from the router, and the type of internet connection you have.
Is the fastest internet speed necessary for regular home use?
The necessity for the fastest internet speed depends on your usage. For regular browsing, emailing, and social media, extremely high speeds might not be necessary. However, for activities like online gaming, streaming in high definition, or working from home with heavy data usage, a faster internet connection may be beneficial.
Does the speed of the internet fluctuate during the course of the day?
Yes, internet speed can fluctuate during the day. This is often due to network congestion when many users are online simultaneously, typically during peak hours. Factors like maintenance, technical issues, or the type of connection you have can also affect the speed.
How often should I do a speed test?
Conducting a speed test occasionally is a good practice to ensure you are getting the speeds you're paying for, especially if you notice a slowdown. Monthly checks or after making significant changes to your network setup could be a reasonable approach. If consistent discrepancies are found, contacting your service provider might be necessary.

