In our modern world, social media is everywhere, deeply ingrained in our daily routines. It profoundly impacts how we communicate, access information, and view ourselves. From our mental well-being to our relationships and productivity, it touches many aspects of our lives. To better navigate this digital landscape, we need to examine our personal social media habits. This assessment aims to help us understand how we use social media individually, shedding light on its effects and enabling us to make informed choices for a more balanced and meaningful life.
Assessing Social Media Usage
Frequency of Usage
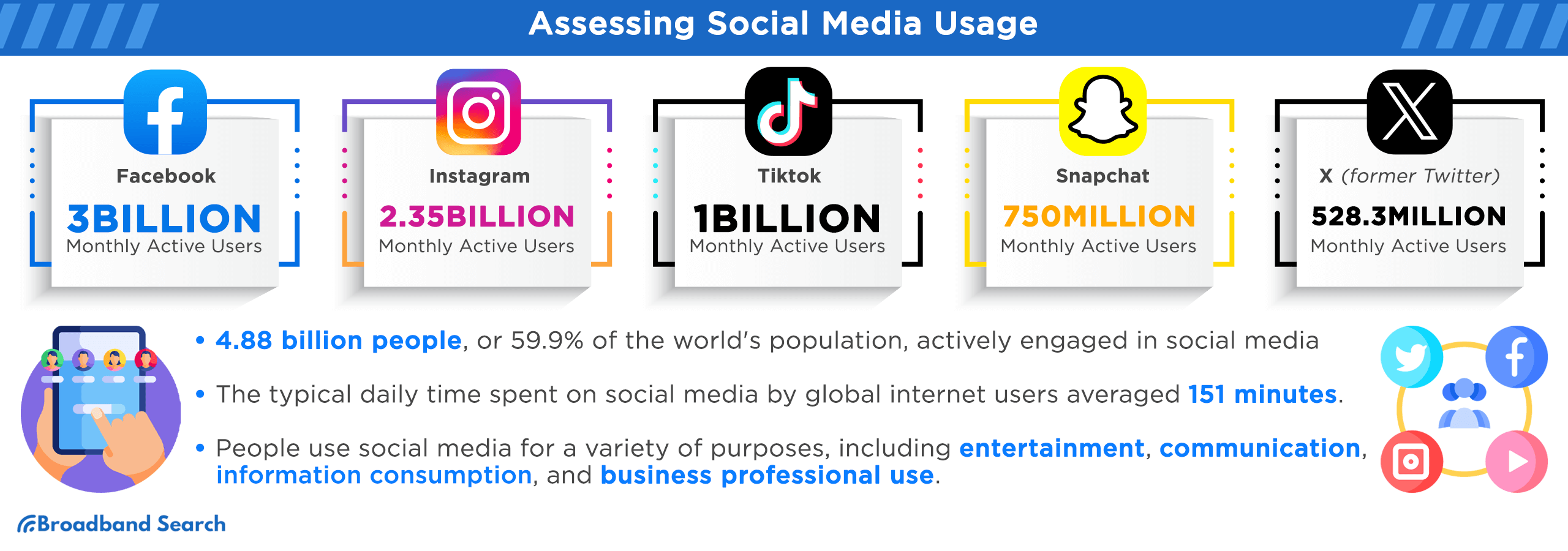
- Daily Engagement: In July 2023, the global count of internet users stood at 5.19 billion, representing 64.6 percent of the planet's inhabitants. Among these, Statista reports that 4.88 billion, equivalent to 59.9 percent of the world's population, actively participated in social media.
- Weekly Usage: The significance of weekly engagement with social platforms lies in the fact that 49% of Facebook users and 59% of Instagram users accessed these platforms daily in 2021, according to the Pew Research Center.
Time Spent
- Average Time Per Day: In 2022, the typical daily social media engagement for global internet users reached 151 minutes per day, showing a slight increase from the 147 minutes recorded in the prior year, according to Statista's findings.
- Total Time Per Week: Weekly time allocation carries substantial implications for both productivity and well-being. Excessive social media usage has consistently been associated with reduced productivity.
Platforms Used
Facebook continues to dominate the social media landscape, boasting an impressive 3 billion monthly active users as of the second quarter of 2023. It's worth noting that the platform achieved the two-billion active user mark in the second quarter of 2017, accomplishing this remarkable milestone in just over 13 years.
X/Twitter
X/Twitter's utilization is in harmony with several behaviors, notably real-time news consumption. Statista's data reports that the platform presently counts 528.3 million monetizable monthly active users, affirming its significant reach.
Instagram exerts a substantial influence on user behavior, a fact underpinned by the platform's vast reach. The most recent data from DemandSage indicates that Instagram boasts over 2.35 billion monthly active users, solidifying its position as a key player in the social media landscape.
Snapchat
According to Oberlo, Snapchat currently boasts an impressive 750 million monthly active users. Furthermore, Snapchat has reported substantial growth in one of its latest features, Spotlight, which promotes short-form video content. In Q2 2023, Spotlight's monthly active user count surged by 51% year over year, surpassing the 400 million mark, signifying its rapid adoption and popularity.
TikTok
TikTok's prominence is steadily ascending, with a noteworthy over 1 billion monthly active users globally in 2023. This achievement firmly establishes TikTok as one of the fastest-growing platforms on a global scale.
Purpose of Usage
- Entertainment: Social media plays a substantial role in providing entertainment. As indicated by Pew Research Center's 2018 data, a percentage of users believe that social media is a suitable platform for entertainment (9%). Fewer still argue that it offers a space for self-expression (7%) or provides a means for teenagers to seek support from others (5%) or to acquire new knowledge in general (4%).
- Communication: Similarly, the same report highlights that 40% of respondents perceive social media as having a positive impact due to its facilitation of communication and interaction with others. Many respondents specifically note how social media has simplified staying in touch with loved ones and friends, as well as forging connections with new acquaintances.
- Information Consumption: In a survey conducted in 2023 by Statista, it was found that 78% of respondents from Nigeria rely on social media for news, while only 23% of Japanese respondents shared the same sentiment. A significant portion of global social media users acknowledge their lack of trust in these platforms as sources of news. However, paradoxically, they continue to access these networks regularly.
- Business/Professional Use: Professional networking on platforms like LinkedIn is integral, given its 950 million members, with 50% of Americans with a college degree using it.
Content Consumption
Types of Content Consumed: Content encompasses various forms such as text, images, and videos. According to SproutSocial, approximately 66% of consumers find short-form videos to be the most engaging among all social media post types. This highlights short video content's significant appeal and impact in capturing the audience's attention and engagement.
Frequency of Content Sharing: Social media sharing habits play a significant role in shaping information dissemination and engagement. According to the Pew Research Center's findings, teenagers have shifted their approach to sharing specific types of information on social media platforms.
While these platforms are inherently designed to encourage information sharing and network expansion, most teenagers do not adopt a fully public approach. The results of a 2012 survey highlight this:
Teens are generally willing to share:
- Their real name (92%)
- A photo of themselves (91%)
- Interests, such as favorite movies, music, or books (84%)
- Their birth date (82%)
- School name (71%)
- City or town of residence (71%)
However, fewer teens are willing to disclose:
- Their relationship status (62%)
- Email address (53%)
- Videos of themselves (24%)
- Cell phone number (20%)
Content Creation: As reported by Social Media Today, incorporating images into content not only boosts traffic but also drives more clicks and conversions. Photos, videos, and infographics have a distinct advantage in capturing user attention compared to text. Notably, social media posts featuring images and videos tend to garner significantly more likes, shares, and overall engagement than those relying solely on text updates.
Notification and App Usage
Frequent notification checks can prove disruptive, as an article from cbn reveals that people, on average, check their phones approximately every 12 minutes.
This habitual behavior is particularly pronounced among teens in the United States, as indicated by a 2018 survey conducted by the Pew Research Center. Notably, 72% of teenagers admit to sometimes checking messages or notifications immediately upon waking up, with 44% acknowledging that they often engage in this behavior.
Follower/Friend Count and Interaction
The size of one's social network significantly shapes their online behavior. According to Pew Research Center data from 2014, among adult Facebook users, the average number of friends is 338 (mean), and the median number stands at 200 (midpoint). In practical terms, this means that half of all Facebook users have more than 200 friends, while the other half have fewer.
Interestingly, the data also reveals generational differences. Younger users tend to maintain substantially larger friend networks than their older counterparts. Specifically, 27% of Facebook users aged 18-29 have more than 500 friends in their network, whereas 72% of users aged 65 and older have 100 friends or fewer.
Use of Hashtags and Trends
Incorporating hashtags holds substantial importance, as revealed by Sprout Social, where posts featuring at least one hashtag experience an average increase of 12.6% in engagement.
Furthermore, active engagement with trending topics exemplifies the ever-evolving nature of social media. Notably, popular hashtags like #BlackLivesMatter has garnered global attention and extensive engagement, with many users frequently employing the hashtag in solidarity with the broader social movement or highlighting specific related issues.
Impact on Mental Health
Satisfaction with Social Media Usage
Amidst a remarkable surge in online activity during the COVID-19 pandemic, the satisfaction of users with social media platforms witnessed an unexpected decline in the past year. Despite the increased usage, the overall user satisfaction score for social media registered a modest 70 on a scale of 1 to 100, marking a 2.8% decrease. It's worth noting that platforms like Instagram, LinkedIn, Pinterest, Twitter, and YouTube saw decreases in user satisfaction ranging from 1% to 4%.
However, in contrast to this trend, Facebook, Snapchat, and Tumblr managed to defy the odds, demonstrating slight gains in user satisfaction, ranging from 1% to 3%, as indicated by the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI).
Additionally, a 2020 survey conducted by the Pew Research Center among U.S. adults unveiled a significant perspective on social media. A substantial 64% of respondents perceived social media as having a primarily negative impact on the current state of affairs in the country. Conversely, only a mere one in ten Americans believed that social media platforms predominantly had a positive influence on the nation's trajectory. Furthermore, one-quarter of respondents believed that these platforms had a neutral effect, neither being predominantly positive nor negative.
Comparison of Social Media Usage with Mental Health Indicators
Depression
The impact on depressive symptoms carries substantial weight, as supported by a 2020 study conducted by the National Institute of Health (NIH). This study unearthed a noteworthy 70% increase in self-reported depressive symptoms among individuals engaged in social media use.
Furthermore, social media's potential to induce depression is exacerbated when it portrays an idealized version of life, emphasizing fun and excitement while masking deeper struggles. Another study underscored the link between depression and the time spent on Facebook by adolescents, revealing a positive correlation. Notably, individuals who dedicated the majority of their time to online activities and meticulously curating their online image on social networking sites were found to exhibit symptoms of major depression.
Anxiety
A recent publication from the National Institute of Health (NIH) delves into the intricate relationship between social media use and social anxiety, particularly among college students, given the significant surge in social media adoption among young people over the past decade.
College students, who frequently engage with the internet, may find their psychological well-being in social interactions influenced by their use of social media platforms. Research suggests that using these platforms can contribute to personal social anxiety. Several theories provide insight into the mechanisms underlying the link between social media use and social anxiety.
According to self-presentation theory, individuals may become more attuned to potential negative evaluations from others and may even assume that others harbor negative perceptions of them based on their online self-presentation. This heightened sensitivity can lead to social anxiety.
Additionally, classical social comparison theory suggests that individuals often use others as reference points for self-evaluation, particularly when they lack concrete reference material. Passive use of social media, without active communication, can lead to increased upward social comparison, where individuals compare themselves unfavorably to others, further contributing to social anxiety.
Stress
A 2020 thesis revealed a connection between social media use and stress. Using social media during work hours can increase stress, as it combines personal issues with work-related problems. People with high daily stress levels tend to use social media more frequently to change their mood and seek support from others. However, this frequent use of social media can lead to even more stress and disrupt daily life. Addictive social media use can worsen stress, creating a cycle where stress drives more social media use.
This study also confirmed previous research showing that social media usage is linked to perceived stress levels, affecting both men and women. Women, in particular, seem more vulnerable to stress caused by social media use.
Effects on Self-Esteem and Body Image
An exploration of the impact of Instagram, as reported by a new media specialist, reveals a complex interplay between its effects on young people's mental health. While Instagram offers opportunities for self-expression, self-identity development, community building, and emotional support, it also harbors negative consequences that can have profound implications.
Notably, Instagram has been associated with a host of detrimental effects, particularly on body image and sleep patterns. It fosters an environment that promotes negative self-comparisons based on appearance, leading to heightened body image concerns. This consistent link between social media use and body dissatisfaction is a significant contributor to mental health challenges among young people.
Moreover, the impact on self-esteem is a prevalent issue, as highlighted by a Huffington Post poll in 2017. This poll found that a substantial 60% of social media users admitted that their self-esteem had been negatively affected by their online experiences. Additionally, more than half (51%) reported that social media had increased their feelings of insecurity regarding their appearance.
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) and Social Comparison
The phenomenon of FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) represents a significant and problematic attachment to social media, with far-reaching consequences across various aspects of life. FOMO is closely linked to a spectrum of negative experiences and emotions, encompassing sleep deprivation, diminished life competence, heightened emotional stress, adverse effects on physical well-being, anxiety, and compromised emotional control.
The Social Media Victims Law Center has conducted illuminating research shedding light on the pervasive presence of FOMO among social media users. Their findings reveal that the constant craving to stay connected and avoid missing out on digital experiences compels individuals to check their notifications incessantly. Paradoxically, this excessive digital engagement often comes at the expense of genuine, real-life relationships and meaningful activities.
Statista's research provides further insights into the global prevalence of FOMO:
- In the United States, as early as 2013, 56% of social media users reported experiencing FOMO, underscoring its deep-seated roots in digital culture.
- In Poland, the phenomenon has been notably pronounced among the younger generation, with 59% of 15- to 19-year-olds in the country reporting FOMO experiences in 2021.
- In Italy, the pervasiveness of FOMO was evident in 2017, as a significant 67% of Italian social media users grappled with this phenomenon.
Privacy and Security Awareness
Awareness of Privacy Settings
In the realm of online privacy, a pivotal study conducted by Jones and Soltren in 2005 uncovered intriguing patterns in users' behavior and awareness on social media, particularly on Facebook.
It was revealed that a substantial 74% of users possessed awareness of the available privacy options on Facebook. However, despite this awareness, only 62% actively utilized these privacy settings. This discrepancy suggests a noteworthy gap between knowledge and action among social media users.
Intriguingly, the study also delved into the extent to which users voluntarily shared personal information. Astonishingly, over 70% of users willingly divulged demographic details, such as age, gender, location, and interests, emphasizing a willingness to expose aspects of their identity.
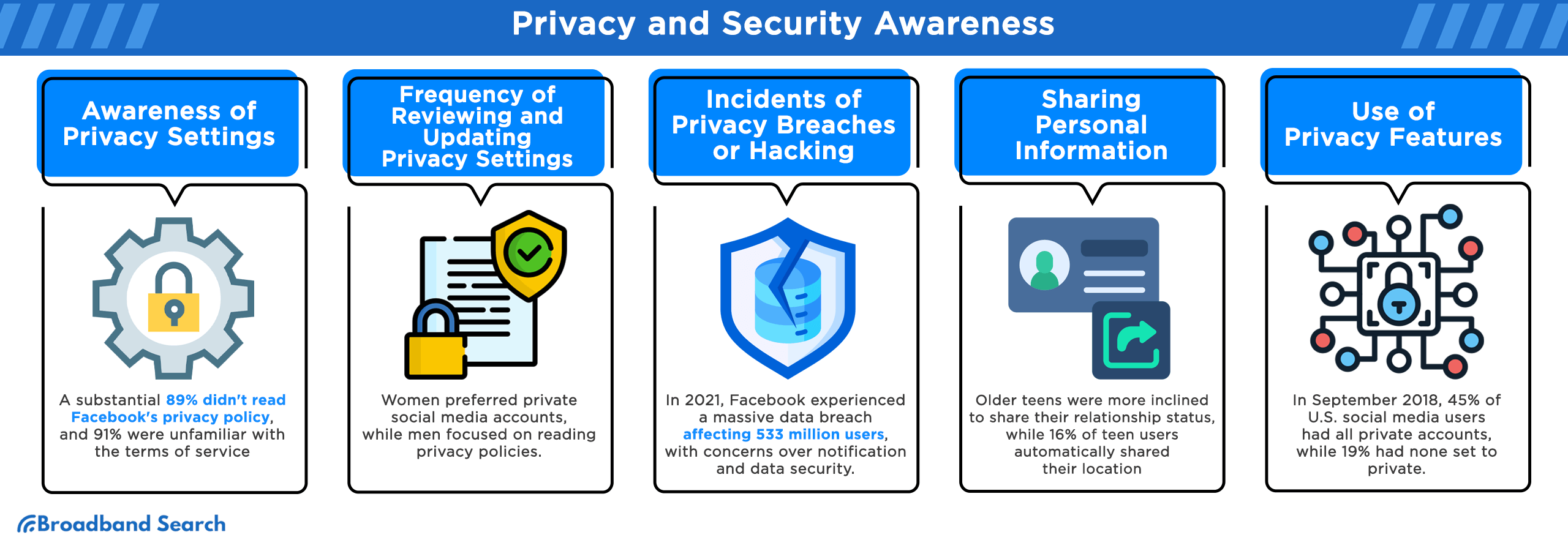
Moreover, a notable trend emerged, indicating a degree of disregard for both privacy settings and the terms of service outlined by Facebook. A substantial 89% of users admitted to never having read the platform's privacy policy, while an even more staggering 91% exhibited unfamiliarity with the terms of service.
Frequency of Reviewing and Updating Privacy Settings
A survey conducted by ViaSatSavings involved 1,000 participants in the United States, aged 18 and above, with the aim of gaining insights into their attitudes toward social media privacy. The findings paint an intriguing portrait of how different demographics approach and perceive privacy on social media platforms.
Gender disparities were evident, with women exhibiting a greater inclination to set their social media accounts to private. In contrast, men displayed a higher tendency to engage with and read privacy policies. This discrepancy suggests varying priorities and approaches to privacy within these two groups.
A notable 71% of respondents expressed the habit of checking their advanced privacy settings when they join a new social media platform. Delving deeper, it was revealed that 55% of these vigilant users were female, while 45% were male. This underscores the significance of privacy settings, especially among women, in the context of social media.
Age also played a pivotal role in shaping privacy practices. Respondents aged 54 and above emerged as the demographic most likely to keep their social media accounts public. More than 15% of this age group opted not to activate any privacy settings. Following closely, respondents in the 18-24 age bracket were the second-most likely to maintain public accounts, with 11% choosing not to engage in any privacy settings.
Incidents of Privacy Breaches or Hacking
The landscape of social media platforms has been punctuated by a series of high-profile incidents that have significantly underscored their vulnerability and the far-reaching implications of privacy breaches.
One of the most glaring examples was the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal that unfolded in the 2010s. This controversy centered around the unauthorized collection of personal data from millions of Facebook users by the British consulting firm Cambridge Analytica. The harvested data was primarily intended for political advertising purposes, serving as a stark reminder of the potential misuse of user information on social media.
Another noteworthy incident occurred in 2021 when Facebook experienced a massive data breach, affecting over 533 million users. Surprisingly, Facebook opted not to notify more than 530 million of these users whose personal data had been compromised in a breach that predated August 2019. The exposure of this data in a public database raised significant concerns about the platform's security practices and user data protection.
In addition, the 2020 Twitter hack resonated as a significant security breach, particularly for high-profile individuals like Elon Musk and Barack Obama. This incident revealed vulnerabilities within the platform's security infrastructure. The hacker, 23-year-old Joseph James O'Connor, a British citizen known by the online alias PlugwalkJoe, was arrested in July 2020. O'Connor was reported to have successfully breached over 100 Twitter accounts, including those of Apple, Uber, Kanye West, Bill Gates, Joe Biden, Barack Obama, and Elon Musk.
Sharing Personal Information
Personal details shared on profiles: As per a 2012 survey conducted by Pew, a significant trend emerged among teen social media users regarding the sharing of personal information on their profiles or primary accounts. Notably, a substantial 82% of these users willingly disclosed their birthdates, offering insights into their personal lives. Additionally, 62% of teen users chose to share their relationship status.
This trend was further dissected by age demographics, revealing that older teen social media users exhibited a higher propensity for disclosing their relationship status compared to their younger counterparts. Specifically, 66% of older teens engaged in this practice, whereas 50% of younger teens did the same.
Sharing of location information: Intriguing insights from the same survey unveiled a distinctive trend among teen social media users concerning the automatic inclusion of location in their posts. While the focus initially centered on basic profile information, a notable 16% of teen social media users opted to activate features that automatically tagged their location when making posts. This deliberate choice to share location data showcased a nuanced dimension of how some teenagers engage with social media platforms, emphasizing the significance of geolocation features in their digital interactions.
Use of Privacy Features
Statista offers a unique perspective on the prevalence of private social media accounts among users in the United States as of September 2018. Delving into the data, it becomes apparent that there is a diverse landscape of privacy preferences among social media users.
Among the respondents, a significant 45% indicated that all of their social media accounts were configured as private, highlighting their proactive approach to safeguarding their digital presence. On the contrary, an intriguing 19% of respondents took a different stance, revealing that none of their social media accounts were set to private.
Social Media Content and Behavior
Types of Content Posted
PR Newswire's 2019 report highlights the diverse landscape of social media content creation among users:
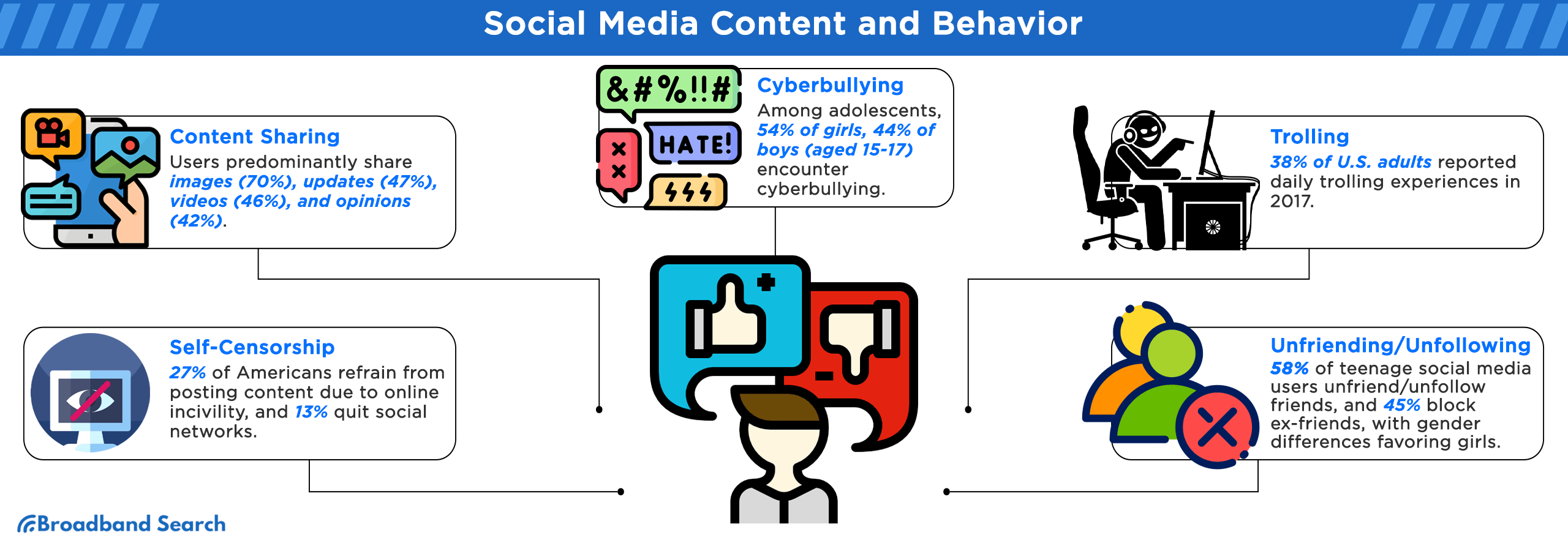
- Approximately 70% of users actively share images, signifying the prevalent use of visual content.
- In comparison, 47% of users opt for updates and announcements.
- Videos are a preferred choice for 46% of users, underscoring the significance of multimedia content.
- Opinions find their place in the social media sphere, with 42% of users sharing their viewpoints.
Online behavior
Cyberbullying: Recent data from the Pew Research Center underscores the prevalence of cyberbullying experiences among adolescents in the United States, revealing varying rates based on gender and age:
- Among girls aged 15 to 17, approximately 54% have encountered at least one of six cyberbullying behaviors.
- For boys in the same age group (15 to 17), the percentage slightly decreases to 44%, indicating a gender difference in cyberbullying experiences.
- Among 13 to 14-year-olds, both boys and girls report similar rates, with 41% acknowledging at least one cyberbullying encounter.
Trolling: Statista's survey, conducted in August 2017 to gauge internet trolling experiences among adults in the United States, uncovered a noteworthy trend: 38% of respondents reported encountering trolling behavior on social media platforms daily.
Online etiquette and civility: A 2019 study published in Science Direct delves into the realm of social media interactions related to politics, shedding light on the perceived differences compared to offline exchanges. According to the study, many users characterize social media political interactions as less respectful, conclusive, civil, and informative when contrasted with offline discussions.
Additionally, the study findings reveal that roughly 27% of Americans have refrained from posting content online after witnessing others experience harassment, showcasing the impact of online incivility on self-censorship. More than 10% (13%) have taken the significant step of ceasing to use a social network altogether due to their observation of uncivil behavior among other users.
Frequency of Unfriending/Unfollowing
According to a 2015 report by the Pew Research Center, teenage users of social media and cell phones exhibited distinct patterns in managing their online social circles:
- A notable 58% of these teens had chosen to unfriend or unfollow individuals they had previously considered friends, highlighting the fluid nature of online relationships.
- Additionally, 45% of teens had opted to block an ex-friend, demonstrating their proactive approach to curating their online connections.
Furthermore, gender differences in these behaviors were evident:
- Among teenage girls who use social media or cell phones, 63% had unfriended or unfollowed an ex-friend, compared to 53% of boys.
- Girls also tended to be more inclined to block someone after ending a friendship, with 53% of social media- or cellphone-using girls employing this strategy, compared to 37% of boys.
Social Media and Productivity
Impact on Academic/Professional Performance
A 2018 research study conducted by the San Francisco-based non-profit organization, Common Sense Media, delved into the impact of social media on teenagers' daily lives. The study, titled "Social Media, Social Life: Teens Reveal Their Experiences," encompassed interviews with over 1,100 teenagers aged 13-17 across the United States. Notably, the majority of these teens demonstrated a keen awareness of how social media applications, such as Instagram and Snapchat, can divert their attention from real-life priorities.
The study revealed that social media is a significant distraction for teenagers. Approximately 57% of the interviewed teenagers acknowledged that it often hinders their focus on homework assignments. Additionally, around 54% of the participants admitted to occasionally neglecting the people they were physically present with in favor of browsing social media apps.
Recent market data compiled by Gitnux reveals a significant trend in workplace behavior, shedding light on the extent of social networking site usage during working hours. The statistics indicate that a substantial 73% of employees are actively engaging with social networking sites while at work, primarily for personal purposes.
Time Spent on Social Media During Work/School Hours
A 2021 study conducted by the National Institute of Health (NIH) unveiled significant patterns in students' social media usage. The findings indicate that a noteworthy 57% of students dedicate more than three hours to social media during the daytime, while an additional 34% continue to engage with social media during nighttime hours
A recent report published by the Society for Human Resource Management has brought to light an interesting trend among U.S. employees. The data indicates that a noteworthy 48% of these employees allocate a significant portion of their workday, up to four hours, to engage in personal social media activities during official working hours.
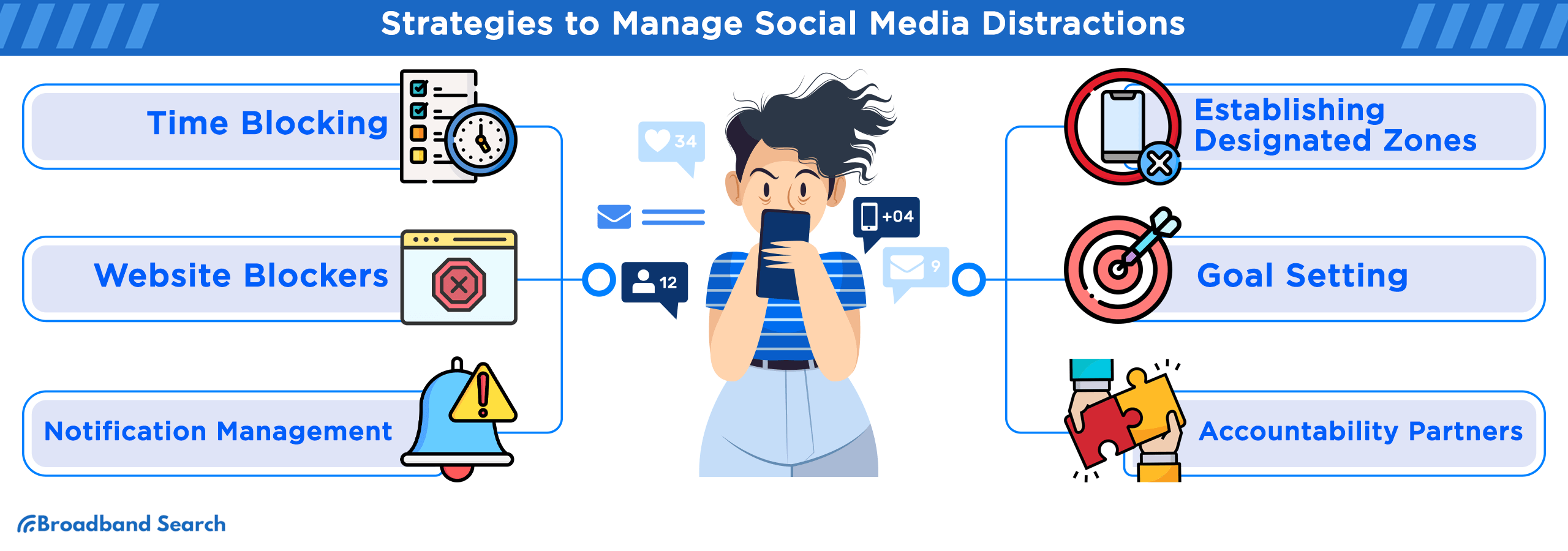
Strategies to Manage Social Media Distractions
To combat the distractions posed by social media, individuals can employ several strategies:
- Time blocking: Allocate specific time intervals for checking social media, limiting interruptions during productive work or study sessions.
- Website blockers: Utilize browser extensions or apps that temporarily block access to social media sites during designated periods.
- Notifications management: Turn off non-essential notifications to minimize interruptions and maintain focus.
- Establishing designated zones: Create physical spaces or areas free from electronic devices and social media to promote productivity.
- Goal setting: Set clear goals and deadlines for tasks to maintain motivation and minimize the temptation of social media.
- Accountability partners: Share productivity goals with peers or colleagues to encourage mutual support in staying on track.
Final Thoughts
The assessment of social media habits reveals the pervasive nature of these platforms in our daily lives, with billions of users worldwide, social media has become an integral part of modern existence. Users actively engage through text, images, and videos, shaping their digital presence.
However, this extensive usage carries significant implications. It can impact mental health, with links to stress, anxiety, and depression. Additionally, awareness of privacy settings and responsible sharing of personal information are vital considerations. To ensure a healthier and more responsible relationship with social media, individuals must practice mindful consumption, prioritize privacy and security, and actively contribute to a positive online environment.
In essence, understanding and managing one's social media habits are critical in striking a balance between the benefits and challenges these platforms present, ultimately leading to a more fulfilling digital life.
FAQ
Why is it important to assess social media habits?
Assessing social media habits is crucial because these platforms are an integral part of modern life. Understanding our usage patterns can help us strike a balance between the benefits and potential downsides, such as mental health implications and privacy concerns.
How prevalent is social media usage globally?
As of July 2023, approximately 4.88 billion people, or 59.9% of the world's population, use social media. This statistic underscores the widespread adoption of social platforms across the globe.
How can individuals improve their social media habits?
To enhance their social media habits, individuals can start by setting boundaries, managing privacy settings, and being mindful of their content consumption. Additionally, promoting positivity and respectful online interactions can contribute to a healthier online environment.
What recommendations are provided for responsible social media usage?
It is recommended to practice mindful consumption, prioritizing privacy and security, and actively contributing to a positive online environment. These actions can help individuals strike a healthier balance with social media.
How does social media usage affect productivity and academic/professional performance?
Social media can be a distraction, affecting productivity at work or school. The article highlights the impact on academic and professional performance, emphasizing the need for strategies to manage these distractions effectively.

