U.S. households often pay more for internet than those in many other countries. This makes it even more important for Americans to learn how to maximize their existing internet connection without taking on unnecessary costs. But no matter who you are or where you live, you are likely looking to get the most bandwidth for your buck.
Key Takeaways
- The FCC defines broadband internet as having a minimum download speed of 100 Mbps and a minimum upload speed of 20 Mbps.
- Many free tips can improve speed before you consider costly equipment upgrades or paying for a higher-tier internet plan.
- From closing background applications and clearing your browser history to using QoS and switching to a less busy Wi-Fi channel, a number of free optimizations can dramatically increase your internet speed.
How Do You Check Your Current Internet Speed?
If your internet is slower than your provider stated it would be, it's worth testing your own speed. Providers quote "up to" speeds, but real use varies throughout the day, especially during peak usage periods or where data caps are active.
For accurate results, use a trusted tool. We recommend checking our list of the best internet speed test sites to find a reliable tool. We recommend using TestMySpeed for fast, easy internet speed test results.
For the most accurate results, pause any active downloads and connect your computer directly to the router via Ethernet rather than WiFi. We also recommend running the test when network traffic is low.
While the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) sets broadband standards, your personal needs may vary. Remember that speed is affected by congestion, outdated hardware, and WiFi interference. Run tests periodically to determine if your connection is stable or if it is time to contact your provider.
How Can I Increase My Internet Speed?
You don't have to spend a fortune for high-speed internet that actually delivers. In fact, there are many free and easy ways for consumers to get the fast internet access they need.
Easy Fixes to Boost Internet Speed
1. Close Background Applications
Processes such as cloud backups, updates, and streaming are actually bandwidth hogs that silently use internet capacity. The slow internet on your computer and the faster internet on another device indicate that the culprit behind slowed internet access could be unnecessary background programs.
Close the background programs and any unrequired apps running on your computer to improve internet speed. Even when idle, social media sites such as Facebook, YouTube, Snapchat, and Instagram continue to use internet bandwidth. By shutting down these apps when you aren’t using them, you can prevent internet slowdowns when streaming services or gaming.
2. Restart Your Devices and Router
Restarting fixes small bugs that tend to accumulate gradually. If your router is not functioning optimally, it is also a good idea to restart it. Just like when restarting your smartphone or computer, it is that simple. The process will depend on how old your router is, so check our guide on how to reset your router for specific instructions.
Unplug the device for 10 to 30 seconds, plug it back in, and allow it to reboot. This resets the internal settings that may be causing performance issues. For specific instructions, read our guide on how to reset your router. If you see specific indicator lights flashing, check our guide to modem and router lights to diagnose the issue.
3. Clear Your Cache and Browser History
The accumulation of cache results in slowed browsing, where your web browser has to sift through outdated information. With each visit, your browser saves text, images, and videos for faster access in the future, but it eventually leads to congestion.
If websites load at a slow rate or display outdated content, it is time to clear your internet browser cache for a fresh load of the latest versions. Clearing browser history will also enhance your level of privacy since hackers can monitor past history related to your internet activities for the purpose of advertisements.
4. Scan for Viruses and Malware
Malware can also hijack bandwidth, causing your internet connection to slow down without your knowledge. Malware can either steal your information or simply soak up system resources.
If you ever notice that your computer has malware, it is important to perform a full system malware scan. Malware removal software can remove malware from your computer, restoring its speed and safeguarding your information. For more on protecting your network, learn how to secure your internet connection.
5. Check If Your Plan Has Data Caps
With some ISPs, the amount of internet data consumed in a month is limited, and once this limit is exceeded, your internet speed will be slowed down. To avoid such problems, it is essential to understand how much internet data your internet package allows every month.
Read our tips for approaching your data cap to manage usage better. If your internet speed is slowed down for any reason, perform a speed test to verify if you are being throttled.

Router Tweaks to Increase Internet Speed
Your hardware plays a massive role in your connection quality. Before making adjustments, it is helpful to understand how modems and routers affect internet speed.
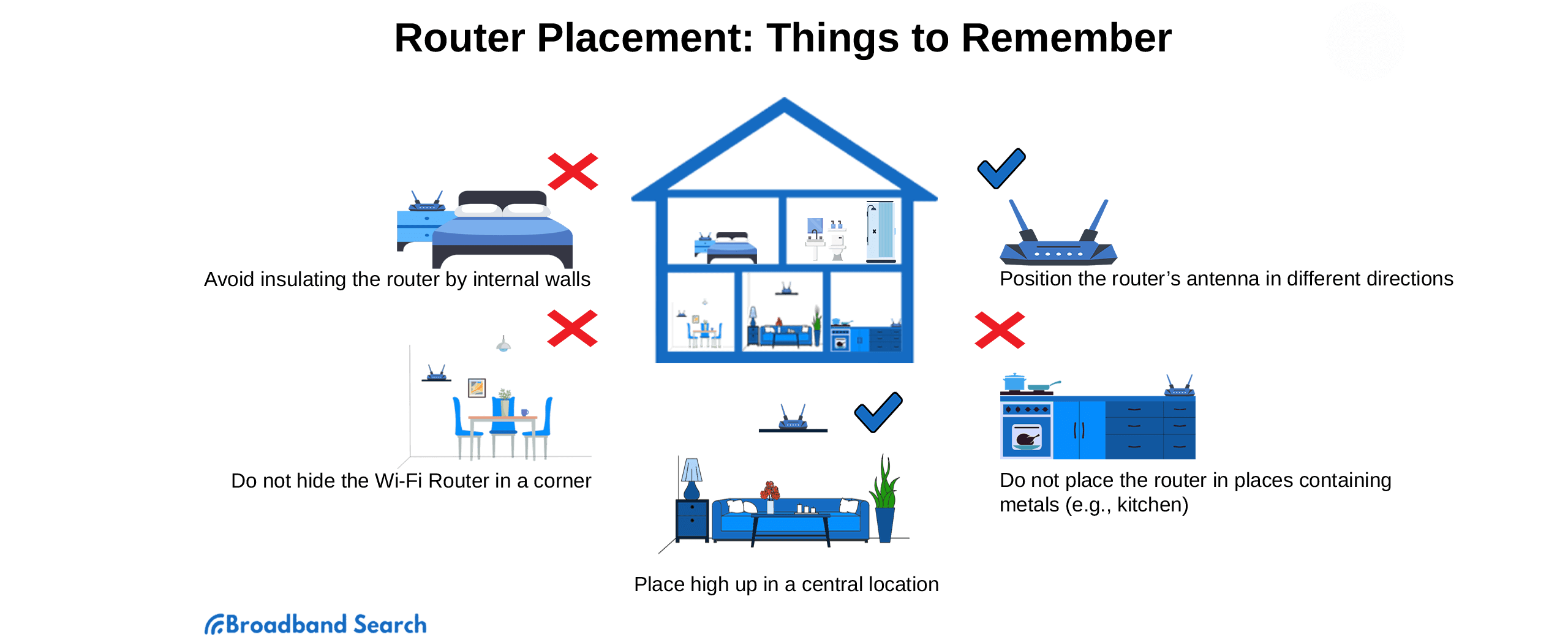
1. Move Your Wi-Fi Router for Improved Signal
Router placement directly affects Wi-Fi strength. For best results, position your router in a central, elevated location away from thick walls, metal appliances, and heat sources. For a detailed breakdown, see our guide on the best place to set up your router.
Avoid interference from devices like microwaves or baby monitors, which can weaken the signal. If coverage remains inconsistent, check out our guide on common home Wi-Fi problems to troubleshoot further.
2. Update Your Drivers and Router Firmware
Keeping device drivers and router firmware updated enhances both speed and security. Firmware acts as the operating system for your router; updating it patches vulnerabilities and can improve performance. Understanding your network adapter settings can also help ensure your computer isn't the bottleneck.
3. Utilize Quality of Service (QoS) from Your Router
With QoS, you can set local priority for important traffic so that streaming and gaming occur without interruptions, leaving larger downloads for later. Even if you are using a connection that’s only 15 Mbps, your YouTube stream will occur at a constant rate, and your computer will run ongoing downloads in the background. This is particularly useful for those who play online video games; see our guide on games that benefit from better internet.
4. Find a Less Busy Wi-Fi Channel
Congestion on your Wi-Fi channel can lead to slowed internet speeds. This is a particular problem in apartment buildings and crowded regions. Evaluate your internet using Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android and Wireless Diagnostics for Mac to see the least used channels. Restart your internet router, and it will automatically shift to a different, faster channel. You can learn more about the different hardware involved in our breakdown of Wi-Fi box types.
5. Switch to the 5 GHz Frequency
Your Wi-Fi router has two different frequencies: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz frequency has a longer range and lower bandwidth, making it suitable for browsing. The 5 GHz frequency has faster speeds, making it suitable for gaming, video calling, and streaming.
Connecting the Wi-Fi to 5 GHz will provide faster speeds when speed is needed the most.
6. Kick Off Inactive or Unwanted Users
Too many connected devices can use up bandwidth, causing everything to run slowly. Disconnect the ones that are inactive, unknown, and unnecessary, and protect your network by creating a strong password so that only approved people can access it. To secure guest access, we recommend following our essential guide to setting up guest Wi-Fi.
Equipment Tweaks to Improve Internet Speed
1. Try a Wired Ethernet Connection
Since it transmits its information directly without any interruptions, the speed and reliability of Ethernet will always surpass that of Wi-Fi. Whenever it’s possible, it’s advisable to use wired internet connectivity for your gaming computer, streaming stations, and laptops used for office setups.
2. Use Wi-Fi Range Extenders or a Mesh Network
Wi-Fi range extenders can be an inexpensive way (starting at about $20) of extending your Wi-Fi range into areas that previously had none, albeit with spotty success. Alternatively, a mesh Network, though pricier, is undoubtedly a more powerful way of fully networking your home. You can even create a mesh network with 5G home internet to improve coverage without traditional cables.
3. Adjust Router Antennas
If your router has external antennas, you can turn them slightly to get more efficient signals or sometimes towards areas that need more signals, such as other floors or rooms of a house. For fixed wireless users, antenna placement is critical—see our troubleshooting fixed wireless antennas guide.
Can Changing Your DNS Server Improve Internet Speed?
It will improve web site loading, but it won’t increase your download and upload speeds. DNS affects how quickly websites and apps start loading by reducing lookup delays.
Public DNS can be more reliable: Providers like Google and Cloudflare often offer faster response times, better uptime, and global redundancy compared to ISP DNS.
Added security and consistency: Many public DNS services include phishing protection, encrypted queries, and more stable performance depending on location and network conditions.
Optimizing Your DNS Settings
While upgrading bandwidth usually costs money, changing your Domain Name System (DNS) is a free tweak that can make the internet feel faster.
DNS acts as the internet's phonebook, translating website names (like broadbandsearch.net) into IP addresses that computers can understand. By default, you use your ISP's DNS server. However, third-party public DNS servers from companies like Google (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) can often resolve these "lookups" faster than your ISP.
ISP-provided vs. Public DNS servers
- ISP DNS: Often subject to congestion during peak hours and may have outdated security protocols.
- Public DNS: Designed for speed and often supports advanced privacy features like DNS over HTTPS.
Changing your DNS won't increase your raw download numbers (Mbps), but it can significantly reduce latency, making pages start loading snappier. For a deeper look at how internet infrastructure comes together, explore how the internet works.
Strategy: Internet Usage During Off-Peak Hours
One of the most effective zero-cost ways to improve speeds is simply adjusting when you perform high-bandwidth tasks. Networks often experience packet loss and slowdowns during "peak hours"—typically between 7:00 p.m. and 11:00 p.m.—when your neighbors are all streaming and gaming simultaneously.
According to EarthLink, cable internet connections are shared with the neighborhood, meaning "rush hour" traffic affects everyone on the node. By scheduling large file downloads or system updates for off-peak times (like overnight or early morning), you can avoid this congestion.
You can also use this time to perform maintenance tasks. Check our guide on internet usage during off-peak hours for specific strategies. If you suspect your ISP is intentionally slowing you down, you might be experiencing throttling. Learn more about bandwidth throttling here.
What If These Free Fixes Aren’t Enough?
If your internet speeds remain low even after you make hardware adjustments and optimize settings, you may have to contact your provider. Limited availability, blocking, and outdated packages are common provider issues that can negatively impact service.
Your choice of internet equipment can also cause speed and reliability problems. Outdated routers and modems will simply not support modern internet speeds. You may need to upgrade your cable modem if it is several years old.
If none of the above tips address your speed issues, it may become necessary to look for other internet services that are more dependable and economical. You can use our tool to choose an internet provider that better suits your needs.
FAQ
What is good internet speed?
For a multi-device home, solid download speeds begin at about 100 Mbps, and solid upload range from 10 to 20 Mbps.
What is good internet speed for gaming?
Experts recommend a minimum download speed of 25 to 50 Mbps download with low latency for competitive gaming, Upload speeds should fall between 5 and 10 Mbps.
What speed of internet do I need for streaming?
Streaming full HD material consumes approximately 5 Mbps, and 4K streaming consumes approximately 25 Mbps or more.
What is the maximum internet package available in my neighborhood?
Different local internet service providers offer different packages in different neighborhoods. Run a speed-test utility and examine provider packages for your ZIP code to determine the highest tier available to you.
How Can I Surf Smarter and Faster?
From repositioning your router to updating firmware, there are many steps you can take to improve internet speed without spending a dime. First, test, don’t tweak, to see if it’s a problem with your system or your internet service provider.
Simply restart the equipment, shut down background process-intensive apps, erase the cache, and perform system security checks. Optimize your Wi-Fi by adjusting your router’s location, updating its firmware, turning on QoS, and setting channels that are less congested. Secure your internet by connecting to the 5GHz band or through an Ethernet cable.