Wired vs. Wi-Fi Internet: Which Connection Is Right for You?
Your internet connection shapes everything from your morning video calls to your evening streaming sessions. With two main options: Wired ethernet and Wi-Fi.
Understanding their differences can help you make the best choice for your needs. Whether you're setting up a home office, gaming setup, or simply want reliable internet throughout your house, this guide breaks down the pros and cons of each connection type with real data to help you decide.
Understanding Wired Internet Connections
Wired internet uses physical ethernet cables to connect your devices directly to your router or modem. Think of it as a dedicated highway between your device and the internet—no traffic jams, no detours.
How Ethernet Connections Work
Ethernet cables transmit data using electrical signals through copper wires or light signals through fiber-optic cables. Your device plugs directly into the network via an ethernet port, creating a stable, direct connection.
Common ethernet cable types include:
- Cat5e: Supports speeds up to 1,000 Mbps (1 Gbps) at distances up to 328 feet
- Cat6: Handles up to 10 Gbps for shorter distances, with better interference protection
- Cat6a: Maintains 10 Gbps speeds over longer distances with enhanced shielding
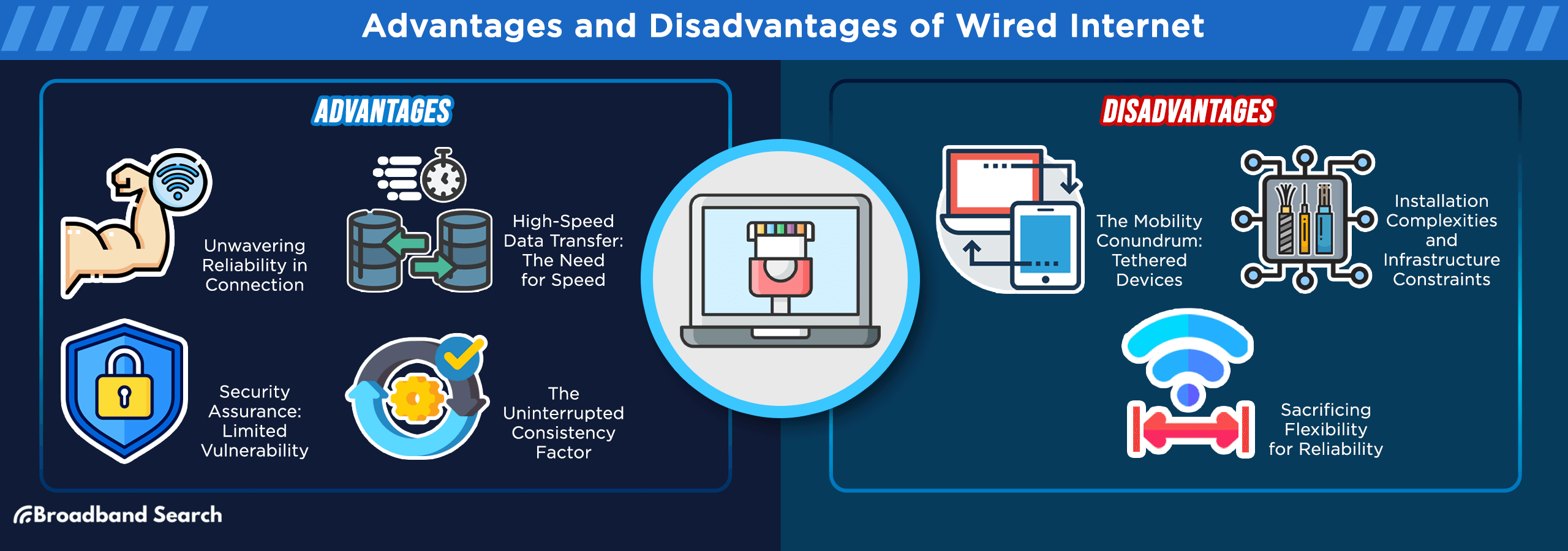
Where Wired Connections Excel
Gaming and Esports: Professional gamers rely on ethernet for consistent low latency. According to HighSpeedOptions, wired connections typically provide 1-5ms lower latency than Wi-Fi, which is crucial when milliseconds matter.
Video Conferencing: Remote workers benefit from stable upload speeds for clear video calls without interruptions or quality drops.
Content Creation: Uploading large video files or backing up data happens faster with consistent wired speeds.
Smart Home Hubs: Devices like security systems and home automation controllers perform better with reliable wired connections.
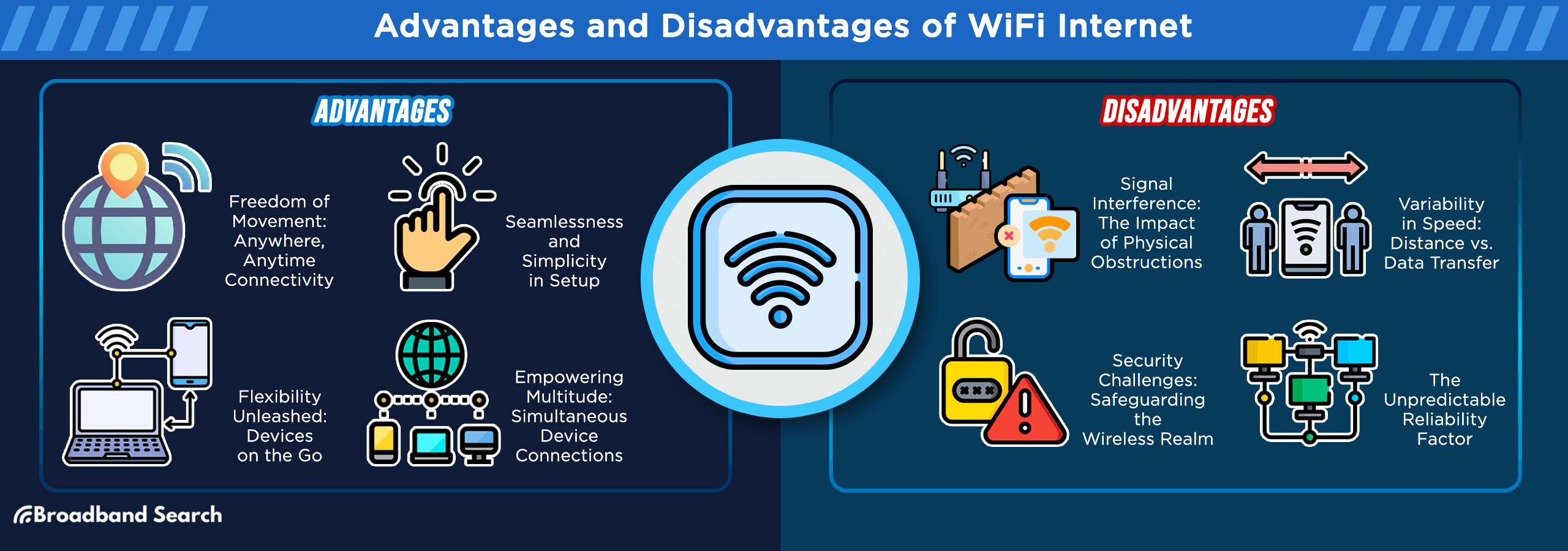
Understanding Wi-Fi Connections
Wi-Fi uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly between your devices and router. Modern Wi-Fi operates on two main frequency bands: 2.4 GHz (longer range, slower speeds) and 5 GHz (shorter range, faster speeds).
Current Wi-Fi Standards and Speeds
| Wi-Fi Standard | Maximum Speed | Real-World Speed | Release Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) | 600 Mbps | 50-100 Mbps | 2009 |
| Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) | 3.5 Gbps | 200-500 Mbps | 2013 |
| Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) | 9.6 Gbps | 500-1,000 Mbps | 2019 |
| Wi-Fi 6E | 9.6 Gbps | 500-1,200 Mbps | 2021 |
Source: Broadband Search Wi-Fi Standards Guide
Where Wi-Fi Shines
Mobile Devices: Smartphones, tablets, and laptops depend on Wi-Fi for internet access throughout your home.
Flexibility: Move freely while staying connected—perfect for working from different rooms or relaxing on the patio.
Multiple Device Support: Modern routers handle 50+ connected devices simultaneously, supporting smart homes and families with many gadgets.
Easy Setup: Connect new devices in seconds by selecting your network and entering the password.
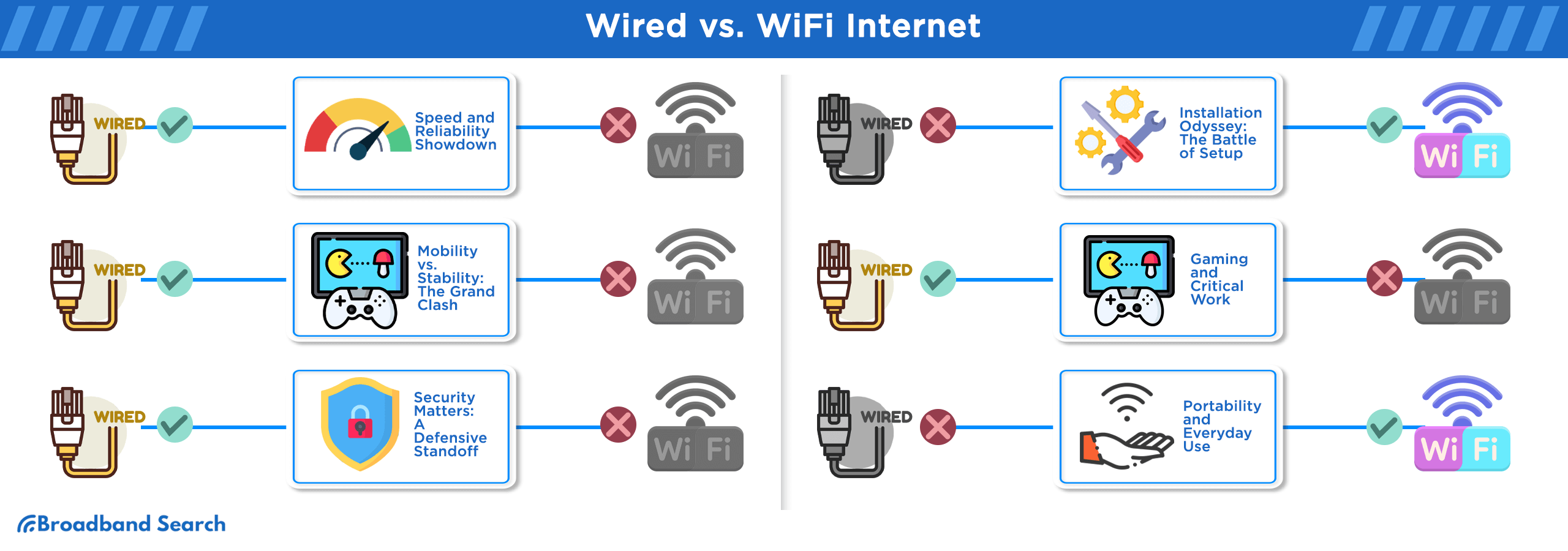
Head-to-Head Comparison
Speed and Performance
Wired Advantage: Ethernet delivers consistent speeds matching your internet plan. A 1 Gbps connection provides nearly 1 Gbps consistently.
Wi-Fi Reality: Actual speeds vary by distance, obstacles, and interference. A 500 Mbps Wi-Fi connection might deliver 200-400 Mbps in real use.
Testing by testmyspeed.com shows wired connections maintain 90-100% of advertised speeds, while Wi-Fi typically achieves 40-80%.
Reliability and Stability
Wired Connections:
- ✅ Immune to interference from other devices
- ✅ Consistent performance regardless of distance
- ✅ No signal dropouts due to obstacles
- ❌ Limited to cable length and ports
Wi-Fi Connections:
- ✅ Works throughout your home's coverage area
- ✅ Supports unlimited devices (within reason)
- ❌ Affected by walls, floors, and other electronics
- ❌ Speed decreases with distance from router
Security Considerations
Wired Security: Physical access required for interception makes ethernet inherently secure. Data travels through cables, not broadcast through the air.
Wi-Fi Security: Requires proper encryption (WPA3 recommended) and strong passwords. According to cybersecurity research, 43% of cyber attacks target small businesses, often through unsecured wireless networks.
Security Best Practices for Wi-Fi:
- Use WPA3 encryption (or WPA2 minimum)
- Create strong, unique passwords
- Enable network isolation for guest access
- Regularly update router firmware
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Choose Wired When You Need:
Maximum Performance:
- Gaming with competitive advantage
- 4K/8K video streaming without buffering
- Large file transfers or backups
- Professional video editing or streaming
Critical Reliability:
- Home office video conferencing
- Point-of-sale systems
- Security cameras and monitoring
- Server or NAS connections
Choose Wi-Fi When You Want:
Flexibility and Convenience:
- Mobile device connectivity
- Easy setup for guests
- Clean appearance without cables
- Multiple room coverage
Cost-Effective Solution:
- Connecting many devices affordably
- Avoiding installation complexity
- Upgrading older homes without rewiring
The Hybrid Approach
Many users benefit from both connection types:
- Wired: Desktop computers, gaming consoles, smart TVs, and workstations
- Wi-Fi: Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smart home devices
This approach maximizes performance where it matters while maintaining convenience for mobile use.
Future-Proofing Your Connection
Emerging Technologies
Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be): Expected in 2024, promising speeds up to 30 Gbps and improved reliability in crowded environments.
Fiber Ethernet: Residential fiber connections now offer symmetrical speeds up to 10 Gbps, making wired connections faster than ever.
Mesh Networks: Advanced Wi-Fi systems provide consistent coverage throughout larger homes, reducing Wi-Fi's traditional range limitations.
Planning for Tomorrow
Consider your long-term needs when choosing connection types:
- Bandwidth Growth: Internet usage increases 20-30% annually according to Cisco's Visual Networking Index
- Device Proliferation: Average homes will have 50+ connected devices by 2025
- Work-from-Home Trends: Reliable connectivity remains crucial for remote work success
Installation and Cost Considerations
Wired Connection Costs
DIY Installation: $50-200 for cables and basic equipment
Professional Installation: $150-500 per room for new cable runs
Equipment: Ethernet switches ($30-200), cables ($10-50), wall plates ($20-100)
Wi-Fi Setup Costs
Router Purchase: $50-400 depending on features and coverage area
Mesh Systems: $200-600 for whole-home coverage
Professional Setup: $100-300 for complex installations
Optimizing Your Internet Experience
Wired Connection Tips
- Use Quality Cables: Cat6 or Cat6a for future-proofing
- Minimize Cable Length: Shorter runs maintain signal quality
- Organize Cables: Proper management prevents interference
- Test Connections: Verify speeds match your internet plan
Wi-Fi Optimization Strategies
- Router Placement: Central location, elevated, away from interference
- Channel Selection: Use Wi-Fi analyzer apps to find clear channels
- Bandwidth Management: Quality of Service (QoS) settings prioritize important traffic
- Regular Updates: Keep router firmware current for security and performance
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Wired Connection Problems
Slow Speeds: Check cable condition, connections, and network equipment
No Connection: Verify cable integrity and port functionality
Intermittent Issues: Inspect for cable damage or loose connections
Wi-Fi Connection Problems
Weak Signal: Move closer to router or add Wi-Fi extenders
Slow Speeds: Reduce interference, update drivers, or upgrade router
Frequent Disconnections: Check for overheating, update firmware, or adjust power settings
Conclusion: Match Your Internet to Your Needs
Both wired and Wi-Fi connections serve important roles in modern connectivity. Wired excels in performance, reliability, and security for stationary devices requiring maximum bandwidth. Wi-Fi provides essential flexibility and convenience for mobile devices and general household use.
Your ideal setup likely includes both options, strategically implemented based on each device's needs and usage patterns. Consider your specific requirements, budget, and future plans when making connectivity decisions.
The key is matching your connection type to your actual needs rather than assuming one option fits all situations. Whether you choose the stability of ethernet or the flexibility of Wi-Fi—or both—understanding these technologies helps you create the best possible internet experience for your home or office.
FAQ
Can I use both wired and Wi-Fi at the same time?
Yes, most devices can use both connections simultaneously. Your device will typically prioritize the wired connection for better performance while maintaining Wi-Fi for flexibility.
How much faster is wired internet compared to Wi-Fi?
Wired connections consistently deliver 90-100% of your internet plan's speed, while Wi-Fi typically provides 40-80% depending on conditions. For a 500 Mbps plan, expect 450-500 Mbps wired vs. 200-400 Mbps via Wi-Fi.
Is it worth running ethernet cables through my house?
This depends on your needs and budget. Consider ethernet for areas with stationary devices requiring maximum performance (home offices, entertainment centers, gaming areas). Professional installation costs $150-500 per room but provides long-term benefits.
What's the most secure connection option?
Wired connections are inherently more secure since data travels through physical cables rather than broadcasting wirelessly. However, properly secured Wi-Fi networks using WPA3 encryption and strong passwords provide adequate security for most users.
How do I know if my internet problems are due to Wi-Fi or my internet provider?
Test your speed using a wired connection directly to your modem. If wired speeds match your plan but Wi-Fi speeds are significantly lower, the issue is likely your Wi-Fi setup rather than your internet service.
Can I Use Both Ethernet and Wi-Fi in the Same Home?
Yes. Hybrid networks can provide connected ports and access points that use Ethernet cables to connect while Wi-Fi networks are in place simultaneously.