The router serves as the heart of our home's digital universe, connecting multiple devices to the internet and ensuring seamless communication between them. However, like all tech devices, routers have a lifespan, and over time, their performance can deteriorate. Recognizing the signs that you need a new router can be the difference between uninterrupted streaming or gaming sessions and frustrating lag or disconnections.
A 2019 study by IDC highlighted that a reliable network can enhance user satisfaction by up to 30%. This underscores the significance of having a dependable router in place. After all, in today's digital era, a stable and robust connection is not just a luxury but a necessity.
Signs That Indicate You Need a New Router
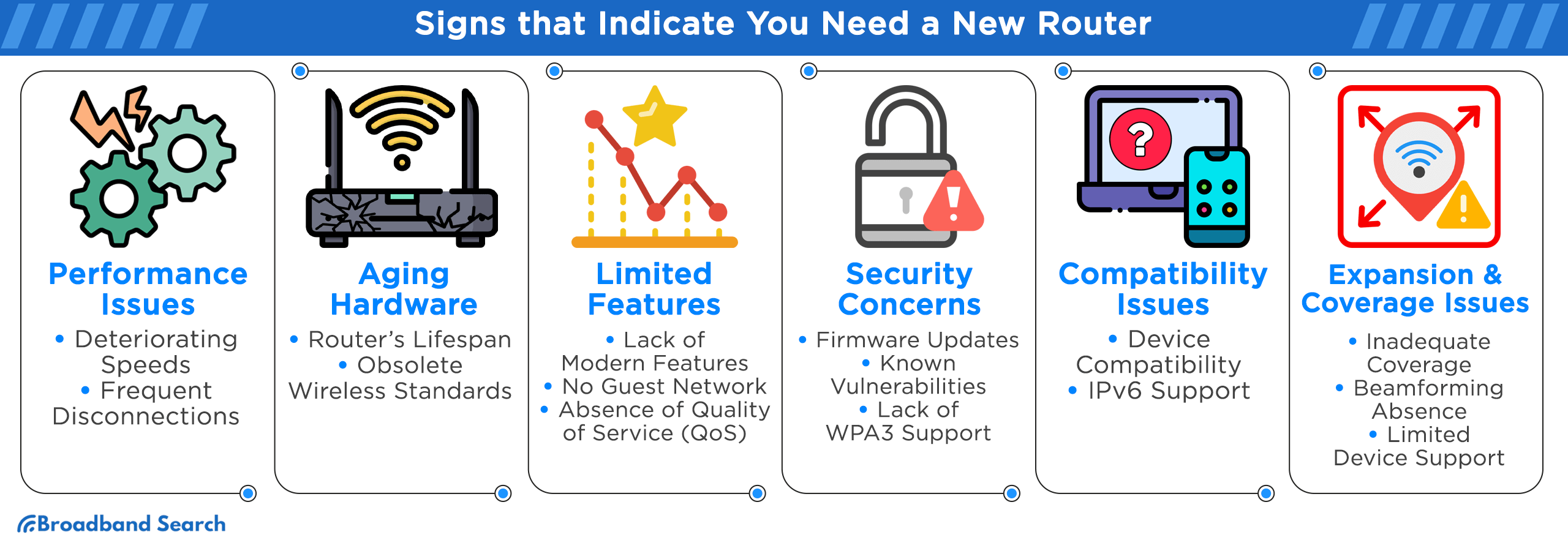
Performance Issues
Slow speeds hinder downloads and streaming, while disconnections disrupt work and communication flows, culminating in a frustrating and inefficient web experience for users across various platforms.
Deteriorating Speeds
- Slow Download/Upload Speeds: Slow download and upload speeds significantly hamper online activities. According to Akamai's State of the Internet report, a mere 1-second delay in page load can lead to a 7% loss in conversions. Imagine a small business owner struggling to process transactions due to slow speeds, potentially losing customers and revenue, highlighting the urgent need for addressing these speed-related issues effectively.
- Constant Buffering: Constant buffering is a glaring symptom of deteriorating network speeds, significantly disrupting the streaming experience. A paper by Professor Ramesh K. Sitarman of the University of Massachusetts asserts that viewers abandon videos after a mere two-second delay. For instance, educators relying on smooth video streams to conduct classes face engagement loss from students, making effective teaching and learning challenging amidst persistent buffering interruptions.
- Web Pages Loading Slowly: Web pages loading slowly is a silent productivity killer. A study by Google indicates that 53% of mobile users abandon a site if it takes over three seconds to load. Think of online shoppers during peak sale hours: delayed webpage loading not only frustrates the user but can also lead to lost sales, underlining the imperative of optimal site speed.
Frequent Disconnections
- Devices Losing Connection: Devices constantly losing connection pose a pervasive challenge in the digital realm. Research by the IDC reveals that network downtimes can cost businesses up to $100,000 per hour. Imagine an e-trader executing time-sensitive transactions; even brief disconnections can lead to significant financial setbacks. Such inconsistencies underscore the pressing need for robust, uninterrupted network infrastructures for seamless digital engagement.
- Frequent Router Reboot Necessity: Requiring frequent router reboots to maintain connectivity is a telling sign of network instability. A study by ZK Research found that 41% of employees waste up to a full work week annually due to network issues. For freelancers dependent on a stable internet, constant reboots translate into substantial lost income and time, emphasizing the importance of a stable, reliable network connection.
Aging Hardware
Aging hardware, characterized by surpassed router lifespan, obsolete wireless standards, and physical damage, invariably compromises network performance. These elements collectively contribute to reduced functionality and reliability, necessitating the evaluation and timely replacement of antiquated equipment to ensure seamless, efficient digital connectivity and operation.
Router’s Lifespan
- Typical 4-5 Years Duration: With a general lifespan of 4-5 years, routers eventually fall behind rapid technological advancements, becoming obsolete. This obsolescence can be detrimental for users working remotely, as an aging router may not support the necessary speeds and security protocols, hindering professional activities.
Obsolete Wireless Standards
- Old Protocols (e.g., 802.11b/g): Routers employing obsolete standards, such as 802.11b/g, compromise network speed and security. An Accenture report notes that outdated tech annually costs businesses 1.8 trillion dollars in lost productivity. Imagine a cafe whose outdated router supports only older standards; customer satisfaction and retention are inevitably jeopardized due to inferior connectivity.
Physical Damage
- Damaged Antenna: Physical damage, like a damaged antenna, severely affects router performance, leading to inconsistent and weakened signals. In critical applications, such as remote medical monitoring, a faltering signal due to damaged hardware could have serious implications, jeopardizing the reliability of data transmission and patient care, thereby emphasizing the imperative for maintaining hardware in pristine condition.
- Worn Ports: The gradual wear and tear of physical components in aging hardware, such as worn ports, can significantly impact network reliability and functionality. Picture a scenario where a small business relies on multiple wired connections for daily operations. When ports become worn and unreliable, it leads to frequent connectivity issues, disrupting productivity.
Limited Features
The absence of modern features like dual or tri-band support, MU-MIMO, beamforming, guest networks, and Quality of Service (QoS) functionalities can leave users with an outdated and less capable network infrastructure, impacting both speed and security.
Lack of Modern Features
- No Dual/Tri-Band Support: Aging routers often suffer from limited features, notably the absence of dual or tri-band support. This deficiency can prove detrimental, especially in households with multiple connected devices. Imagine a scenario where a family experiences sluggish internet while simultaneously streaming movies, online gaming, and video conferencing due to the router's inability to efficiently distribute bandwidth across various frequencies. Modern features like dual/tri-band support are crucial for optimizing network performance in today's digital landscape.
- Absence of MU-MIMO, Beamforming: A common drawback of aging routers is the absence of essential modern features like MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output) and beamforming. Imagine a home office setup where multiple family members are concurrently engaged in video conferences and online gaming. Without MU-MIMO and beamforming, the router struggles to provide stable connections, leading to lag, dropped calls, and overall suboptimal user experiences.
No Guest Network
The absence of a guest network in aging routers can pose security and convenience challenges for households and businesses alike. Imagine hosting guests who require internet access while safeguarding your primary network. Without a dedicated guest network, sharing access credentials becomes necessary, potentially compromising security. Modern routers equipped with this feature allow visitors to connect seamlessly, keeping the main network secure while ensuring a hassle-free online experience for all.
Absence of Quality of Service (QoS)
The absence of Quality of Service (QoS) functionality in aging routers can lead to inefficiencies in network traffic management. Picture a home where multiple devices vie for bandwidth, including essential activities like remote work and video conferencing. Without QoS, there's no mechanism to prioritize critical traffic, potentially resulting in choppy video calls or delayed file uploads. The inclusion of QoS is vital for optimizing network performance, ensuring that vital tasks run seamlessly in a crowded digital landscape.
Security Concerns
With the importance of regular updates and a lack of manufacturer support for old models, safeguarding network integrity becomes paramount. These challenges necessitate proactive measures to protect against evolving cyber threats.
Firmware Updates
- Importance of Regular Updates: Regular firmware updates are the linchpin of router security. A report by the Ponemon Institute reveals that 60% of data breaches occur due to unpatched vulnerabilities. Picture this: a home network with an outdated router falls victim to a cyberattack, jeopardizing personal data and privacy. Timely updates, often overlooked, are imperative to mitigate such risks, ensuring your router is equipped to defend against evolving cyber threats.
- Lack of Manufacturer Support for Old Models: Security concerns related to firmware updates are amplified by the lack of manufacturer support for aging router models. Studies have shown that a significant percentage of routers are no longer receiving updates from their manufacturers, leaving them vulnerable to emerging threats. Consider a scenario where a business continues to rely on an unsupported router; it becomes an enticing target for cyberattacks, highlighting the importance of modernizing network infrastructure for robust security.
Known Vulnerabilities
- Unpatched Security Issues: Unpatched security issues can lead to catastrophic data breaches, potentially affecting both individuals and organizations. Imagine a scenario where a hacker exploits a well-documented vulnerability in an aging router, compromising sensitive information. Mitigating such risks demands proactive measures, emphasizing the significance of regularly updating and fortifying network defenses to safeguard against evolving cyber threats.
Lack of WPA3 Support
Security concerns in aging routers extend to the absence of WPA3 support, a modern encryption standard crucial for safeguarding networks. According to the Wi-Fi Alliance, only 15% of Wi-Fi devices in homes support WPA3. Imagine a business environment where sensitive data flows over an outdated network lacking WPA3 protection. This vulnerability can expose critical information to potential threats, underscoring the urgency of upgrading to routers that prioritize the latest security protocols.
Compatibility Issues
Compatibility issues in the realm of technology encompass various facets, such as device compatibility and IPv6 support. These difficulties can impact the seamless integration and functionality of devices and networks, requiring careful consideration and troubleshooting to ensure smooth operations.
Device Compatibility
- Issues Connecting New Devices: Device compatibility issues often emerge when attempting to integrate new technology into existing setups. A study by Gartner suggests that 65% of IT professionals encounter such challenges. Visualize a scenario where a company invests in state-of-the-art equipment, only to face difficulties integrating it with legacy systems.
- Performance Problems with New Tech: Compatibility issues stemming from device connectivity can lead to significant performance problems when integrating new technology. Imagine a situation where a business invests in cutting-edge devices, only to encounter connectivity hurdles that hinder productivity. Whether it's smart office equipment or personal IoT devices at home, ensuring seamless integration is vital for unlocking the full potential of modern technology and maximizing operational efficiency.
IPv6 Support
- Necessity of Supporting IPv6: The necessity of IPv6 support in networking infrastructure cannot be overstated. Studies show that the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses has accelerated IPv6 adoption, with 30% of the world using IPv6 as of 2021. In a world where every device requires a unique IP address, envision the chaos if an organization's network lacks IPv6 support: network limitations, security risks, and operational inefficiencies.
Expansion & Coverage Issues
Expansion and coverage issues in the realm of networking often manifest as inadequate coverage, the absence of beamforming technology, and limited device support. These challenges can hinder the seamless expansion of network coverage and connectivity, requiring strategic solutions to ensure robust network performance.
Inadequate Coverage
- Signal Doesn’t Cover Entire Home: Picture a residence with rooms or areas that remain Wi-Fi dead zones, hindering online activities and causing frustration. Such scenarios underscore the significance of addressing coverage issues effectively. Robust network expansion strategies and technology enhancements are imperative to ensure seamless connectivity throughout the entire premises.
Beamforming Absence
- Importance of Direct Signal Technology: The absence of beamforming technology in network expansion and coverage can significantly impact signal strength and reliability. Picture a crowded coffee shop where patrons struggle to maintain reliable Wi-Fi connections due to the lack of directed signals. Beamforming, a crucial feature, ensures a focused, efficient signal delivery, enhancing connectivity and optimizing the user experience.
Limited Device Support
- Problems with Many Connected Devices: Limited device support is a pressing concern in the age of IoT and smart homes, where numerous connected devices vie for network resources. Studies indicate that 63% of homes have more than ten connected devices. Visualize a scenario where a family's router struggles to accommodate these devices, causing disruptions in connectivity and demanding a robust solution for seamless device integration.
Practical Strategies for New Router
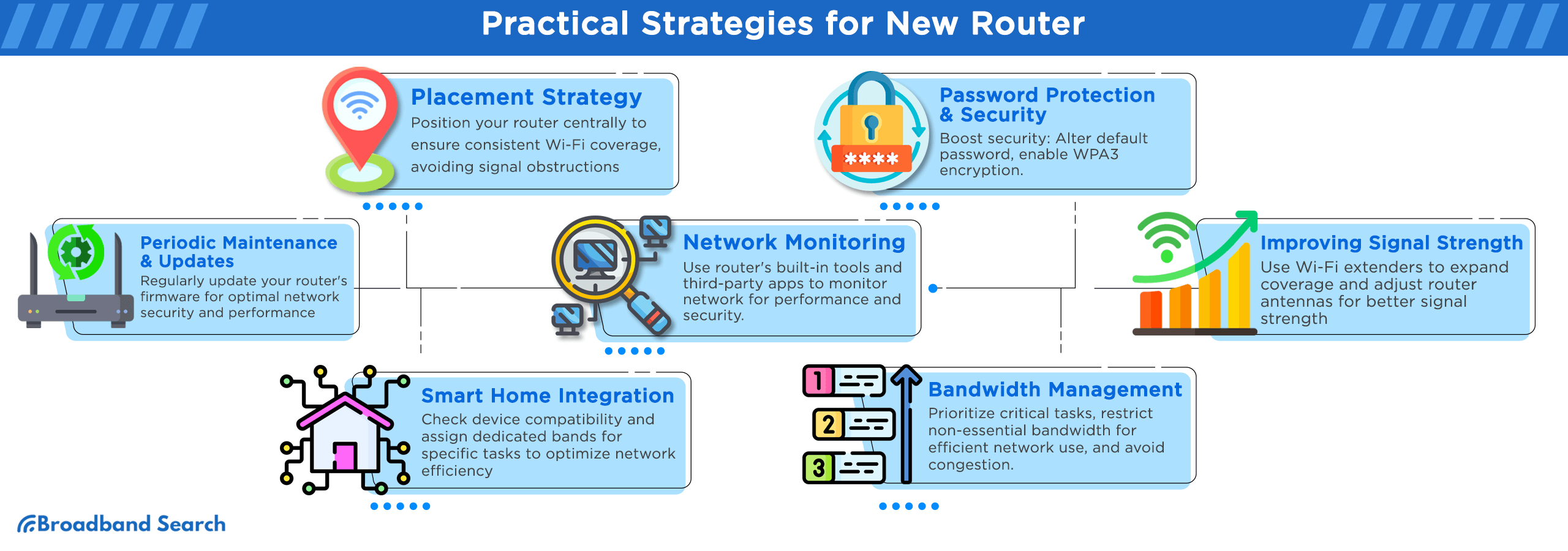
Placement Strategy
Strategic positioning ensures efficient coverage, minimal interference, and seamless connectivity, making it a fundamental aspect of achieving a reliable and high-performing home or office network.
- Central Location: Positioning the router centrally within your home or office ensures equitable coverage. Imagine a family where everyone needs a strong Wi-Fi signal, from the home office to the living room. Central placement minimizes signal dead zones, providing reliable connectivity throughout the space.
- Avoid Obstructions: Steer clear of signal-blocking obstacles like large metal objects, mirrors, or appliances. In a kitchen filled with metallic appliances, positioning the router nearby can lead to signal interference and weak connections. By keeping it away from such obstructions, you ensure a clear, uninterrupted Wi-Fi signal for all your devices.
Password Protection & Security
Ensuring a strong, unique password and implementing additional security measures is crucial in safeguarding your network from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
- Changing Default Password: It's crucial to change the manufacturer's default password to a strong, unique one. Imagine a scenario where a router's default password remains unchanged, leaving it vulnerable to unauthorized access. By setting a robust password, you ensure that only authorized users can access your network, enhancing overall security.
How to Update Your Router Password
- Identify Your Router’s Model Number: Look for this information on the device’s packaging, on a sticker on the router, or within the Device Web Interface, applicable to routers, firewalls, or IP cameras.
- Find the Default IP Address: Refer to your Router Manual or Handbook. Typical default IP addresses are 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1; however, this can vary based on the router model and manufacturer.
- Locate Default Username and Password: These credentials are often found in your Router Manual, on a sticker on the router’s bottom or back, or within the Device Web Interface. Typically, the default username is ‘admin’ and the password is either ‘admin’ or ‘password’.
- Proceed with Password Update: Using a computer or mobile device, open a browser (Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or Mozilla Firefox are recommended).
- Input the router’s IP address into the address bar and press ENTER.
- Log in using the default IP address and password.
- Navigate to the password change section, which varies by router model:
- For Linksys: Go to Administration (or Password for older models).
- For VersaLink: Access the Maintenance menu.
- For NetGear: Navigate to Advanced > Setup > Wireless Setup.
- For AT&T: Go to System Password > Edit System Password.
- For ZTE: Under Settings, select either the 2.4 GHz or 5.0 GHz tab.
- Implement the password change. Post-change, the router console will log you out.
- Log back in using your newly updated password.
- Enable WPA3: If your router supports it, enabling WPA3 encryption is essential for enhanced security. Think of a bustling coffee shop with customers connecting to the Wi-Fi network. Enabling WPA3 ensures that sensitive information remains protected from potential eavesdroppers, safeguarding both your data and your users' privacy.
Netgear
- Open a web browser on a device connected to your router.
- Go to www.routerlogin.net to access the login page.
- Log in with the username "admin" and your set password. (Note: Credentials are case-sensitive.)
- Click on "Wireless" to view settings.
- In the "Wireless Network (2.4GHz b/g/n/ax)" section, choose "WPA3-Personal" under Security Options.
- Set your network password in the "Security Options (WPA3-Personal)" section.
- Follow the same steps for the "Wireless Network (5GHz 802.11a/n/ac/ax)" section.
Asus
- Connect to your router using a wired or WiFi connection. Access the web interface via your router's LAN IP or http://www.asusrouter.com.
- Log in with your router credentials. (Reset the router to factory settings to retrieve credentials if forgotten.)
- Navigate to [Wireless] > [General], select the [Band] you wish to configure.
- In [Authentication Method], select [WPA3-Personal].
- Enter the WiFi password in the [WPA Pre-Shared Key] field.
TP-Link
- Access the router's web interface.
- Go to ‘Wireless’ > ‘Wireless Security’.
- Select ‘WPA3-Personal’ from the ‘Version’ drop-down.
- Save and reboot the router if necessary.
Linksys
- Log into the router admin page using a web browser.
- Go to ‘Wireless’ then ‘Wireless Security’.
- Under the ‘Security Mode’ dropdown, select ‘WPA3’ or ‘WPA2/WPA3 mixed mode’.
- Save the changes.
D-Link
- Login to your D-Link router's web interface.
- Navigate to ‘SETUP’ and then ‘Wireless Settings’.
- Under ‘Wireless Security Mode’, select ‘WPA3-Personal’.
- Click ‘Save Settings’.
Periodic Maintenance & Updates
Consistently updating the firmware and scheduling regular reboots ensure the router operates efficiently and securely, safeguarding your network and maximizing its longevity.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Routinely checking and updating your router's firmware is akin to ensuring your vehicle's engine runs smoothly. Neglecting this maintenance, much like skipping regular car servicing, can lead to vulnerabilities and inefficiencies in your network, potentially exposing it to security risks and compromising performance.
How to Update NETGEAR Router Firmware
- Visit: routerlogin.net or routerlogin.com.
- Navigate: Settings (or Advanced) > Administration > Firmware (or Router) Update.
- Click “Check”. For auto-updates, enable Router Auto Firmware Update.
- If new firmware is available, click “Yes” to install.
- Reboot router to complete installation.
How to Update NETGEAR Router Firmware via Nighthawk App
- Tap the router’s image.
- Scroll, tap “Check for Updates”.
- If available, tap “Update”.
- Tap “Next” to reboot and finish installation.
How to Update Asus Router Firmware
- Open browser, visit: router.asus.com
- Navigate: Advanced > Administration > Firmware Upgrade.
- Click “Check” for new firmware.
- If available, click “Firmware Upgrade” and wait for completion.
- Reboot router to finish installation.
How to Update ASUS Router Firmware via App
- Open ASUS router app, go to Settings > Firmware Upgrade.
- Select Check Firmware Version.
- If a new version is found, tap Upgrade Now (or Later).
- Tap OK to complete the upgrade.
How to Update Linksys Router Firmware
- Go to myrouter.local.
- Navigate: Connectivity > Basic.
- Under Firmware Update, click Check for Updates.
- If an update is available, click Click Here.
- In the pop-up, click Yes to update firmware.
- Reboot router by clicking OK.
- Click OK on the completion pop-up to finish.
How to Update Linksys Router Firmware via App
- Tap Menu (three lines) > Network Administration.
- Toggle Automatic Firmware Update on/off.
How to Update TP-Link Router Firmware
- Visit: tplinkwifi.net.
- Navigate: Advanced > System Tools > Firmware Update.
- Click “Check for Upgrades”.
- If available, click “Firmware Upgrade”.
- Reboot router to complete.
How to Update TP-Link Router Firmware via Tether App:
- Tap Tools > System > Firmware Update.
- Tap “Update”.
- Confirm by tapping “Update” again.
- Reboot router to finish installation.
- Rebooting Router: Just as your smartphone benefits from an occasional restart to clear cached data and refresh its performance, scheduling weekly or bi-weekly reboots for your router maintains its efficiency. This simple practice helps prevent memory leaks and ensures your network remains responsive, preventing slowdowns and connectivity issues.
How to Reboot Router
- Disconnect the router's power cable.
- Wait 60 seconds for the power to drain, ensuring a full restart.
- Reconnect the power cable to the router.
- Allow the device to reboot (typically 3-20 minutes), observing the indicator light for device status.
- Perform a speed test to confirm the internet connection is functional.
Network Monitoring
Leveraging built-in tools within routers and exploring third-party network analyzing apps empowers users to proactively identify and address issues, ensuring optimal performance and safeguarding against potential security threats.
- Utilize Built-in Tools: Routers offer invaluable built-in monitoring tools akin to a control tower at an airport. These tools allow users to oversee network traffic in real-time, ensuring a smooth and efficient online experience, much like air traffic controllers ensuring safe, organized flights.
- Third-Party Apps: Consider third-party network analyzing apps like Wireshark, Fing, or GlassWire. These tools provide insights into network performance and security, helping you detect and mitigate potential threats. Imagine a small business monitoring its network traffic for unusual patterns. Third-party apps offer comprehensive data analysis to fortify network defenses and maintain uninterrupted operations.
Improving Signal Strength
Employing practical strategies like Wi-Fi extenders and adjusting antennas ensures robust connectivity. These measures are akin to fine-tuning a musical instrument, ensuring every corner of your space resonates with a strong and reliable Wi-Fi signal.
- Using Wi-Fi Extenders: Wi-Fi extenders, akin to strategically placed signal boosters, expand your network's reach, ideal for large homes or offices. Assume a residence with rooms far from the router struggling with weak signals. Wi-Fi extenders amplify coverage, ensuring seamless connectivity throughout, just as a larger orchestra hall fills every corner with music.
- Adjusting Antennas: Properly adjusting router antennas is like tuning an instrument for the best sound quality. In a crowded workspace, envision an office where the router's antennas point in random directions, causing signal interference. By positioning them correctly, you optimize signal strength and ensure a clear network connection, akin to achieving harmony in a band.
Smart Home Integration
- Embracing smart home integration requires meticulous planning and strategic network management. By conducting compatibility checks and dedicating specific bands to smart devices, you can ensure a seamless and efficient smart home ecosystem.
- Compatibility Check: Before setting up your new router, it's essential to ensure compatibility with your existing devices. Imagine connecting a cutting-edge router to older devices that can't fully utilize its capabilities. By verifying compatibility, you'll guarantee seamless integration, optimizing your network for peak performance and allowing all devices to work together harmoniously.
- Dedicated Band: Utilizing a dedicated band for specific tasks can enhance your network's efficiency. Picture a home office scenario where video conferences are a daily occurrence. Assigning a dedicated band for this purpose ensures uninterrupted video calls, even when other devices are active on the network. This smart allocation of resources optimizes your network for various needs.
Bandwidth Management
Prioritizing critical tasks and limiting bandwidth for non-essential applications ensures efficient network utilization. These tactics empower you to allocate network resources efficiently, ensuring that crucial tasks receive the attention they deserve while preventing congestion and slowdowns.
- Prioritization: Effective bandwidth management involves prioritizing critical tasks. Imagine a scenario where you're working from home and need seamless video conferencing. Prioritizing this task ensures minimal disruptions, guaranteeing that your important meetings run smoothly, even when other devices are online.
- Limiting Bandwidth: In a bustling household with numerous devices, limiting bandwidth for specific applications can prevent congestion. Consider a scenario where file downloads slow down web browsing. By setting limits on bandwidth-hungry activities like downloads, you maintain a balanced network, ensuring that everyone enjoys a consistent online experience. This strategy maximizes your network's efficiency and prevents slowdowns.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
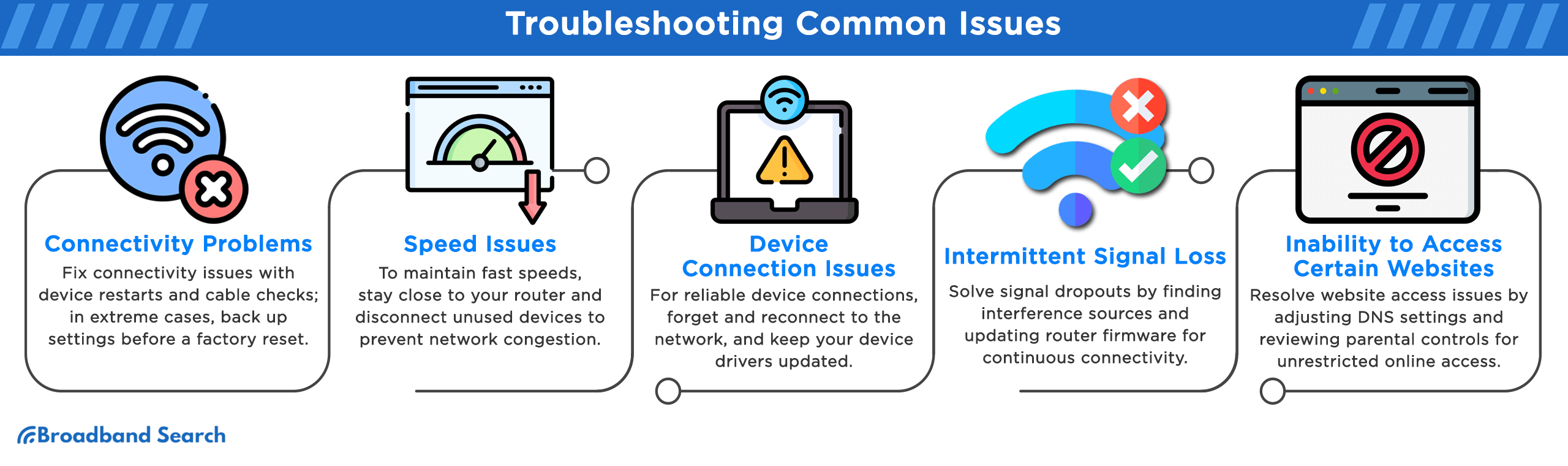
Connectivity Problems
Basic troubleshooting steps include restarting devices, verifying cables, and ensuring the router is powered on. In dire situations, a factory reset might be necessary, though caution must be exercised to back up settings beforehand.
- Basic Troubleshooting: When faced with connectivity problems, start with simple steps. Restart devices—like you'd reboot a computer for optimal performance. Check cables, ensuring they're securely connected, similar to inspecting a live concert's wiring to avoid audio glitches. Verify the router's power status, much like ensuring the stage lights are on before a musical performance begins.
Router Troubleshooting Guide
Follow these steps for basic router troubleshooting after IP address-related issues have been addressed:
Check Wired Connections:
- Disconnect all cables from modem, router, and computer.
- Power off modem and router; shut down the computer.
- Connect modem to router using an Ethernet cable: Modem's Internet port to router’s WAN or LAN port.
- Link computer to router via a second Ethernet cable plugged into one of the router’s numbered ports.
- Power up the modem, wait a minute, then power up the router. After another minute, turn on the computer.
Re-run Router Setup Disc:
- If unable to connect to the router after confirming wired connections, your router might be defective.
- During setup, verify connection settings and credentials with your Internet Service Provider.
Test with a Second Computer (if available):
- If no computer can connect, the issue lies with the router or modem.
Repeat IP Address Troubleshooting:
- If connectivity issues persist post-troubleshooting, seek further assistance from your Internet Service Provider or router’s manufacturer.
- Factory Reset: As a last resort, consider a factory reset. However, exercise caution and remember to back up your settings first. It's akin to a musical encore—a reset brings a fresh start, but preserving your notes ensures the symphony continues without missing a beat.
How to Factory Reset Your Router Using the Physical Reset Button:
- Ensure the router is powered on.
- Locate the reset button, usually on the router's back or bottom.
- Using a paperclip, press and hold the reset button for 30 seconds.
- Release and wait for the router to restart.
If your router lacks a reset button, follow these steps via the Configuration Interface:
- Input your router’s IP address into a web browser. (Check your device if you're unsure of the IP.)
- Log in using your credentials. Default login details can be found on the router.
- Navigate to 'System' or 'System Tools' (exact naming varies by router).
- Select 'Restore' or 'Factory Default'.
- Confirm the reset and wait for the router to reboot.
Speed Issues
Maintaining an optimal distance from the router ensures fast speeds. Overcrowded networks, much like an overcrowded room, can slow things down; it's crucial to disconnect unused devices to regain speed and ensure efficient network performance.
- Distance from Router: Maintaining a reasonable distance from your router is essential for avoiding connectivity problems. Imagine a home office scenario where a distant room suffers from sluggish internet due to excessive distance. Staying within a suitable range ensures faster speeds and robust connections.
- Overcrowded Network: Overcrowded networks, like crowded highways during rush hour, can lead to slowdowns. In a household with numerous devices connected, such as smart TVs, gaming consoles, and smartphones, some devices may suffer from poor connectivity. Disconnecting unused devices alleviates congestion, ensuring a smoother online experience for all users.
Device Connection Issues
Whether it's a smartphone, laptop, or IoT device, ensuring reliable connections is crucial. By addressing common issues like IP conflicts and outdated drivers, you can streamline device connectivity and ensure uninterrupted access to your network.
- Forget & Reconnect: Troubleshooting connectivity problems can be as simple as having your device forget the network and then reconnecting. Imagine a scenario where your smartphone struggles to connect to your home Wi-Fi. By following this step, you can often resolve such issues swiftly, much like hitting the reset button for seamless network reconnection.
- Update Device Drivers: Ensuring that the wireless adapters on your devices have up-to-date drivers is essential for maintaining a stable connection. Picture a laptop experiencing slow internet speeds due to outdated drivers. Regular updates keep your devices in harmony with the network, optimizing their performance and ensuring a smooth online experience.
Intermittent Signal Loss
Troubleshooting involves a series of strategic steps: identifying interference sources, keeping firmware updated, and maintaining an efficient network environment. These practices ensure uninterrupted connectivity, enhancing your digital experience.
- Check for Interference: Troubleshooting connectivity problems involves identifying potential sources of interference. Picture a scenario where a microwave oven disrupts your Wi-Fi signal. By locating and relocating such devices away from the router, you can ensure a more stable connection, same as rearranging objects that affect your radio reception.
- Firmware Update: Keeping your router's firmware up to date is crucial for optimal performance. In a home office environment, imagine encountering connectivity issues due to outdated router firmware. Updating it ensures your network functions smoothly, comparable with installing software updates for enhanced functionality.
Inability to Access Certain Websites
Experiencing the inability to access specific websites can be vexing. By examining DNS settings and ensuring parental controls are appropriately configured, you can resolve these conflicts and enjoy uninterrupted access to the online content you need.
- DNS Issues: Imagine a situation where your web pages load sluggishly due to unreliable DNS settings. By switching to a trusted DNS provider like Google DNS or OpenDNS, you can enhance your browsing experience, ensuring prompt access to websites.
- Check Parental Controls: In a family setting, parental controls or security settings may inadvertently restrict access to certain websites, much like child-proofing a room. Verifying these settings and ensuring they don't block legitimate content allows for a smoother online experience, especially when using the internet for both work and leisure.unrestricted internet usage, just as you'd remove barriers to access a desired location.
The Takeaway
Recognizing the signs that indicate you need a new router is a crucial step in maintaining a robust home network. We've explored a range of indicators, from deteriorating speeds and frequent disconnections to aging hardware and security concerns. Each of these signals, if left unaddressed, can lead to frustrating experiences, security vulnerabilities, and productivity setbacks.
Now, it's time to take action. As technology continually advances, investing in a new router is not just a matter of convenience; it's an investment in the efficiency, security, and connectivity of your digital world. Don't wait until you're bogged down by connectivity issues or exposed to security risks. Seize the opportunity to enhance your home network by exploring the latest router technologies and enjoy the benefits of a faster, more reliable, and more secure internet experience. Your digital future awaits – make the most of it by upgrading your router today.
FAQ
Will getting a new router increase my internet speed?
A new router can potentially improve your internet speed if your current one is outdated or unable to handle the speed of your internet plan. However, it won’t increase the maximum speed provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Is it better to get a separate modem and router or a combined unit?
Separate units often offer more flexibility and better performance but might be more challenging to set up. Combined units are easier to install and manage, but you might need to replace the entire unit even if only one part fails. Your choice should depend on your specific needs and technical comfort level.
How do I know which type of router is best for my needs?
Consider your internet usage, the size of your living space, the number of devices connecting to the network, and any specific features you need (like parental controls or guest networks). Reading product reviews, consulting buying guides, and considering recommendations from reliable tech websites can also guide your decision.
What's the difference between a single-band, dual-band, and tri-band router?
Single-band routers operate on the 2.4GHz frequency band, which is slower and can get crowded. Dual-band routers operate on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, offering a faster and less congested 5GHz option. Tri-band routers have an additional 5GHz band, allowing even more devices to connect at higher speeds without interference.
Should I rent a router from my ISP or buy my own?
Renting might be convenient, but in the long run, it's usually more expensive than buying. Purchasing your own router gives you the freedom to choose a model that fits your needs, often resulting in better performance and features. Additionally, owning your equipment allows you to upgrade or change ISPs without changing your home network setup.