Complete Guide to Fiber Optic Home Networking
Fiber optic networks are the backbone of the internet’s future. Unlike traditional copper-based connections, fiber delivers unmatched speed, reliability, and efficiency. Whether you’re streaming in ultra-HD or running a home office with multiple devices, fiber ensures a seamless online experience.
Switching to fiber internet involves learning about its unique components and setup process. BroadbandSearch offers a practical, easy-to-follow guide for anyone looking to set up a home fiber network that breaks down complex tech into simple steps for everyday users.
This guide provides a step-by-step overview to help you understand fiber optic technology, set up your home network, and optimize performance.
What You Need to Know About Fiber Optic Internet
What Is Fiber Optic Internet?
Fiber optic internet transmits data using light over glass or plastic cables thinner than a human hair. Unlike copper cables, which rely on electrical signals, fiber cables are immune to interference and maintain superior speeds over long distances.
Key Features of Fiber Internet:
- Speed: Typically 1-2 Gbps, up to 20x faster than traditional connections.
- Reliability: Minimal interference, even over long distances.
- Simultaneous Device Use: Supports multiple devices without noticeable slowdown.
- Symmetrical Speeds: Upload and download at the same speed.
Why Fiber Is the Future of Broadband
Fiber internet is the foundation of a modern digital lifestyle. It surpasses DSL, cable, and satellite internet in every category, including speed, performance, and scalability. Fiber’s nearly limitless bandwidth also means future-proofing your connection as digital demands grow.
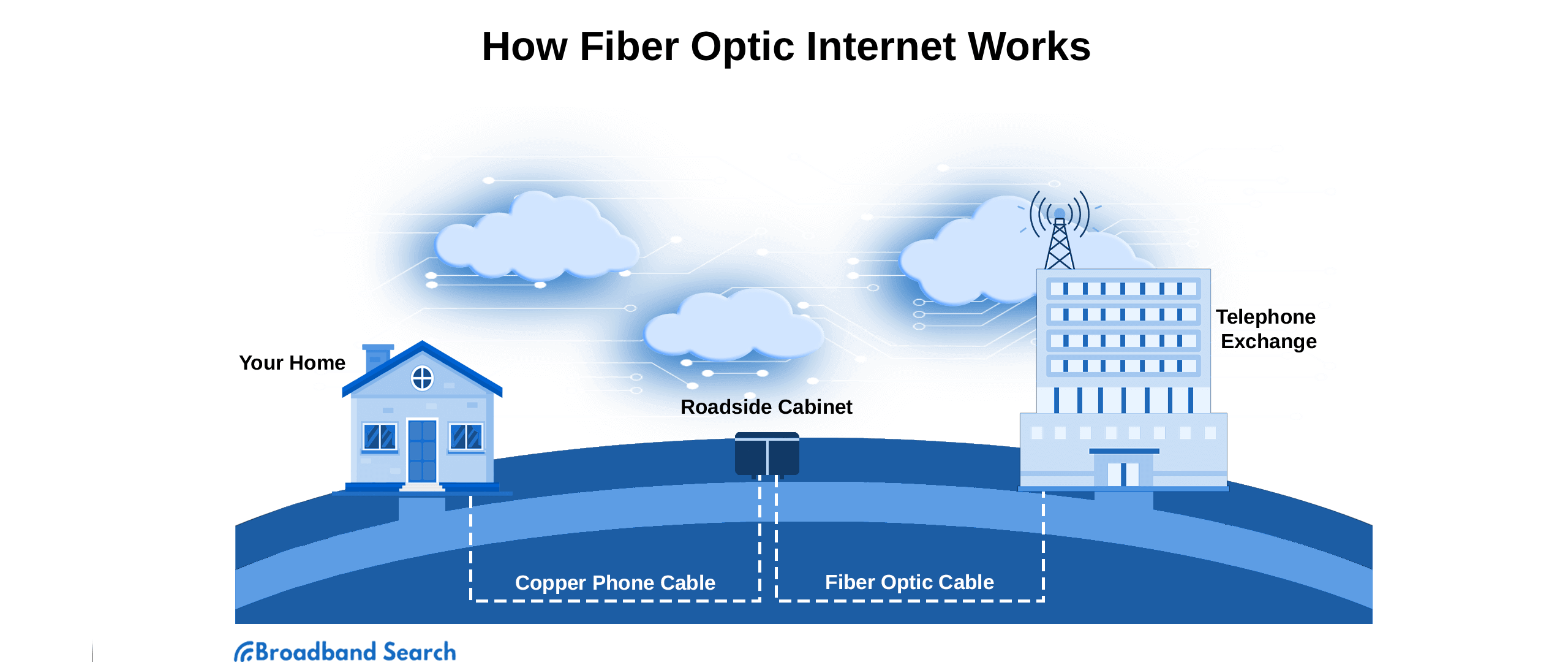
Types of Fiber Optic Internet Connections
While all fiber optic connections are faster than traditional internet, there are three primary types, categorized by how far the fiber cables extend toward your location.
- FTTH (Fiber to the Home): Fastest and most reliable. The fiber runs directly into your home or business.
- FTTC (Fiber to the Curb): Fiber reaches a nearby utility pole or street cabinet before switching to copper or coaxial cables for the final stretch.
- FTTN (Fiber to the Neighborhood): Fiber runs to a central hub serving multiple areas, with copper cables completing the connection to individual homes.

Current Fiber Availability in the United States
Fiber internet is expanding across the U.S., with about 25% of U.S. households currently connected. Installation of fiber infrastructure is steadily increasing, meaning better access and lower costs in the future. Use broadband provider tools to check availability in your area.
Supplies for Setting Up a Home Fiber Optic Network
Transitioning to fiber optic internet requires some specialized equipment. Most ISPs handle the majority of the setup, but you’ll need to manage the in-home network.
Essential Fiber Optic Equipment
1. Fiber Optic Network Cables
Unlike copper, fiber optic cables maintain speed and integrity over long distances. Ensure your home network uses fiber-compatible cables to take full advantage of fiber’s performance.
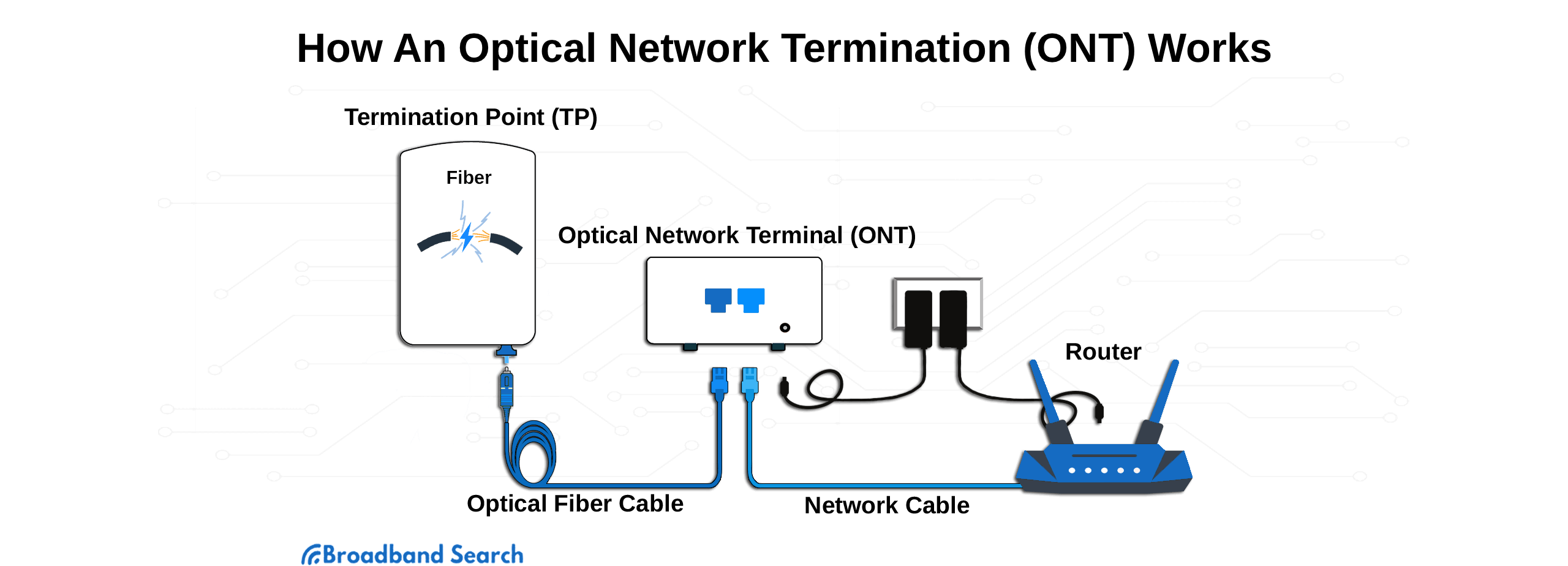
2. Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
Think of the ONT as your fiber modem. It receives the optical signal from your ISP and converts it into data your devices can use.
3. Fiber Modem and Router
A fiber modem, technically a transceiver, decodes fiber signal while the router broadcasts your home Wi-Fi network.
Why Copper Cables Aren’t Ideal
Copper cables suffer from signal degradation, limiting speed and efficiency. Fiber’s digital medium is immune to interference, offering a vast performance boost.
Additional Tools
- Ethernet Cables for wired devices.
- Surge Protectors to safeguard against power fluctuations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Your Fiber Optic Network
1. Check Availability
Use tools like ISP maps to confirm fiber service in your area.
2. Choose the Right Plan
Discuss your household’s needs (e.g., number of users, tasks) to select an appropriate speed and pricing tier.
3. Schedule Installation
Your ISP will install the fiber cables and set up the ONT. The process may take a few hours or a couple of days, depending on infrastructure readiness.
4. Connect ONT to Fiber Router
Use Ethernet cables to link your ONT to your router and begin broadcasting the signal.
5. Set Up Your Wi-Fi Network
Using your router’s admin dashboard, configure your network name (SSID) and password for secure access.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Connection Errors
Check all cable connections, especially between the ONT and router. Ensure you’re using the correct Ethernet port (WAN).
Slow Speeds
Run a speed test via a site like Testmyspeed.com. Compare results with your plan’s promised speeds. Contact your ISP if speeds fall significantly short.
Indicator Lights
Verify that ONT and router indicators are solid green for power and signal. Blinking or red lights signal potential issues.
Why Fiber Internet is Worth It
Fiber optic internet delivers unmatched speed, reliability, and scalability for modern homes. Whether for gaming, streaming, or remote work, its performance sets it apart. While availability is still growing, fiber is the gold standard for broadband connections.
Check availability in your area and give your home network the upgrade it deserves.
FAQ
How does fiber optic internet differ from other broadband internet?
Fiber consists of a completely different set of materials and functions than other types of broadband. The cable interior is glass or plastic filaments rather than copper wire. The signal is digital and generated by flashing laser lights rather than electricity. This redesign of internet service performs better than other broadband connections in every way.
Which is better, Wi-Fi or fiber optic internet?
You can’t strictly compare Wi-Fi and fiber optic internet because they perform different functions. The fiber optic signal brings the capability for high-speed internet to your home. Without Wi-Fi to create a wireless network, you would be limited to only the devices that can plug into an ethernet jack. The bottom line is that Wi-Fi and fiber optic internet work together to create exceptional internet service.
Is fiber internet better than 5G?
Once again, it’s hard to compare these two items straight across. Fiber internet has the advantage of speed but functions in a limited wired environment. On the other hand, 5G service is wireless and pretty fast but not as speedy as fiber. To determine which is “better” requires you to decide which fits best with how you use the internet.
Who offers fiber optic internet in my area?
The best way to locate fiber optic internet in your area is to use our internet provider comparison tool to generate a list of local providers, then check to see which among them offers fiber service.
Is fiber optic internet good for gaming?
Fiber is generally accepted to be the best broadband internet service available for gamers. This is not only due to the sheer speed involved but also to what is called low latency. Latency refers to how quickly signals go from your device to the remote server and back. A delay in signal processing can be the death of you in games that rely on quick, real-time responses.