Fiber optic cables are one of those things you might have heard of or know a bit of information about, but what are they exactly, and when and where are they used? They are a cable used primarily for data transmission that utilizes light pulses. We’ll talk more about what they are made from shortly, but they are used mainly for telecommunications, data transmission applications, and internet services.
They can do many of the jobs copper wires used to do when transmitting information, but they can do those jobs much more effectively. The main reason why copper wires aren’t entirely obsolete for these purposes is that fiber optic wires can be expensive upfront to install (they’re buried in the ground, typically), and they’re installed more often in urban and settled areas. There are efforts for further expansion, given the usefulness of fiber optic cables, but this will take time.
Yet to delay no further, here is what else you need to know about fiber optic cables and what can be done with them:
How Do Fiber Optic Cables Work?
Fiber optic cables transmit data using rapid pulses of light, which are generated by either tiny lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The cable itself is engineered to guide these light pulses over long distances with minimal loss. Light stays inside the cable by bouncing off the inner walls, a process called total internal reflection. This ensures that the signal remains contained within the cable.
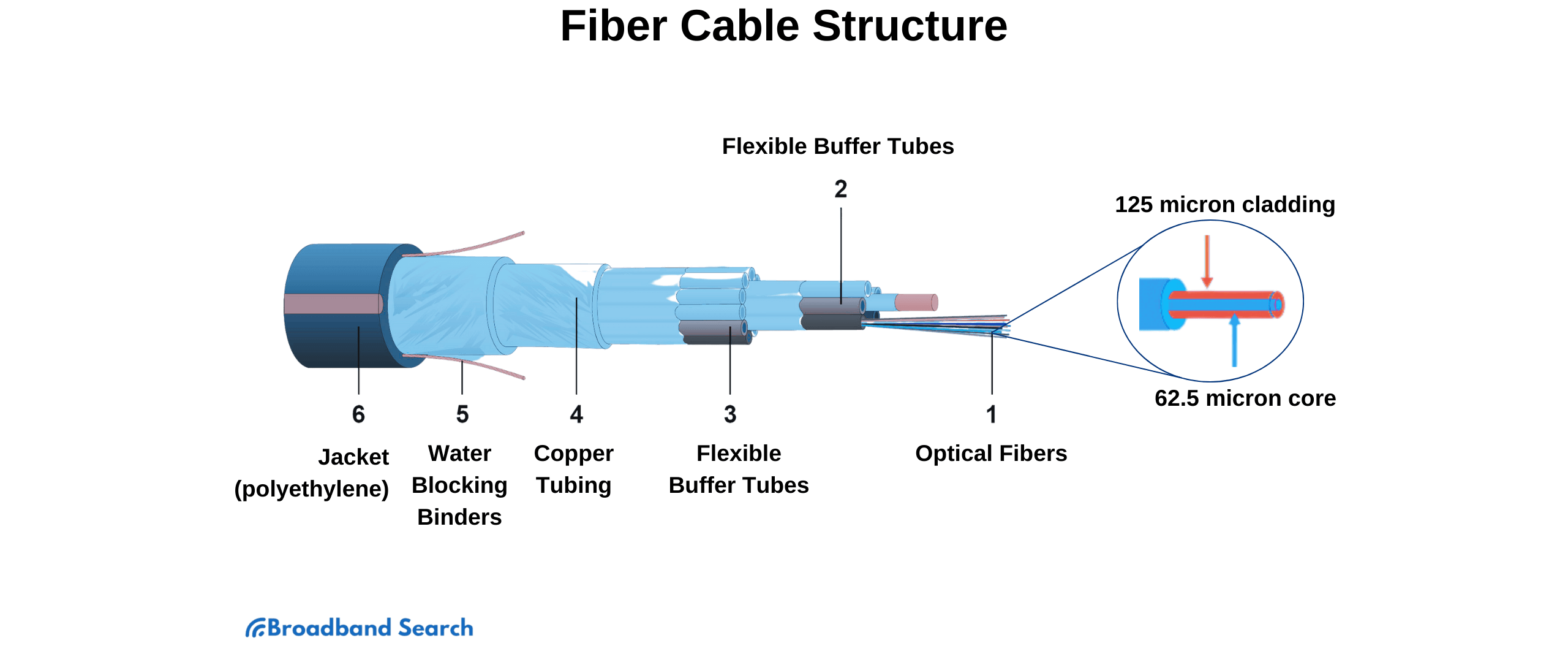
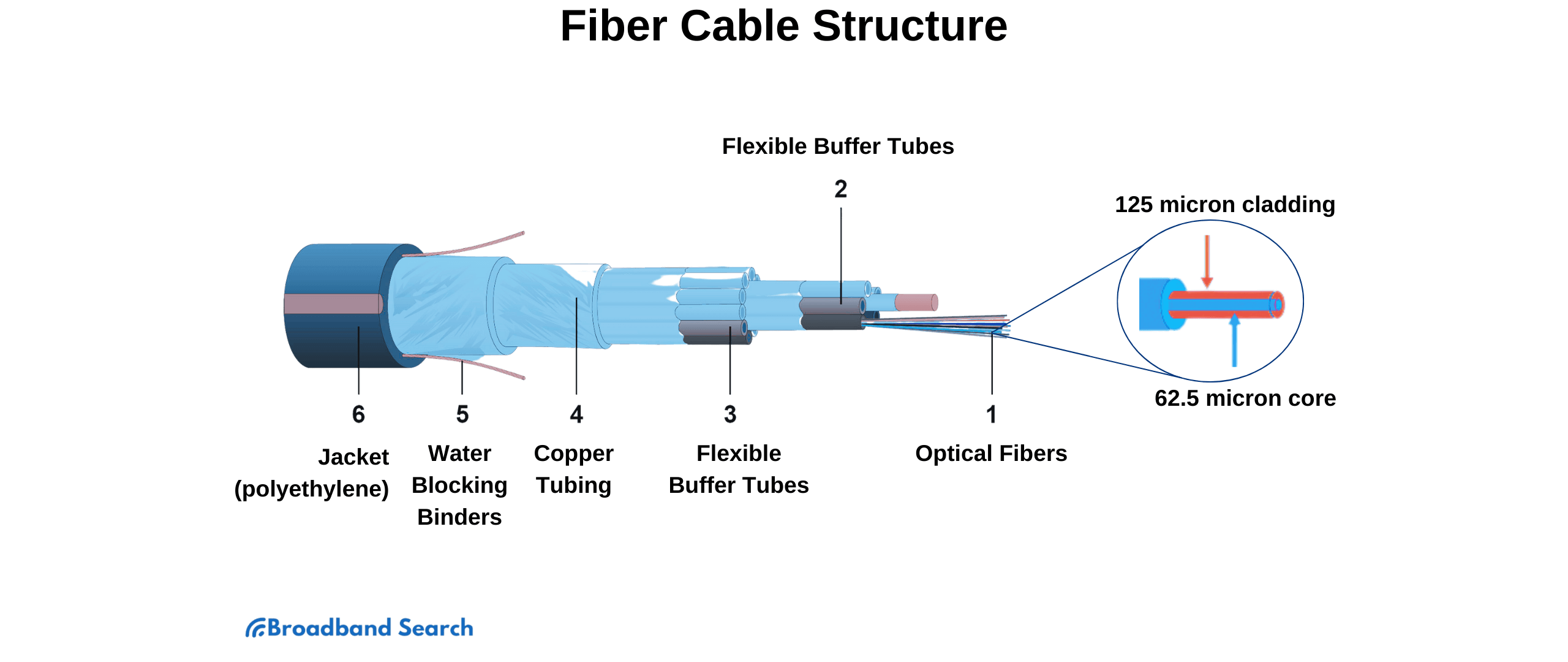
A fiber optic cable has two main components that make this process possible:
- Core: The core is the central part of the cable and is made of refined glass that are about the thickness of human hair. This purity allows light signals to travel over long distances with very little signal degradation, enabling rapid data transmission.
- Cladding: The cladding is a layer of glass or plastic that surrounds the core. It has a different refractive index than the core, which causes the light to reflect inward instead of leaking out. This is what keeps the signal on its path.
Unlike copper cables that use electrical signals, fiber optic cables use light. This fundamental difference allows for much faster data transmission and supports a wider range of frequencies without the signal loss that affects copper or satellite signals.
What Are Fiber Optic Cables Used For?
Fiber optic cables are essential for high-speed data transmission across a wide range of industries. Their ability to move vast amounts of data quickly and reliably makes them invaluable. A strong fiber connection can handle speeds over 2,000 Mbps, which is fast enough to download a two-hour movie in about 17 seconds.
Here are some of the major applications for fiber optic technology:
Telecommunications
The transfer of information is the foundation of telecommunications, so it’s no surprise that fiber optic cables are widely used in this sector. After their initial development, fiber cables became the backbone for landline phone systems, cable television (CATV) networks, and other critical communication services. Because of their high capacity, a single fiber optic strand can easily handle thousands of conversations or data streams at the same time.
Networking
You are likely already familiar with the role fiber optics play in computer networking. Fiber optic cabling forms the foundation for much of our modern networking infrastructure, connecting everything from small offices to entire cities. They are used to build:
- Local Area Networks (LANs): Connect devices within a single building or location.
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs): Link multiple LANs across a city or campus.
- Wide Area Networks (WANs): Span large geographic areas, connecting regions or countries.
By using light to transmit data, fiber optics reduce the chances of errors and lost data packets compared to copper cables. This makes them the superior choice for mission-critical tasks where data accuracy is essential.
Internet and Cable TV
Fiber optic lines are central to delivering modern high-speed internet service. When you hear the term "fiber internet," it refers to an internet connection delivered over these advanced cables. The light pulses carrying data in a fiber internet connection travel at about 70 percent of the speed of light. This incredible speed makes fiber the gold standard for network infrastructure.
Medical
Modern medicine relies on the rapid and accurate transmission of complex data, and fiber optic cables are ideal for critial procedures. Fiber optics allow for the creation of advanced medical instruments that give doctors the ability to see inside the human body with minimal invasion.
Interestingly, the science of fiber optics was developed with medical uses in mind. Doctors, surgeons, and dentists needed a way to illuminate and view internal organs without performing major surgery. Today, this technology is used in endoscopes, arthroscopes, and other diagnostic tools.
Military and Space Applications
Given the massive amounts of data and the need for advanced security in military and aerospace operations, fiber optic cables are the preferred choice. An optical fiber network offers a high level of data security because the signal is contained within the cable and is very difficult to tap without being detected. This makes it ideal for keeping sensitive information safe. Fiber optics are vital for defense communications, avionics, and space exploration, with new uses continuing to emerge.
Automotive
As vehicles become more like computers on wheels, the need to transmit data quickly and reliably within the car has grown. Fiber optic cables are perfect for this, making our cars smarter and safer. Currently, fiber optics are used in vehicle lighting systems and for communication between different electronic control units (ECUs).
Compared to traditional copper wiring, fiber cables save a significant amount of space and weight. This allows for more efficient car design and leaves room for additional safety features. You can find fiber optics in both the interior and exterior systems of modern vehicles.
What Are the Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables?
Fiber optic cables offer several key advantages over traditional copper cables, which is why they have become the standard for high-performance communications.
- High Speeds: Since they use light to transmit data, fiber optic cables can achieve speeds that are far greater than copper cables.
- Long Distance Stability: Fiber can carry signals over much longer distances without the signal degrading, reducing the need for signal boosters.
- Interference-Free: Fiber optic cables are made of glass, so they are not affected by electromagnetic interference (EMI) from power lines or other electrical noise. This results in a cleaner, more reliable signal.
- High Bandwidth: Fiber cables can carry significantly more information than copper cables of the same size. This high bandwidth allows them to handle multiple data streams simultaneously, from video conferencing to online gaming and 4K streaming.
- Durabile and Secure: Fiber optic cables are strong and more resistant to environmental factors than copper. They are also more secure, as tapping into a fiber line is extremely difficult without being detected.
The Impact and Future of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are much more than just the wires that bring us fast internet. They have become a fundamental part of modern life and are a critical component in many of our most important tools and technologies. From enabling global communications to advancing medical procedures, the impact of fiber optics is immense.
As demands for faster, more secure communication grow, fiber optics will continue to expand into new industries and shape the future of connectivity. We hope this guide has given you a clearer understanding of what these remarkable cables do and how they are shaping our connected world.
FAQ
What is dark fiber?
Generally speaking, dark fiber is fiber optic cables and infrastructure that have been laid out and might be ready for use but are not being used. There is no signal running through them, and they have a lot of potential in them. They aren’t used in traditional communications services, so they might be able to be used for private services or other purposes.
Cables themselves aren’t that expensive compared to the costs of laying them, so dark fiber would often be placed down in major areas in anticipation of a greater need. How it will be used down the line remains to be seen.
Does fiber use Cat6?
Fiber optic and Cat6 cabling are entirely different things. Fiber optic cables are what we discussed over the rest of the article, while Cat6 cables are ethernet cables that use twisted copper wires, specifically 4. Cat6 cables use the full capacity of the wire and can be more durable than fiber optic wires, requiring less maintenance.
Each will have its benefits and advantages, and we encourage you to look for a more detailed comparison if you are interested.
Which fiber connector is best?
It can vary based on the job required and the likely placement of the connector. There is no perfect option. If one is looking for a low-cost alternative, no polish and no epoxy options might be best. If ease of installation is most important, look for a polish and no epoxy option. Higher-end requirements that need precision signaling might call for APC fiber connectors. And there are so many more examples. We recommend you consider the use case and research from there.
Do all routers work with fiber?
No, which is why you should be careful to ensure everything works together when getting new internet service or a new router. Some routers (or modem/router combos) are generally made for DSL or cable internet, while others might be made specifically for fiber. Many models will work with practically any service type, but that doesn’t mean it is the default. Be sure to make sure your router is fiber compatible if you want to keep using it.
Can electricity damage fiber optics?
Not particularly. Fiber optic cables are immune to any damage from electromagnetic interference, which is a significant advantage over other cables used for internet service and other purposes. Fiber optic cables are often involved in systems that work with electricity but do not conduct electricity themselves. No heat or visible light comes off of them, so they are usually safe and more likely to get damaged from getting bent or physical means rather than electricity. People working with them need to remain cautious and not look directly at them or risk eye damage.