Data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, and the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) in Canada, have revolutionized how businesses handle and protect personal data. They impact us in ways seen and unseen and rapidly evolve to match the needs of a shifting technology sector.
Consequently, ISPs, as key players in the telecommunications industry, have found themselves at the epicenter of this global shift towards data privacy. We’re here to review how they interact, the key concepts involved, and how these trends and regulations might affect you.
GDPR Compliance Among ISPs
GDPR and its Requirements
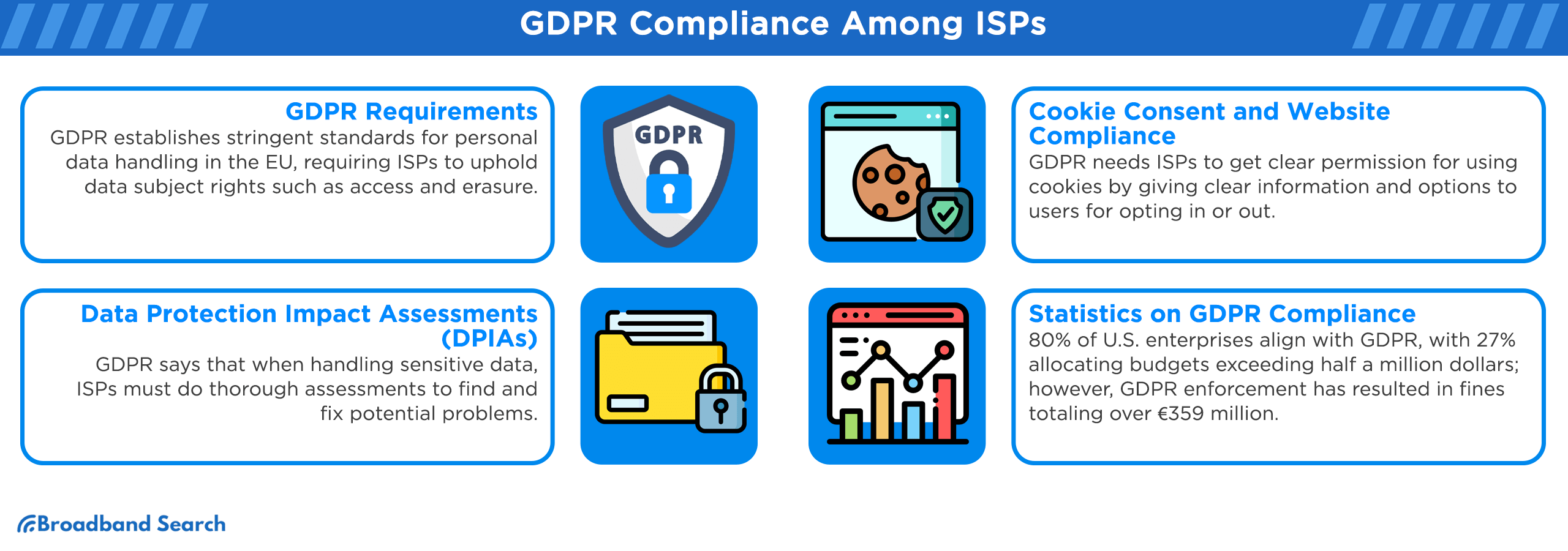
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data privacy framework that sets stringent standards for organizations handling personal data within the European Union. Critical aspects of GDPR compliance for ISPs include:
- Data Subject Rights: The GDPR grants individuals rights over their data, including the right to access, rectify, erase, and object to data processing. ISPs must establish processes to accommodate these rights promptly.
- Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): The GDPR mandates DPIAs for high-risk data processing activities. ISPs must conduct these assessments to identify and mitigate data protection risks effectively.
- Cookie Consent and Website Compliance: The GDPR requires ISPs to obtain clear and informed consent from website visitors for the use of cookies. Compliance involves providing transparent information about data processing activities and allowing users to opt in or out.
Statistics on GDPR Compliance among ISPs
Compliance Rates: Recent data indicates that approximately 80 percent of U.S. enterprises have undertaken measures to align with the GDPR. Notably, 27 percent of these companies allocated budgets exceeding half a million dollars for GDPR compliance initiatives. GDPR enforcement has resulted in substantial fines, totaling over €359 million.
Varied Regional Compliance: Across different regions, knowledge of the GDPR exhibits variations. For instance, in the Nordic region, more than 80 percent of Norwegian internet users were familiar with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) as of 2018. In contrast, at the EU level, approximately 69 percent of individuals aged 16 and above had an awareness of GDPR at the same time.
Case Study: Data privacy has emerged as a pivotal global concern. A study by the Richmond Journal of Law and Technology revealed that in 2017, 92 percent of American companies recognized GDPR compliance as a paramount objective.
Challenges and Common Issues Faced by ISPs in Achieving GDPR Compliance
1. Data Mapping and Documentation
Many ISPs need help with the extensive data mapping and documentation requirements of GDPR. Ensuring a comprehensive record of data processing activities can be resource-intensive.
Recommendation: Implement data mapping tools and document management systems to streamline the process.
2. Consent Management
Obtaining valid and informed consent for data processing is a complex task. Balancing user consent with data collection needs can be challenging.
Recommendation: Improve compliance by providing users with precise and granular options for cookie consent.
3. Data Breach Reporting
GDPR mandates timely reporting of data breaches. ISPs may have difficulties identifying and reporting breaches within the stipulated 72-hour timeframe.
Recommendation: Develop an incident response plan and implement real-time monitoring solutions.
Impact of CCPA on ISP Data Privacy Practices
Introduction to the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) represents a pivotal piece of legislation in the United States' data privacy landscape. The CCPA grants Californian consumers greater control over their personal information and imposes stringent obligations on businesses, including ISPs, that collect or process their data. Key elements of CCPA include:
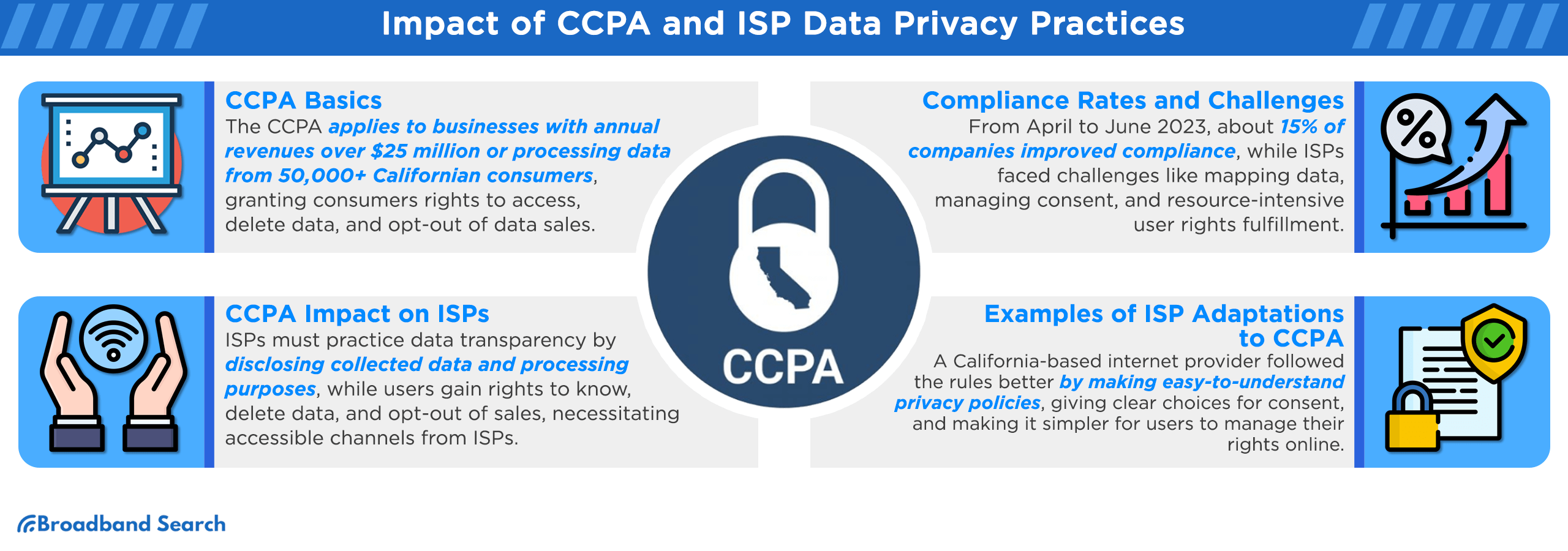
- Scope: CCPA applies to businesses that meet specific criteria, including those with annual gross revenues exceeding $25 million, those that process personal information of 50,000 or more Californian consumers, or those that derive 50 percent or more of their annual revenue from selling personal information.
- Consumer Rights: CCPA affords Californian consumers several rights, including the right to access their data, request its deletion, opt out of the sale of their information, and receive equal service and pricing regardless of their privacy choices.
How CCPA Affects ISPs and Their Data Privacy Practices
- Data Collection and Processing: ISPs, which inherently collect vast amounts of user data, must now be more transparent about their data collection practices. They need to disclose what personal information they collect, the purposes of processing, and whether they sell it.
- Data Subject Rights: CCPA grants Californian users the right to know what data ISPs collect about them, request the deletion of their data, and opt out of data sales. ISPs must provide accessible channels for users to exercise these rights.
Compliance Rates and Challenges Related to CCPA among ISPs
Compliance Rates: In the second quarter of 2023, as per the 6th State of CCPA and CPRA Privacy Rights Compliance Report, significant movements in compliance status were observed among companies. Notably, 14.67 percent of previously non-compliant companies made substantial shifts towards achieving CCPA/CPRA compliance. Among them, 13.33 percent transitioned to manual compliance procedures, while 1.33 percent embraced automated compliance solutions during this period.
Challenges:
a. Data Mapping: ISPs, grappling with vast data volumes, often face difficulties mapping and documenting data flows, a prerequisite for CCPA compliance.
b. Consent Management: Ensuring that user consents are informed and specific presents a challenge, especially regarding the sale of personal information.
c. Data Subject Rights Fulfillment: Responding to access and deletion requests within CCPA's required timelines can be resource-intensive.
Examples of ISPs Adapting to CCPA Regulations
- Transparency: ISPs can follow the example of a prominent California-based ISP that implemented clear, user-friendly privacy policies detailing data collection and processing practices.
- Consent Management: By offering users precise and granular options to decide whether they wish to opt in or opt out of data sales, one company exemplified how CCPA's far-reaching privacy benefits extend to California's 40 million residents..
- Data Subject Rights Handling: Another ISP streamlined its data subject rights management with a dedicated online portal, expediting user requests and enhancing compliance.
Best Practices in Data Protection for ISPs
Overview of Recommended Data Protection Practices for ISPs
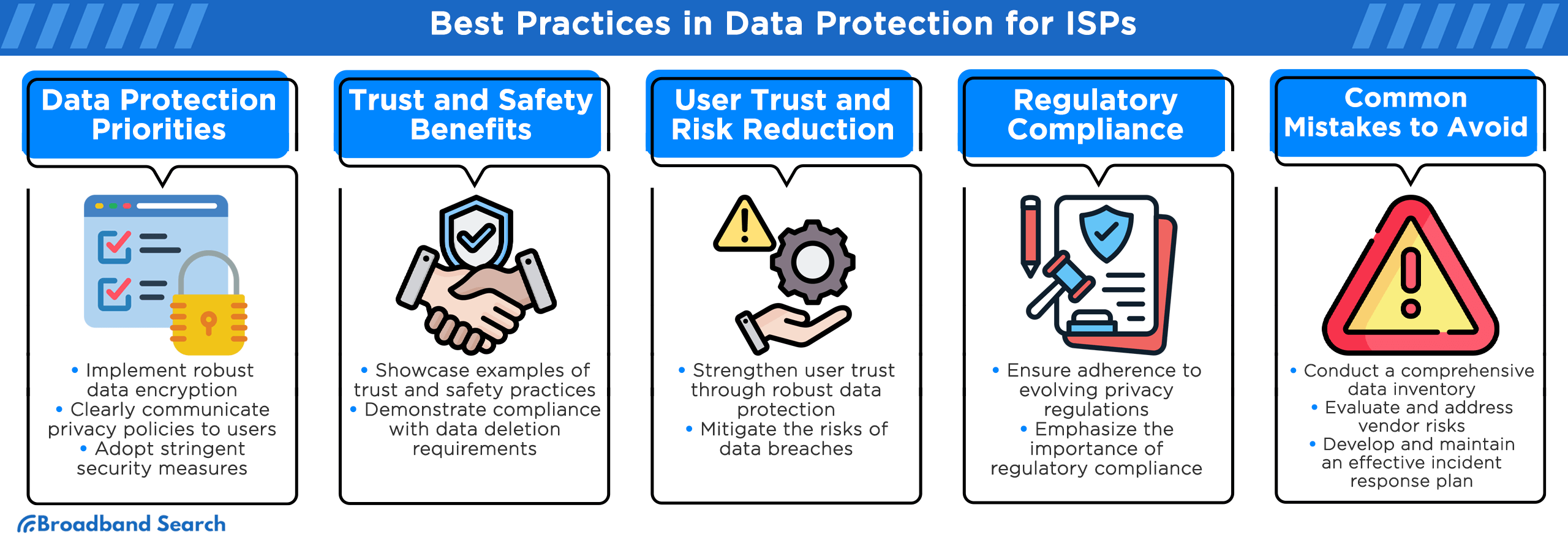
To ensure robust data protection and maintain compliance with evolving data privacy regulations, ISPs should prioritize the following practices:
- Data Encryption: This involves encrypting sensitive user data when stored (at rest) and during transmission (in transit). Leveraging industry-standard encryption protocols like SSL/TLS and AES encryption is essential.
- Clear Privacy Policies: Craft transparent and easily comprehensible privacy policies that detail data collection practices, purposes, and user rights. These policies should align with regulatory requirements such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Robust Security Measures: This involves implementing comprehensive security measures, such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and regular security audits.
Examples of ISPs Implementing Best Practices
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of these best practices:
Enhanced Trust and Safety Practices: A research survey conducted in February 2022, polling online service providers about their trust and safety practices, showcased that providers can effectively detect abuse on their platforms, even in end-to-end encrypted environments. Furthermore, these providers preferred detection techniques that do not necessitate access to the contents of users' files and communications.
Compliance with Data Deletion Requirements: A Comparative Study of the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the 2018 California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) revealed that GDPR aligns closely with the legal judgment in the Google Spain judgment. The judgment emphasizes that internet service providers must delete information that becomes inadequate, irrelevant, no longer relevant, or excessively outside the purposes for which data were initially collected or processed.
Benefits of Adopting Strong Data Protection Measures
The advantages of adopting strong data protection measures extend beyond compliance:
- Strengthened User Trust: When ISPs prioritize data protection, they earn the trust of their users. A 2019 Consumer Survey revealed that 81 percent of consumers are likely to engage with businesses that demonstrate strong data security practices. Moreover, 63 percent of consumers expect companies to consistently protect data, even in situations involving phishing scams or unencrypted Wi-Fi connections.
- Reduced Data Breach Risks: Implementing strong data protection measures is instrumental in minimizing the risk of data breaches. The upward trend in data breach costs is evident when comparing the 2020 and 2021 reports, with costs surging from $3.86 million in 2020 to $4.24 million in 2021. This underscores the cost-effectiveness of preventive measures and emphasizes the importance of robust data protection practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA not only avoids hefty fines but also opens up opportunities for global expansion and collaboration.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Data Protection for ISPs
- Lack of Data Inventory: Failing to maintain a comprehensive inventory of collected data can hinder compliance efforts. ISPs should implement data mapping and classification to understand data flows effectively.
- Ignoring Vendor Risks: Overlooking third-party vendor risks can expose ISPs to data breaches. ISPs should implement robust vendor management and due diligence processes.
- Inadequate Incident Response Planning: Not having a clear incident response plan can result in costly data breaches. ISPs should develop and test incident response procedures to minimize damage in case of a breach.
Data Subject Rights Management by ISPs
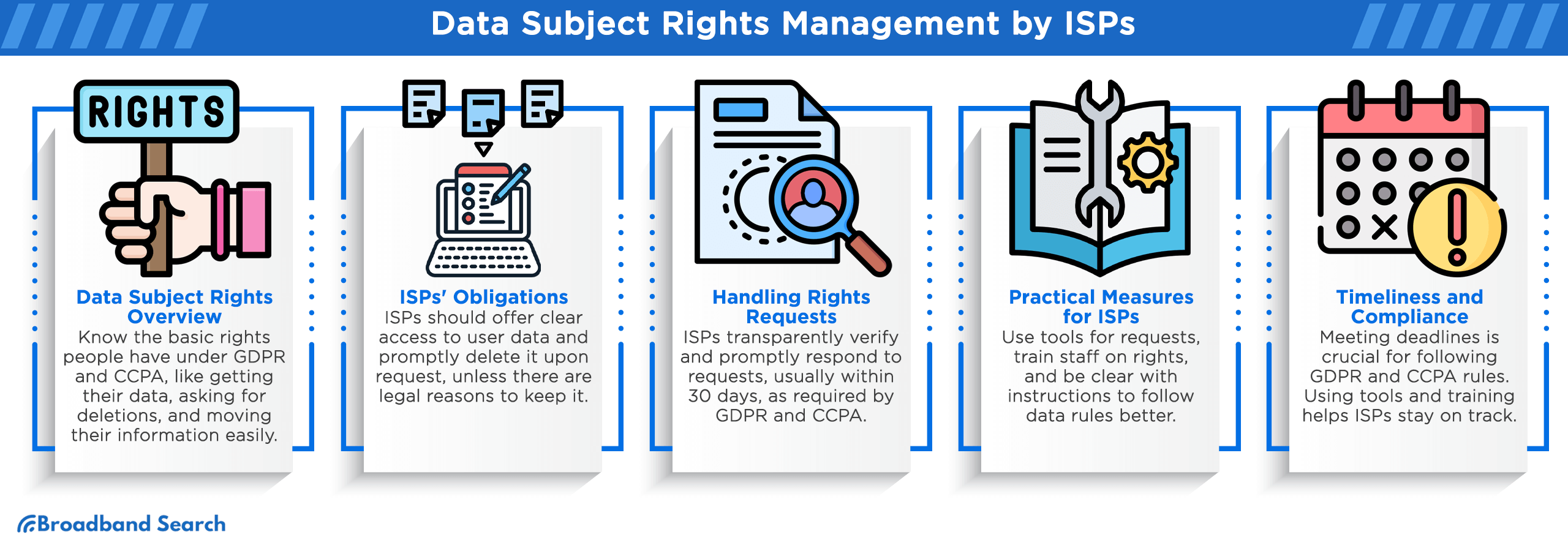
Data Subject Rights under GDPR and CCPA
Data subject rights are fundamental to data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. For ISPs, understanding these rights and fulfilling their obligations is crucial:
- Right to Access: Under both GDPR and CCPA, users have the right to request access to the personal data that ISPs hold about them. ISPs must provide this information in a clear and understandable format.
- Right to Deletion: Data subjects have the right to request the deletion of their data. ISPs must promptly delete the data unless there are legal grounds for retaining it.
- Right to Portability: GDPR grants data subjects the right to receive their data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format. They can then transmit this data to another service provider.
How ISPs Handle Data Subject Rights Requests
ISPs manage data subject rights requests through the following steps:
- Transparency: ISPs must maintain transparent processes for users to exercise their rights. They should provide clear instructions on making requests, and users should easily access request forms or contact details.
- Verification: Verification processes ensure that data requests come from the actual data subjects. ISPs need to verify the identity of the requester securely.
- Timeliness: GDPR and CCPA stipulate specific timelines for responding to data subject rights requests. ISPs must act promptly, typically within 30 days, to address these requests.
Practical Tips and Tools for ISPs
To streamline data subject rights processes and maintain compliance, ISPs can implement the following:
- Request Management Tools: Invest in request management software to help automate and track data subject rights requests.
- Staff Training: Regularly train staff on data subject rights compliance to ensure they understand the nuances and can respond effectively.
- Transparency: Maintain clear and accessible information on your website about data subject rights and how users can exercise them.
ISP Compliance with ePrivacy Regulations
ePrivacy Regulations and Their Significance
The following aspects of ePrivacy regulations are pivotal in safeguarding online communication privacy and user consent:
- User Consent for Online Tracking: ePrivacy regulations demand clear and informed user consent for online tracking, cookies, and similar technologies. ISPs must ensure that users have control over their data and can opt in or out of tracking practices.
- Communication Privacy: ePrivacy rules protect electronic communications, safeguarding the confidentiality of communications and ensuring that ISPs do not engage in unauthorized interception or surveillance.
Challenges Faced by ISPs in Adhering to ePrivacy Rules
ISPs encounter several challenges in achieving compliance with ePrivacy regulations:
- Cookie Consent Management: Effectively securing valid and informed consent for cookies represents a multifaceted challenge. Users require clear and comprehensive information regarding tracking practices and their choices. Alarmingly, a study conducted in 2020 exposes a concerning statistic that 55% of websites' consent tools do not offer users the proactive ability to customize their cookie consent settings.
- User Education: ISPs must ensure that users understand the implications of their consent choices. This is an ongoing challenge.
Innovations and Strategies Employed by Compliant ISPs
Compliant ISPs employ innovative strategies to meet ePrivacy requirements:
- Transparent Cookie Consent Mechanisms: Compliant ISPs implement user-friendly and transparent cookie consent mechanisms. They provide clear information about tracking activities, making it easier for users to make informed choices.
- Privacy by Design: ISPs that excel in compliance prioritize privacy by design in their services and products. They integrate data protection principles into their systems and processes from the outset.
- Continuous Compliance Monitoring: Compliant ISPs regularly monitor and update their compliance efforts to align with evolving ePrivacy regulations. This includes keeping cookie consent banners up to date and ensuring the legality of data processing activities.
Internet Privacy Laws and Online Data Security Standards
Internet Privacy Laws and Their Evolution
Internet privacy laws have undergone substantial transformations over recent decades, mirroring the heightened significance of data protection in the digital era. According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), 137 out of 194 countries have enacted legislation to protect data and user privacy.
How ISPs Adapt to Changing Privacy Laws and Security Standards
ISPs adapt to evolving privacy laws and security standards by implementing various strategies:
- Technological Integration: Some ISPs embrace emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance security and compliance efforts. These technologies can detect and mitigate threats in real time.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: ISPs conduct regular security audits and assessments to ensure they align with changing regulations and standards. This proactive approach helps identify vulnerabilities and maintain compliance.
- User Education: ISPs invest in user education and awareness initiatives to ensure their customers understand privacy policies, security practices, and their rights under data protection laws.
Regulatory Compliance in Telecommunications
Regulatory Bodies Overseeing ISPs and Telecommunications
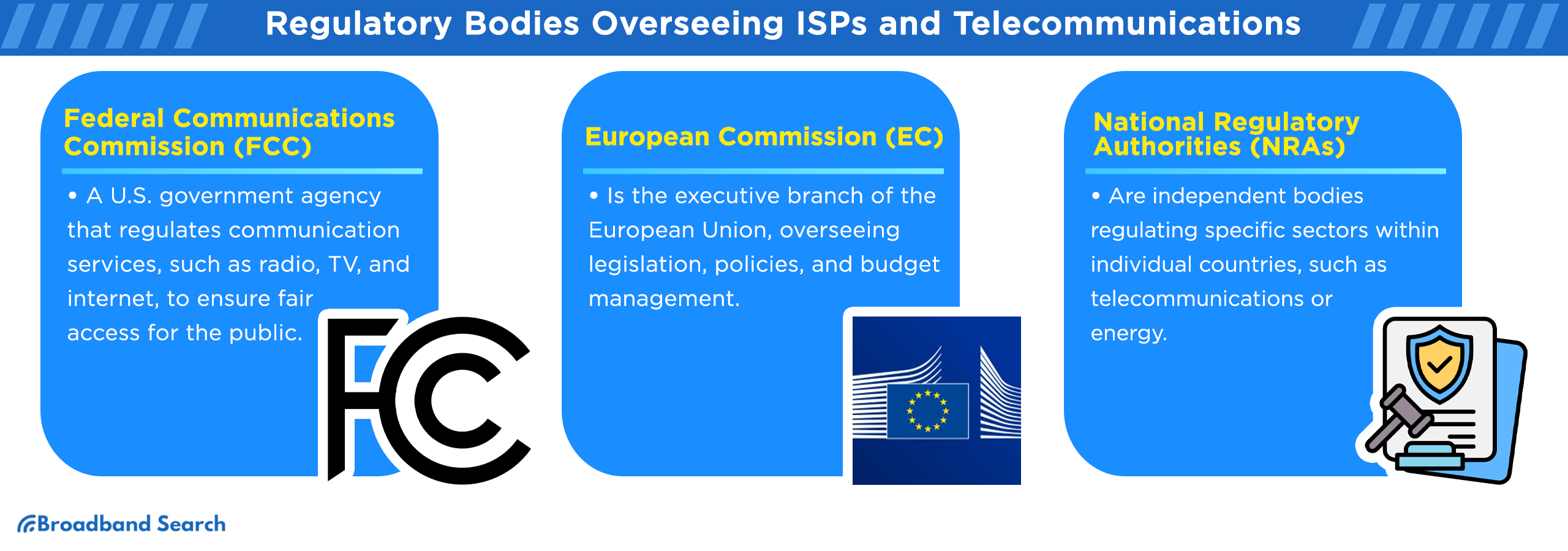
The telecommunications sector is subject to oversight by various regulatory bodies, each playing a crucial role in ensuring compliance:
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC): The FCC is the primary regulatory authority overseeing ISPs and telecommunications in the United States. It enforces rules related to net neutrality, broadband deployment, and consumer protection, shaping the regulatory landscape for ISPs.
- European Commission (EC): In the European Union, the EC takes a lead role in regulating telecommunications and ISPs. It enforces policies that promote competition, consumer rights, and the Digital Single Market.
- National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs): Many countries have NRAs responsible for regulating telecommunications within their borders. These entities ensure compliance with national and regional telecommunications laws.
Key Compliance Challenges Faced by ISPs in the Telecommunications Sector
ISPs encounter several compliance challenges in the telecommunications sector:
- Complex Regulatory Environment: The telecommunications sector is characterized by a complex web of regulations at the national and international levels, making compliance a daunting task.
- Net Neutrality Controversies: ISPs must navigate the ever-evolving net neutrality landscape, where changes in regulations can significantly impact their operations and business models.
- Data Privacy: ISPs often handle vast amounts of user data, necessitating compliance with stringent data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA.
- Emerging Technologies: The introduction of new technologies, such as 5G and IoT, brings novel regulatory challenges that ISPs need to address.
- Global Expansion: ISPs looking to expand internationally must grapple with diverse regulatory regimes, adding complexity to their compliance efforts.
ISP Regulatory Audits and Assessments
Explanation of Regulatory Audits and Assessments for ISPs
Regulatory audits and assessments for ISPs are systematic evaluations conducted by regulatory agencies to ensure compliance with established rules and regulations. Regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States or the European Commission (EC) in the European Union, oversee these audits and assessments.
How ISPs Prepare for and Undergo Regulatory Inspections
ISPs undertake several steps to prepare for and successfully undergo regulatory inspections:
- Documentation Gathering: ISPs compile comprehensive documentation showcasing their compliance efforts. This includes records of network performance, customer complaint resolution, privacy policies, and security measures.
- Cooperation with Regulators: ISPs maintain open lines of communication with regulatory agencies, ensuring a cooperative approach. They address regulators' inquiries promptly and transparently, fostering a positive regulatory relationship.
- Internal Audits: ISPs often conduct internal audits and assessments to identify and rectify compliance gaps before regulatory agencies initiate inspections.
Outcomes and Lessons Learned from Regulatory Audits
- Compliance Success Stories: ISPs that successfully pass regulatory audits demonstrate their commitment to legal and ethical standards.
- Areas for Improvement: Regulatory audits identify areas where ISPs can enhance compliance.
- Continual Improvement: ISPs use audit findings as a basis for continual improvement.
User Privacy Policies in Broadband Services
Role of User Privacy Policies in ISP Compliance
User privacy policies are pivotal components of ISP compliance efforts, addressing several essential items:
- Transparency: Privacy policies provide transparency by outlining how ISPs collect, use, and protect user data.
- Informed Consent: Privacy policies inform users about their rights and enable them to make informed decisions regarding data sharing and consent. Users can choose to opt in or out of specific data processing activities.
- Legal Requirement: In many jurisdictions, having a clear and accessible privacy policy is a legal requirement for ISPs.
- Accountability: Privacy policies hold ISPs accountable for their data handling practices.
The Bottom Line
Our exploration of ISP data privacy compliance rates has provided critical insights into the telecommunications industry's dynamic landscape of data protection. We've observed positive trends, with numerous ISPs demonstrating their commitment to safeguarding user data.
Yet some challenges remain. Complex regulatory environments, evolving standards, and the intricacies of user data rights remain persistent hurdles for ISPs.
Regardless of these challenges, though, consumers' trust in ISPs is on the line. We strongly encourage ISPs to proactively implement the recommended best practices and strategies outlined throughout our exploration. By doing so, they enhance their data privacy efforts and cultivate trust with customers and regulators alike.
FAQ
Why is unwavering dedication to user data protection crucial?
Unwavering dedication to user data protection is vital for building trust with both customers and regulators. Trust is a cornerstone for a secure digital future where user data is treated with care and respect.
How can ISPs stay updated on evolving regulations and standards?
ISPs can stay informed by regularly monitoring updates from regulatory agencies, participating in industry associations, and seeking out legal counsel or compliance experts to interpret and apply evolving regulations effectively.
What role do regulatory audits play in ISP compliance efforts?
Regulatory audits are conducted by authorities to evaluate ISPs' compliance with data protection laws and regulations. They help ensure that ISPs adhere to required standards and practices.
How often should ISPs update their user privacy policies?
ISPs should update their user privacy policies regularly, mainly when there are changes in data practices, regulatory requirements, or technological advancements. Users should be notified of policy updates.
How can ISPs handle data subject rights requests effectively?
ISPs should establish transparent and efficient processes for handling data subject rights requests. This includes verifying the requester's identity, responding promptly, and documenting their responses for compliance purposes.