Introduction: Why Your Internet Bill Keeps Rising
When you sign up for the internet, the sticker price is rarely the final cost. Hidden fees buried in the fine print can make your monthly bill much higher than expected. Common culprits include equipment rental fees, data overage charges, and early termination penalties.
Let's take a look at the hidden costs, analyze their financial impact, and explore the regulatory and market dynamics related to the cost of internet service.
Key Takeaways for Consumers
- Hidden fees significantly inflate internet costs.
- Price hikes are often tied to profit goals, limited competition, and consumer demand.
- Regulation plays a central but contested role in price fairness.
- Consumers can reduce costs by identifying hidden fees, comparing options, and choosing ISPs with transparent pricing.
The Evolution of ISP Pricing Models
Historical Context
In the early days of the consumer internet, providers tried several pricing models.
- Hourly Rates: Users paid for every hour they spent online, sort of like how early phone calls worked.
- Flat Monthly Fees: A set, fixed price paid each month for unlimited internet use, which became the standard.
- Tiered Plans: Users could choose a plan based on their needs and budget. The faster the speed, the higher the cost.
Case Example
In December 1996, America Online (AOL) shifted from an hourly billing model to a flat-rate plan of $19.95 per month for unlimited dial-up internet access. It dramatically increased their user base and helped popularize the internet, but it also caused severe service disruptions and a major public relations crisis.
For example, a standard plan with AOL was $9.95 per month for 5 hours, plus $2.95 for each additional hour. This pay-by-the-hour model discouraged users from staying online for long periods.
Early Promises of Affordability
The internet first arrived with the promise of being affordable and accessible to all. It was advertised as an educational tool and a way to communicate within everyone's financial reach.
In 2004, President Bush supported this vision, publicly advocating universal high-speed internet access by 2007, but failed to outline a strategy to achieve it. Ever since, providing fair access to information regardless of background has faced significant challenges.
Who Are the Most Popular Internet Service Providers in the U.S.?
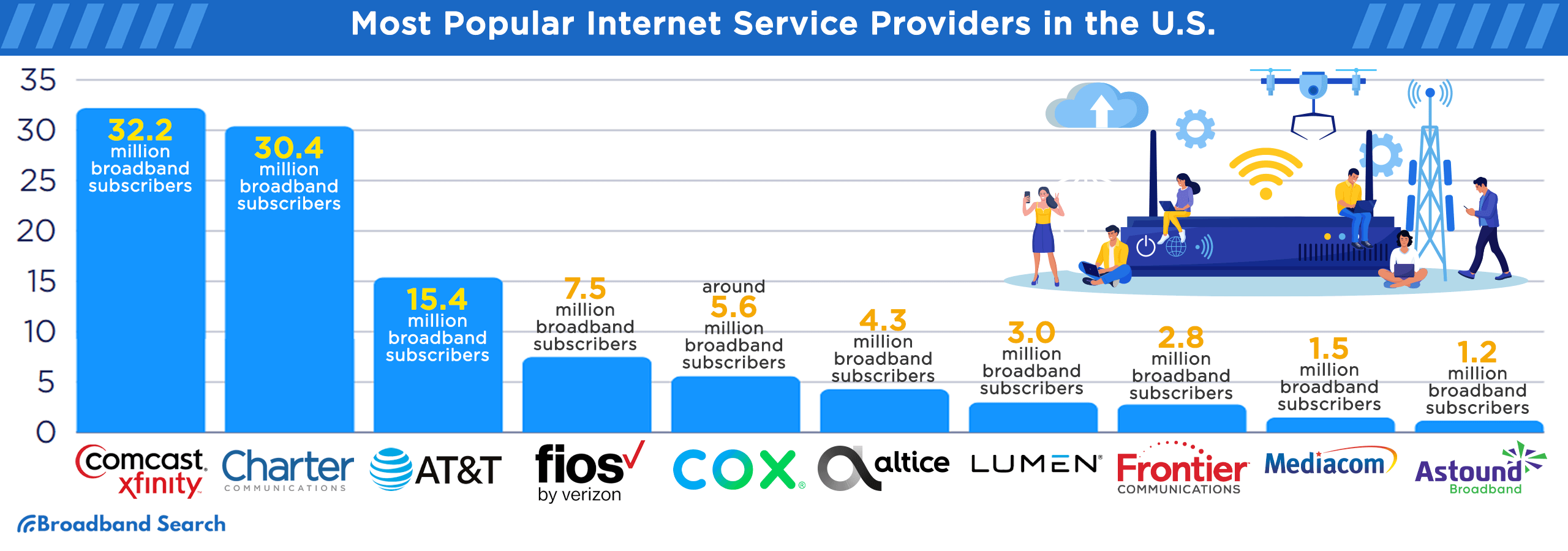
The following list ranks the 10 most popular ISPs in the U.S. based on their subscriber numbers:
- Comcast (Xfinity): With 32.2 million broadband subscribers, Comcast is a major cable and internet provider.
- Charter Communications (Spectrum): Charter serves 30.4 million broadband subscribers and offers cable and internet services.
- AT&T (AT&T Fiber): AT&T, known for its fiber optic broadband service, has 15.4 million broadband subscribers.
- Verizon (Verizon Fios): Verizon provides internet services under the Verizon Fios brand and serves 7.5 million wireline broadband subscribers.
- Cox Communications (Cox Internet): Cox has approximately 5.6 million broadband subscribers and offers cable and internet services.
- Altice USA (Optimum and Suddenlink): Altice USA, operating under the Optimum and Suddenlink brands, serves 4.3 million broadband subscribers.
- Lumen Technologies (Quantum Fiber and CenturyLink): Lumen Technologies has 3.0 million broadband subscribers and offers telecommunications and internet services.
- Frontier Communications (Frontier): With 2.8 million broadband subscribers, Frontier Communications provides telecommunications and internet services.
- Mediacom Communications (Xtream): Mediacom, offering services through the Xtream brand, serves approximately 1.5 million broadband subscribers.
- Astound Broadband: Astound Broadband boasts over 1.2 million broadband subscribers.
How Does Limited Competition Affect Internet Service Prices?
The lack of meaningful competition among major ISPs often leads to higher prices, fewer service options, and reduced incentives for providers to improve speeds or customer service.
- Higher monthly prices. Limited competition means higher prices. Without pressure from rivals, internet providers act as monopolies, inflating rates and unfairly burdening low-income families.
- Paying more for speed. A 2025 analysis found that the lack of meaningful competition for high-speed internet (100+ Mbps) is most pronounced, affecting over 96% of U.S. counties.
- Less incentive to innovate. Without competition, monopoly internet providers have no reason to improve service, leading to slower speeds and leaving many areas behind.
How Are Consumers Reacting to Lack of Provider Competition?
Consumers are increasingly unhappy with the costs of their internet service. The American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) gave the Internet Service Provider (ISP) industry a low score of 68, showing just how unhappy consumers are with internet bills.
Common consumer complaints about pricing include:
- High monthly bills: Many find their internet bills too high for the quality and speed they get.
- Hidden fees: Equipment rental charges and other surcharges add to customer frustration.
- Limited choice: In some areas, a lack of competition allows ISPs to charge higher prices
- Price hikes: Customers report frequent increases in their internet service costs.
- Promotional pricing: Customers feel misled by low introductory rates that later go up significantly.
Case Study: Rural vs. Urban Consumer Internet Costs
Rural consumers often pay more for slower, less reliable internet than people in cities. The reasons for this disparity include the higher costs of building internet infrastructure in sparsely populated areas, a lack of competition among providers, and the lower average incomes in many rural communities.
- Higher monthly fees: One study by BroadbandNow found that in late 2020, the average monthly cost for a basic broadband connection was nearly $13 higher in rural zip codes.
- Worse value: Another study from Senator Gene Yaw's office found that rural customers often receive a systematically inequitable service, paying more for slower internet speeds.
- Lack of services: Some rural areas have only one internet provider option, creating effective monopolies that leave consumers with no alternatives for competitive pricing or service quality. This lack of choice often forces rural consumers to pay higher rates for minimal service.
How Do I Identify Hidden Fees in My Internet Bill?
Uncovering the true cost of your internet service requires a careful review of your monthly statement. Identifying hidden administrative and equipment changes beyond the advertised base price can save you money in the long run.
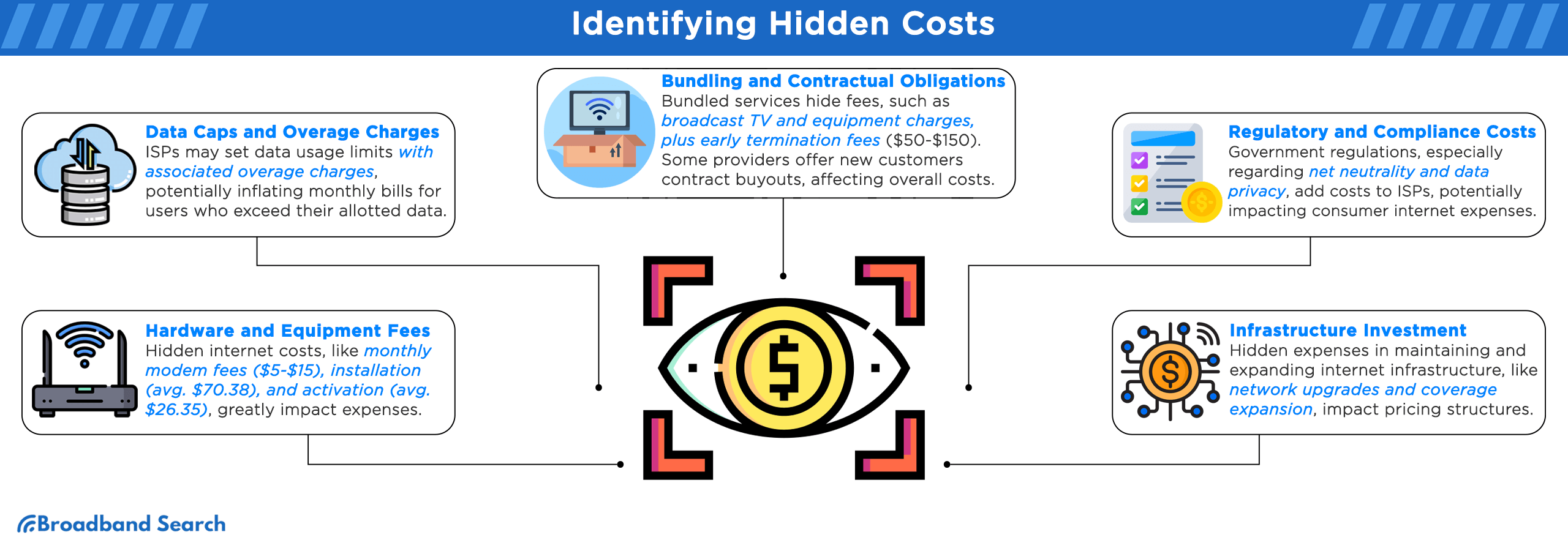
Equipment and Installation Charges
- Modem and Router Rental Fees: ISPs often charge $5 to $15 per month for modem and router rental.
- Installation Fees: On average, installation fees in the New America Org dataset are about $53.74, while activation fees are around $27.79.
- Activation Fees: Expect to pay initial setup fees averaging $50 to $70 for installation and $26 for activation in the U.S.
Case Study: Costs of Renting vs. Owning Internet Equipment
Choosing between renting and buying equipment (modem, router, or gateway) for over two years is a financial decision based on the frequency of use, household budget, and tax considerations.
Renting is typically more cost-effective for short-term or intermittent use because of lower upfront and maintenance costs. Buying is often better for more frequent and long-term use, plus there could be some tax benefits.
Data Caps and Overage Fees
- Data Usage Limits: Because activities like downloading games and streaming video consume huge amounts of data, heavy gamers and streamers are especially vulnerable to the additional fees and speed limits that ISPs impose when monthly data caps are exceeded.
- Financial Impact Analysis: Streaming video can easily cause a household to exceed its internet data cap, leading to over $240 in annual overage fees. These penalties often increase in tiers as more data is used.
When reviewing your internet bill to identify hidden costs, it is also crucial to verify the data cap terms in your plan. Many providers have a monthly data limit (often 1 TB or 1.2 TB), and if you exceed the limit, you will be hit with costly data overage charges, usually in $10 increments.
Bundling and Contract Penalties
- Hidden fees within bundled services: Bundled internet, cable TV, or phone services can hide extra costs. Some of the common hidden fees include broadcast TV, regional sports, equipment rentals, installation, and activation. Most of these fees might not be clear up front, but they can increase your monthly bill.
- Early termination fees. ISPs often charge a penalty for canceling your contract before the end date. Some of these fees can be high — typically between $50 and $150 — making it expensive to switch providers.
| Fee | Typical Range | When It Applies | How to Reduce/Eliminate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gateway (modem/router) rental | $5–$15/mo | Provider-supplied equipment | Buy compatible device; ask for rental waiver |
| Installation | $50–$70 one-time | New service or moves | Self-install kit; promo credits |
| Activation | $25–$30 one-time | New service | Ask to waive; bundle with install credit |
| Data overage | $10 per 50 GB | Exceeding cap (e.g., 1 TB) | Unlimited add-on; usage alerts; plan upsize |
| Early termination (ETF) | $50–$150 | Cancel before term end | Negotiate; move-out exception; contract buyout |
| Bundling Fees | $8–$25/mo | TV bundles | Internet-only plan; streaming alternatives |
Disclaimer: Not all of these fees will apply and vary by provider. Some fees are waived/included in monthly cost (i.e. unlimited data, activation costs, etc.)
Regulatory and Compliance Costs
Government regulations, such as net neutrality and data privacy laws, increase internet service providers' operating costs. The extra, and often less visible, compliance costs can lead to higher internet service prices, ultimately paid by consumers.
Infrastructure Investment Costs
ISP expenses include ongoing network upgrades to improve speed and reliability, as well as the cost of expanding coverage, especially in rural areas. The significant costs are often hidden from consumers and influence overall pricing and additional fees.
The balance between necessary investments and over-leveraging for a price hike is a strategic business decision that weighs growth against financial risk. Necessary investments, such as improving service and capacity, are a good reason for a price increase. Over-leveraging, on the other hand, is a gamble that risks long-term financial stability for short-term growth or shareholder returns.
Why Do ISPs Raise Prices? (Business Strategies Explained)
ISPs raise prices primarily due to the high cost of building and maintaining infrastructure, as well as limited competition that gives them market control. The end of introductory promotional rates and the desire to maximize profits also significantly contribute to these price increases.
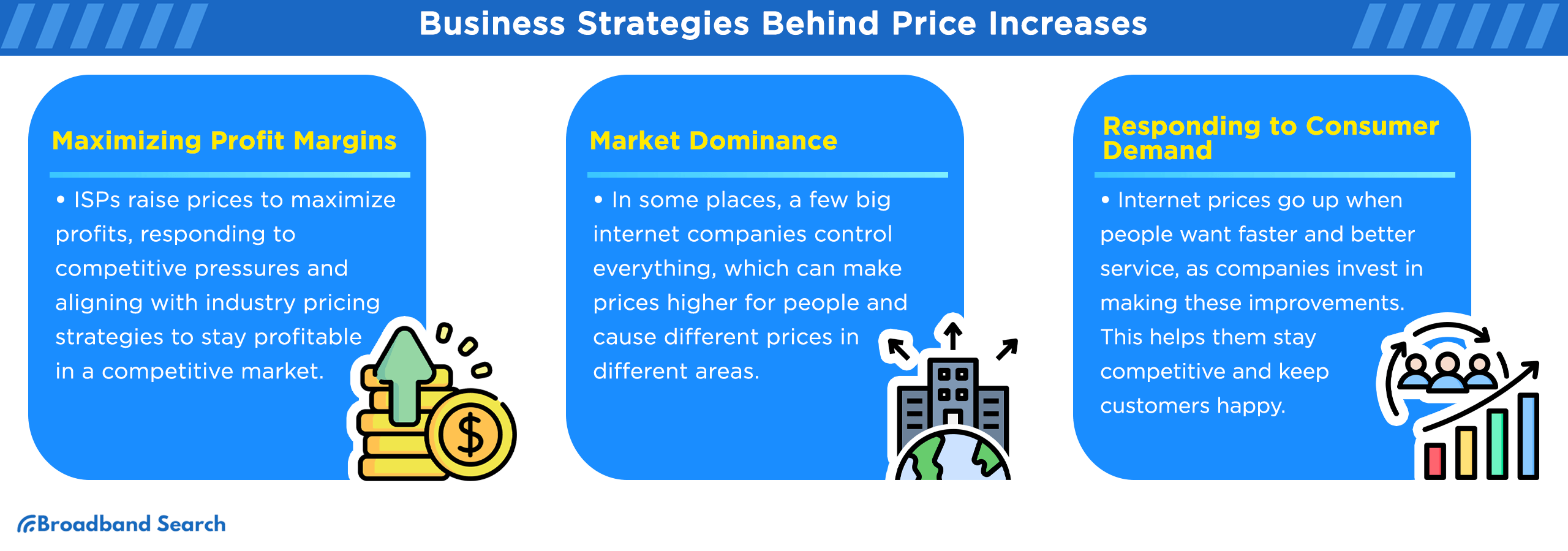
- Profit Maximization: ISPs' pricing strategies aim to increase profits and shareholder value. Internet providers also adjust prices to stay competitive, often following their rivals' pricing strategies, which can lead to higher costs for consumers.
- Market Dominance: The lack of competition allows dominant ISPs to control pricing, often resulting in higher costs for consumers with fewer alternatives. Areas with more ISP competition generally have lower prices and better service. It is particularly noticeable between urban and rural areas.
- Consumer Demand Shifts: Heavy bandwidth-intensive activities, such as streaming and gaming, drive demand for faster internet. To meet this need, ISPs upgrade their networks and technology, potentially leading to price adjustments. The investments allow ISPs to offer faster speeds and better services, helping them stay competitive and meet customer expectations.
Case Example: Streaming Video Demand on Internet Provider Services
The surge in video streaming, driven by Netflix and competitors, has significantly impacted broadband pricing, prompting increases across subscription tiers and broadband plans. Video streaming now accounts for the majority of internet traffic, forcing internet providers to invest more in infrastructure to manage increased bandwidth demand.
What Role Does the Government Have on Internet Pricing Regulation?
Government regulation significantly impacts how ISPs set prices by establishing rules intended to foster a competitive marketplace and protect consumers. Federal agencies work to balance the need for private investment in infrastructure with the goal of ensuring accessible and affordable internet service for everyone.
Key Regulatory Bodies (FCC and beyond)
Regulatory bodies, such as the FCC, oversee the telecommunications and internet industries. The government sets rules and standards for companies like ISPs, regulates pricing, ensures fair competition, and protects consumers. These agencies can enforce rules, impose fines, and make industry-wide decisions.
Deregulation and Its Consequences
Less government oversight, or deregulation, gives ISPs more control over their pricing strategies. The specific change is debated, with proponents arguing it encourages competition and lowers consumer costs.
Critics, on the other hand, worry it could result in less fairness, potential price hikes, and poor business practices as ISPs focus on profitability. As a result, the affordability of internet services for everyday users could be negatively impacted.
Net Neutrality and Consumer Pricing Implications
Net neutrality is the principle that ISPs must treat all internet traffic equally, without blocking or slowing down specific websites or services. Without it, ISPs could create "fast lanes" and "slow lanes," potentially making you pay more for access to certain content or services. This issue affects how much you pay for internet service and what you can do online.
How Do Hidden Fees Impact Consumers?
Hidden fees are a significant financial burden on consumers, often totaling hundreds or thousands of dollars annually.
- Household Budget Example: It is common for an advertised internet service plan of $70 to increase to a final bill of $95 due to taxes, government fees, equipment rentals, and surcharges. The extra charges are often not disclosed in initial advertising, leaving many consumers surprised by the final cost.
- Long-Term Impact: Hidden fees, expiring promotions, and annual price hikes can cause a $50/month internet plan to cost over $5,000 in five years, more than double the estimated $3,000.
- Income Inequality Angle: For low-income families, high internet costs are the main barrier to getting service. Studies confirm a significant income-based gap in home broadband access.
How Can I Avoid Internet Hidden Fees?
Avoiding hidden fees requires being proactive and carefully reviewing your service agreement for extra charges, such as equipment rentals or data penalties. By purchasing your own modem, monitoring data use, and negotiating with customer service, you can take control of your bill and avoid unnecessary expenses.
- Strategies: Consider buying your own equipment, negotiating with your current ISP, or switching to a new transparent provider if you find you're paying excessive hidden fees.
- Tools: Bill comparison calculators, FCC complaints, and consumer advocacy resources empower consumers to make informed decisions, challenge unfair practices, and seek resolution of issues with ISPs.
- Compare Internet Pricing: Independent comparison platforms like BroadbandSearch regularly highlight how hidden fees and unexpected price hikes can turn a seemingly affordable plan into a costly commitment, helping consumers make more informed decisions when choosing an internet provider.
FAQ
What are the most common hidden internet fees?
Common hidden internet fees include monthly equipment rental fees, installation costs, early cancellation penalties, and overage charges for exceeding your data limit.
Why do ISPs charge equipment rental fees?
ISPs charge equipment rental fees to generate additional revenue beyond the monthly service price and to cover the costs of equipment maintenance and replacement. It also helps them make their advertised monthly service costs appear lower and more competitive than they actually are.
Can I avoid early termination fees when switching providers?
You may be able to avoid early termination fees by using the 14-day cancellation period, finding a provider that offers a contract buyout, or switching to a no-contract service. Other options include negotiating with your current provider, especially if you have had service issues, or checking if a move allows you to cancel without a penalty.
How much do hidden fees increase internet bills on average?
Common hidden fees, such as equipment rental, installation costs, and penalties, can significantly increase your internet bill, often by $10 to $30 or more per month after a promotional period.
Which ISPs have the most transparent pricing?
Providers with transparent pricing, like Google Fiber, Verizon Fios, Frontier, and T-Mobile Home Internet, primarily offer fiber or 5G home internet. The internet provider services feature straightforward, no-contract plans with no hidden fees or data caps, and equipment costs are often included.
Why is the internet so expensive?
Internet service is expensive primarily due to a lack of competition in many regional markets and the high cost of building and maintaining physical network infrastructure.
Is unlimited data worth it?
Whether an unlimited data plan is worth it depends entirely on your household's internet usage and the price difference compared to capped plans.
Can I save money by bundling services?
Yes, bundling internet with other services like mobile phone service or cable TV can save you money, but it's not guaranteed and requires careful comparison. The potential for savings often depends on your specific usage needs and the provider's current promotions.
Why did my internet bill go up?
Your internet bill likely went up for one of two primary reasons: a promotional rate expired, or there was an annual price hike or new fees.