Struggling with slow internet speeds and constant buffering? You're not alone. Millions of households deal with unreliable connections that can't keep up with modern demands. But what if there was a solution that could transform your home internet experience entirely?
5G home internet is revolutionizing how we connect at home, offering wireless speeds that rival traditional fiber connections. As our digital lives become more demanding—from remote work to 4K streaming—understanding this technology becomes crucial for making informed connectivity decisions.
Let's explore what 5G home internet really offers, how it works, and whether it's the right choice for your household.
What Is 5G Home Internet?
5G home internet delivers high-speed wireless connectivity directly to your home using fifth-generation cellular technology. Unlike traditional broadband that requires physical cables, 5G internet connects your home through cellular towers, offering a wireless alternative that can match or exceed cable internet speeds.
This technology represents a fundamental shift from previous cellular generations:
GenerationAverage SpeedPeak SpeedKey Features4G32.5 Mbps100 MbpsMobile internet, video calling5G130-240 Mbps1-10 GbpsUltra-low latency, IoT support 5G isn't just faster 4G—it's an entirely new system using advanced architectures, algorithms, and antennas. This enables theoretical speeds up to 10 Gbps and becomes a key driver for smart home technology and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
How Does 5G Home Internet Work?
5G home internet transmits data from nearby cellular towers to a specialized gateway or router in your home. Here's the step-by-step process:
- Signal Transmission: 5G towers broadcast signals across different frequency bands
- Home Reception: A 5G gateway device receives these cellular signals
- Wi-Fi Conversion: The gateway converts cellular signals into Wi-Fi for your devices
- Device Connection: All your home devices connect through this wireless network
Understanding 5G Frequency Bands
5G operates across three main frequency bands, each offering different benefits:
Low-Band (Under 1 GHz)
- Extensive coverage area
- Speeds similar to 4G LTE
- Best for rural areas
Mid-Band (2.4-4.2 GHz)
- Balanced speed and coverage
- Ideal for suburban areas
- Most common for home internet
High-Band/mmWave (24-39 GHz)
- Fastest speeds up to 1 Gbps+
- Limited range
- Primarily in dense urban areas
What Are the Speeds for 5G Home Internet?
5G home internet offers significantly faster speeds than traditional broadband options:
- Average Download Speeds: 130-240 Mbps
- Peak Speeds: 1-10 Gbps (theoretical maximum)
- Typical Real-World Performance: 100-300 Mbps
These speeds vary based on several factors:
- Distance from cell towers
- Network congestion
- Weather conditions
- Type of 5G frequency band used
For comparison, the average US broadband speed is around 100 Mbps, making 5G home internet competitive with traditional options.
Top 5G Home Internet Providers
Verizon 5G Home Internet
Verizon offers two main plans using their Ultra Wideband network:
PlanPriceFeatures5G Home$35-$50/monthBasic high-speed service, no contracts5G Home Plus$45-$70/monthEnhanced speeds, premium features T-Mobile 5G Home Internet
T-Mobile provides nationwide coverage with competitive pricing:
- Price: $30-$50/month
- Coverage: All 50 states
- Best For: Rural and suburban areas
AT&T Internet Air
AT&T offers a straightforward option for smaller households:
- Price: $55/month flat rate
- Speeds: Up to 140 Mbps
- Best For: Small households with basic internet needs
Other Providers
Several regional providers also offer 5G home internet services:
- EarthLink: $35-$55/month with privacy focus
- Regional carriers: Pricing varies by location
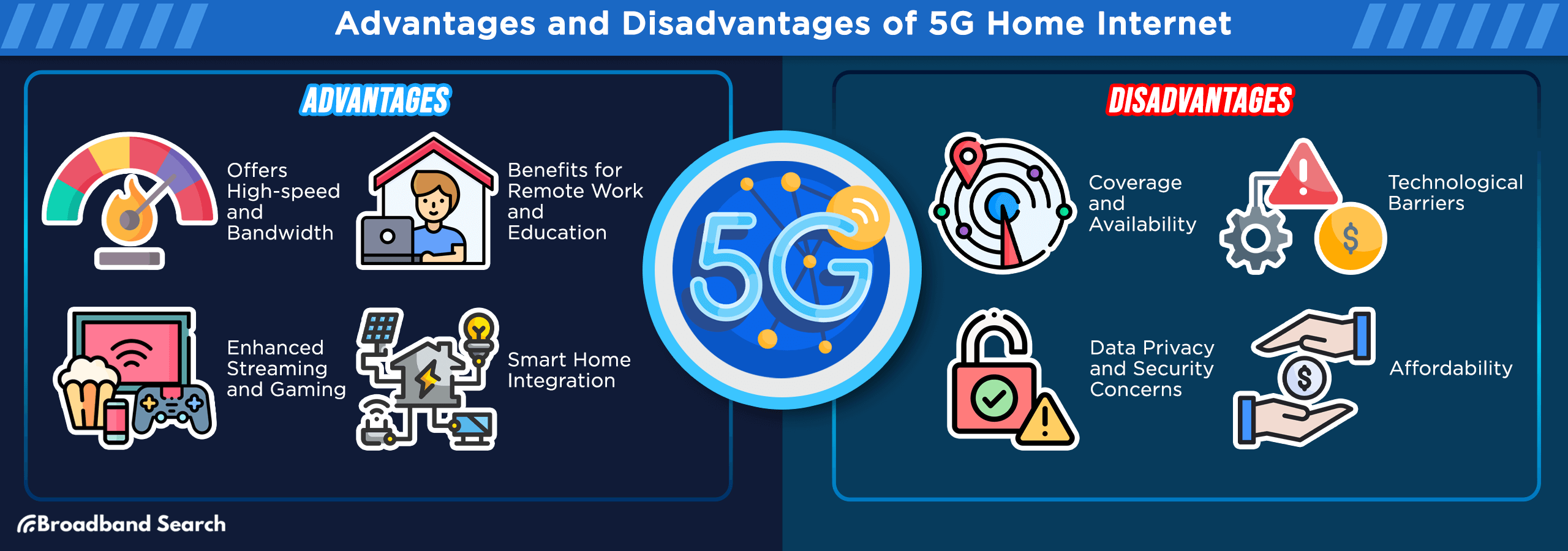
Advantages of 5G Home Internet
Speed and Performance Benefits
- High-speed connectivity: Supports multiple users streaming simultaneously
- Low latency: Reduces lag for gaming and video calls
- Consistent performance: Less susceptible to network congestion than traditional broadband
Installation and Setup Benefits
- No cables required: Eliminates need for professional installation
- Quick setup: Many providers offer plug-and-play installation
- Flexible placement: Gateway can be positioned for optimal signal reception
Coverage Benefits
- Rural accessibility: Reaches areas where traditional broadband isn't available
- Quick deployment: Faster infrastructure rollout than fiber networks
- Backup connectivity: Can serve as secondary internet option
Smart Home Integration
- Multiple device support: Handles numerous connected devices simultaneously
- IoT optimization: Designed for smart home ecosystems
- Future-ready: Supports emerging connected technologies
Challenges and Limitations of 5G Home Internet
Coverage Limitations
- Geographic restrictions: Primarily available in urban and suburban areas
- Rural gaps: Limited availability in remote locations
- Signal obstacles: Buildings and terrain can interfere with reception
Technical Considerations
- Weather sensitivity: Heavy rain or storms may affect signal quality
- Distance limitations: Performance decreases with distance from towers
- Network congestion: Speeds may slow during peak usage times
Cost Factors
- Equipment requirements: May need specialized gateway hardware
- Variable pricing: Costs can fluctuate based on location and demand
- Data considerations: Some plans may include data caps or throttling
Security Considerations
- Wireless vulnerability: Potentially more susceptible to security risks than wired connections
- Privacy concerns: Cellular networks may have different privacy protections
- Network sharing: Connection shared with other cellular users in the area
How 5G Compares to Other Internet Options
Internet TypeAverage SpeedInstallationCoverageMonthly Cost5G Home130-240 MbpsSelf-installUrban/Suburban$30-$70Fiber100-1000+ MbpsProfessionalLimited$50-$100Cable25-300 MbpsProfessionalWidespread$40-$80DSL1-25 MbpsProfessionalWide$30-$60Satellite12-100 MbpsProfessionalNationwide$60-$150 5G vs. Fiber Internet
While fiber offers the most consistent high speeds, 5G provides faster deployment and installation flexibility. Fiber internet requires physical infrastructure that can take months to install, while 5G can be set up immediately where towers exist.
5G vs. Cable Internet
5G eliminates the need for physical cable connections and can offer comparable speeds in strong coverage areas. However, cable internet typically provides more consistent speeds regardless of weather conditions.
Is 5G Home Internet Right for You?
Consider 5G home internet if you:
- Live in an area with good 5G coverage
- Want quick installation without technician visits
- Need reliable speeds for remote work or streaming
- Have limited traditional broadband options
- Want a backup internet connection
5G may not be ideal if you:
- Live in a rural area without 5G towers
- Require guaranteed consistent speeds
- Have access to high-quality fiber internet
- Need unlimited data without any restrictions
The Future of 5G Home Internet
5G home internet adoption is accelerating, with industry experts predicting significant growth in the coming years. Key developments include:
Network Expansion
- Rural coverage: Continued tower deployment in underserved areas
- Infrastructure investment: Billions in 5G network improvements
- Technology advancement: Enhanced equipment and signal processing
Smart Home Integration
- IoT optimization: Better support for connected devices
- Edge computing: Reduced latency for smart home applications
- AI integration: Intelligent network management for optimal performance
Competitive Landscape
- Price competition: Increased competition driving down costs
- Service improvements: Enhanced customer service and support options
- Technology convergence: Integration with other connectivity solutions
Making Your Decision
Choosing the right internet service requires careful consideration of your specific needs. Use our internet speed test to check your current speeds and compare providers in your area to find the best options available.
When evaluating 5G home internet, consider:
- Coverage availability in your specific location
- Your household's speed requirements
- Installation preferences and timeline needs
- Budget constraints and contract terms
- Backup connectivity requirements
Key Takeaways
- 5G home internet offers competitive speeds (130-240 Mbps average) with wireless convenience
- Installation is typically faster and easier than traditional broadband options
- Coverage is currently limited primarily to urban and suburban areas
- Costs range from $30-$70 monthly, competitive with traditional broadband
- Technology is rapidly evolving with improved coverage and capabilities
FAQ
What kind of speeds can I expect with 5G home internet?
Speeds typically range from 100-300 Mbps, with some plans reaching up to 1,000 Mbps. Actual speeds depend on your location, network congestion, and proximity to cell towers.
Do I need special equipment for 5G home internet?
Yes, you'll need a 5G gateway or router provided by your internet service provider. This specialized equipment connects to 5G cellular networks and creates Wi-Fi for your home devices.
How do I check if 5G home internet is available in my area?
Can 5G home internet replace traditional broadband?
In many cases, yes. 5G home internet offers comparable speeds and reliability to traditional broadband, especially in areas with strong 5G coverage. However, performance can vary based on local network conditions.
Is 5G home internet good for gaming?
5G home internet can be excellent for gaming due to its low latency (often under 20ms) and high speeds. However, performance may vary based on network conditions and distance from cell towers.
Ready to explore your internet options? Use our provider comparison tool to find the best internet services available in your area, including 5G home internet options.