The digital age in the U.S. has been profoundly influenced by the evolution of the Internet Service Providers (ISPs) industry. From the nascent days of dial-up connections to the sophisticated networks of today, the ISP landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation, supported largely by the industry's competitive spirit. This competition has not only spurred ISPs to innovate but also ensured that consumers receive enhanced internet services at competitive rates.
Leveraging wired technology, these ISPs provide internet access and other services like web hosting. The rise in internet use, combined with government support for broadband expansion, has led to more people getting online, especially in rural areas and businesses. The industry's earnings have climbed and predicted to reach $567.3 billion by the end of 2025. This growth got an extra push during the COVID-19 pandemic when everyone needed reliable internet. Furthermore, newer, better networks have helped companies save on costs and increase their profits.
Historical Overview
In the contemporary era, it's hard to envision life without an internet connection. However, there was a time when this vital utility was a rarity. The beginnings of the internet were characterized by the distinctive "handshake" used for connecting computers.
The Handshake Era: Before the advent of ISPs, the primary mode of computer connectivity was through phone lines. Computers would "call" each other, establishing a connection in what was termed as a "handshake." These early computers used cassette tapes and distinctive sounds to instruct the computer during this process, making the connection audible to users.
Public Access Points: The Internet's Exclusive Domain: Before the widespread reach of ISPs, the internet was confined to public access points located in specific institutions like universities and government establishments. This scenario meant that internet access was exclusive, with many barriers regarding who could access it and when.
Commercial ISPs Enter the Scene: The government initially had restrictions against commercial ISPs. However, in 1985, this changed with the introduction of the first commercial ISP, "The World." Despite its dial-up nature, its popularity surged, leading to the National Science Foundation lifting the ban on commercial ISPs in 1991.
DSL: The Dawn of Broadband: The onset of the Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) marked a significant shift from the slower dial-up connections. Using phone lines, DSL provides faster internet speeds, particularly benefiting those closer to urban centers.
The Rise of Cable Broadband: 1996 witnessed the introduction of cable broadband, utilizing the cable TV infrastructure to offer even faster data transmission than DSL. This form of connection was especially beneficial for densely populated areas.
Fiber Optics: Speed of Light: ISPs soon transitioned to fiber-optic lines, ushering in an era of unprecedented internet speeds. These flexible glass strands allowed data transfer at the speed of light, revolutionizing internet connectivity.
Satellite Internet: Bridging the Rural Gap: Despite these advancements, rural areas were often left behind due to the high costs associated with infrastructure development. Satellite internet emerged as a solution, using signals transmitted from space to home antennas. This technology enabled rural consumers, especially those with a clear view of the southern sky, to experience faster internet speeds.
Evolution of Competition and Market Dynamics: Over the years, competition among ISPs intensified, leading to continuous innovations and service improvements. Market leaders emerged, and the landscape continually evolved, shaping the way consumers experience the internet today.
This historical journey of ISPs in the U.S. underscores the rapid technological advancements and the industry's commitment to making the internet accessible to all.
Current State of the ISP Market
Today, the Internet Service Providers (ISPs) market stands as a testament to the dynamic interplay of technological advancements and consumer demands. While the industry has seen remarkable innovations and expansion over the years, it has not been without its challenges. Notably, industry revenue has grown with an estimated value of $500.30 billion in 2024.
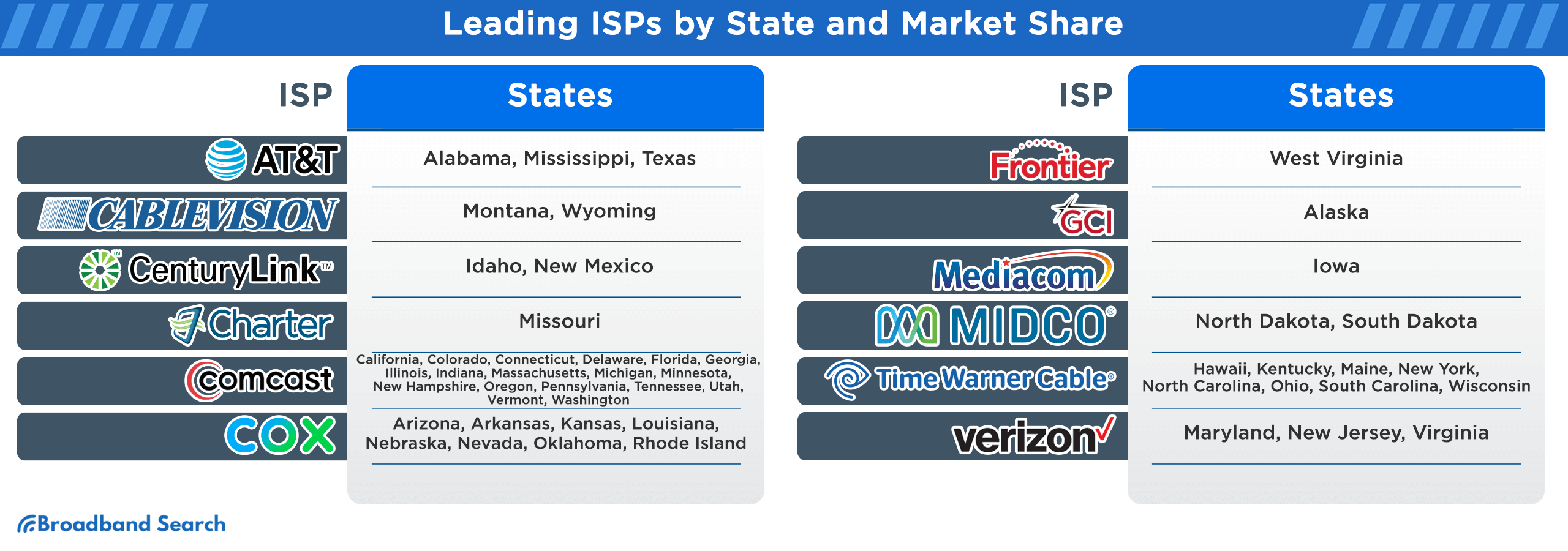
Leading ISPs by State Based on Market Share
Across all 50 states, these 12 companies stand out as the frontrunners in the ISP landscape. Their dominance is a testament to their service quality, infrastructure, and strategic presence. While some have a broad national footprint, others have carved niches in specific regions, reflecting the diverse and competitive nature of the ISP market in the U.S.
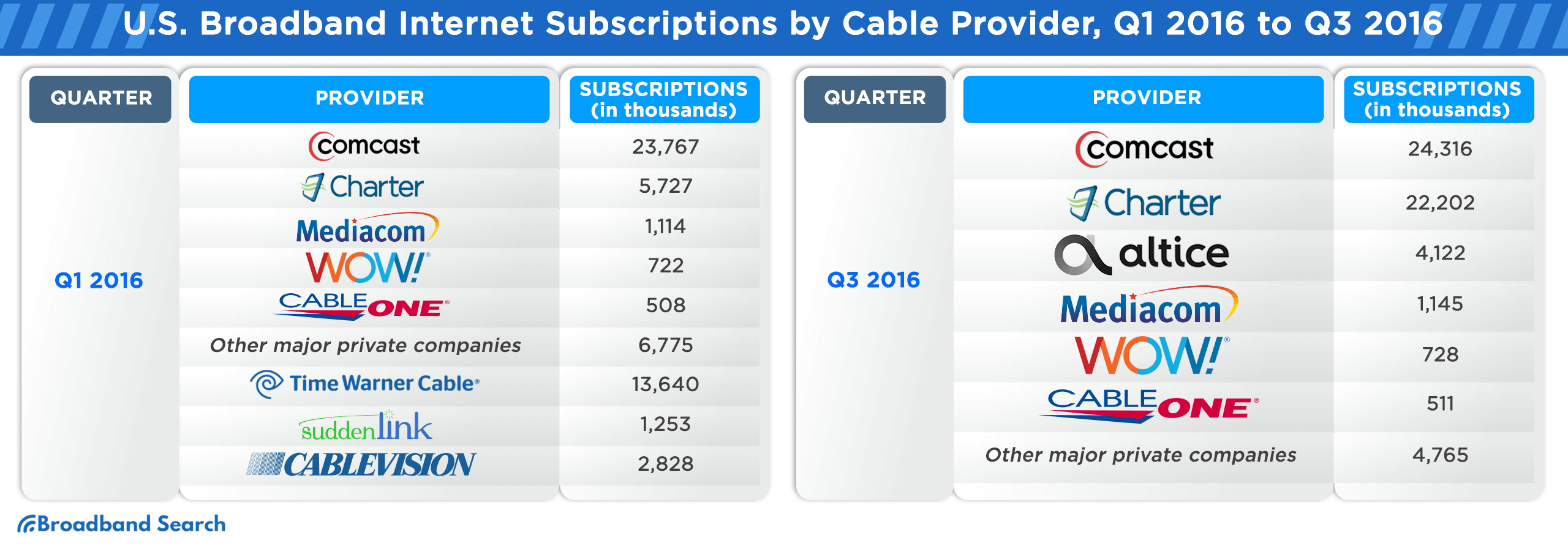
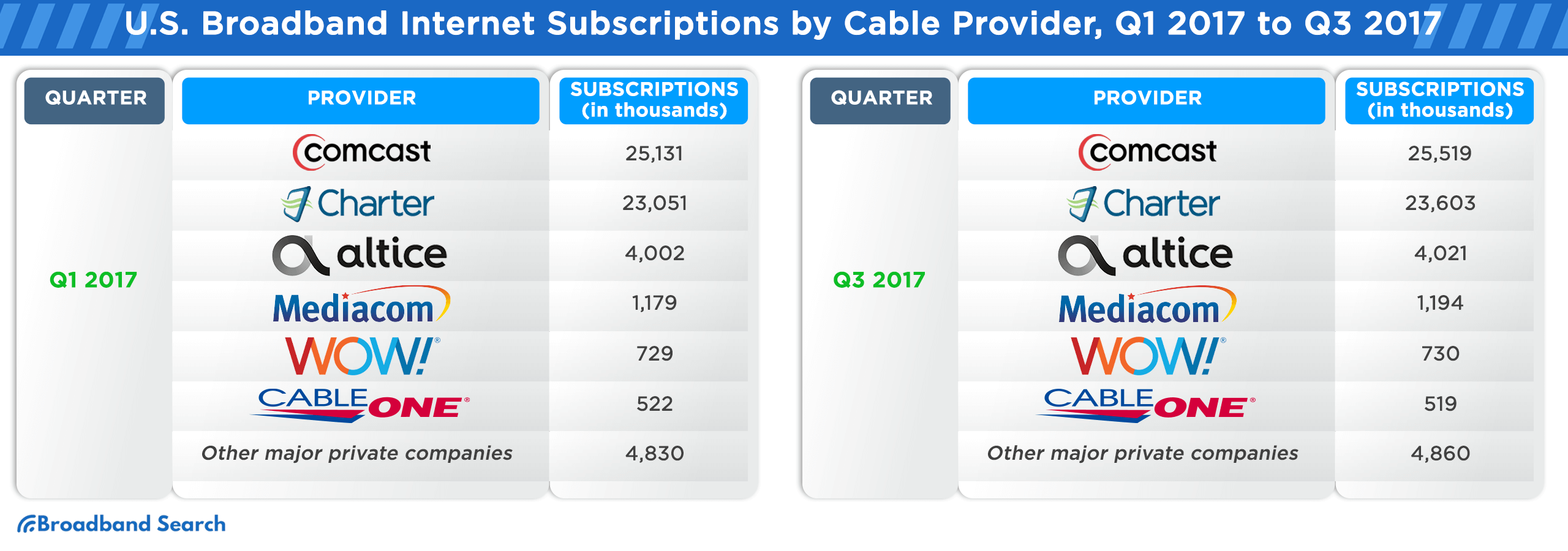
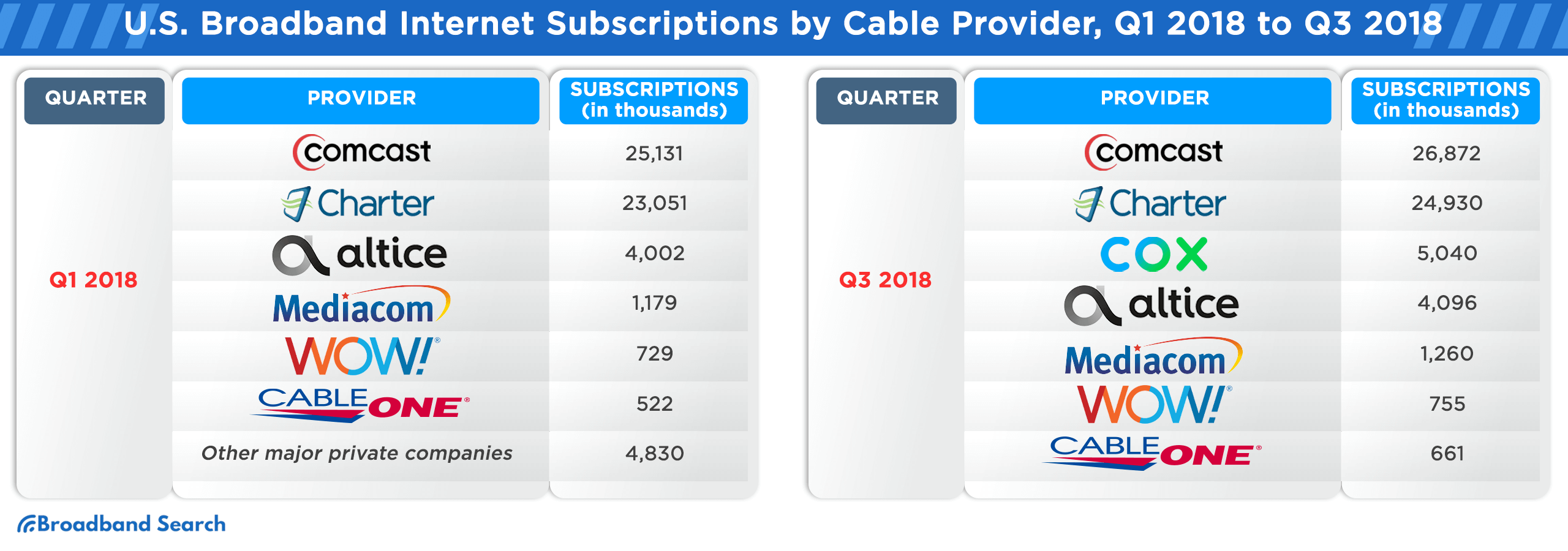
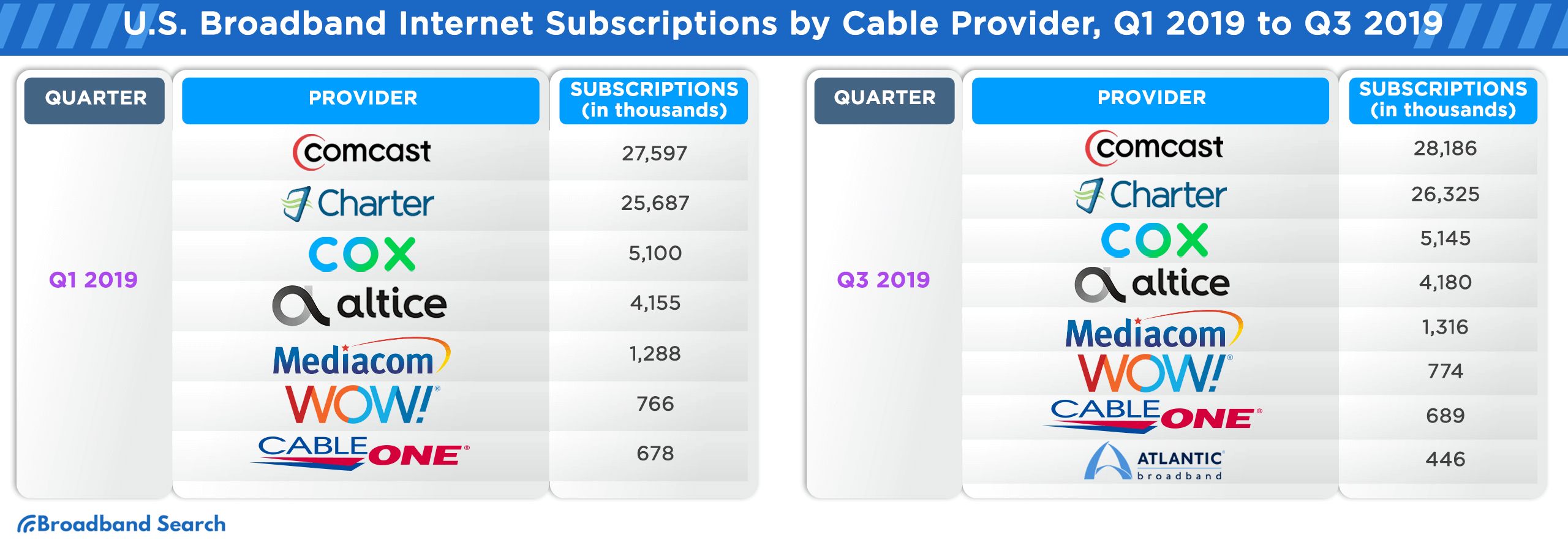
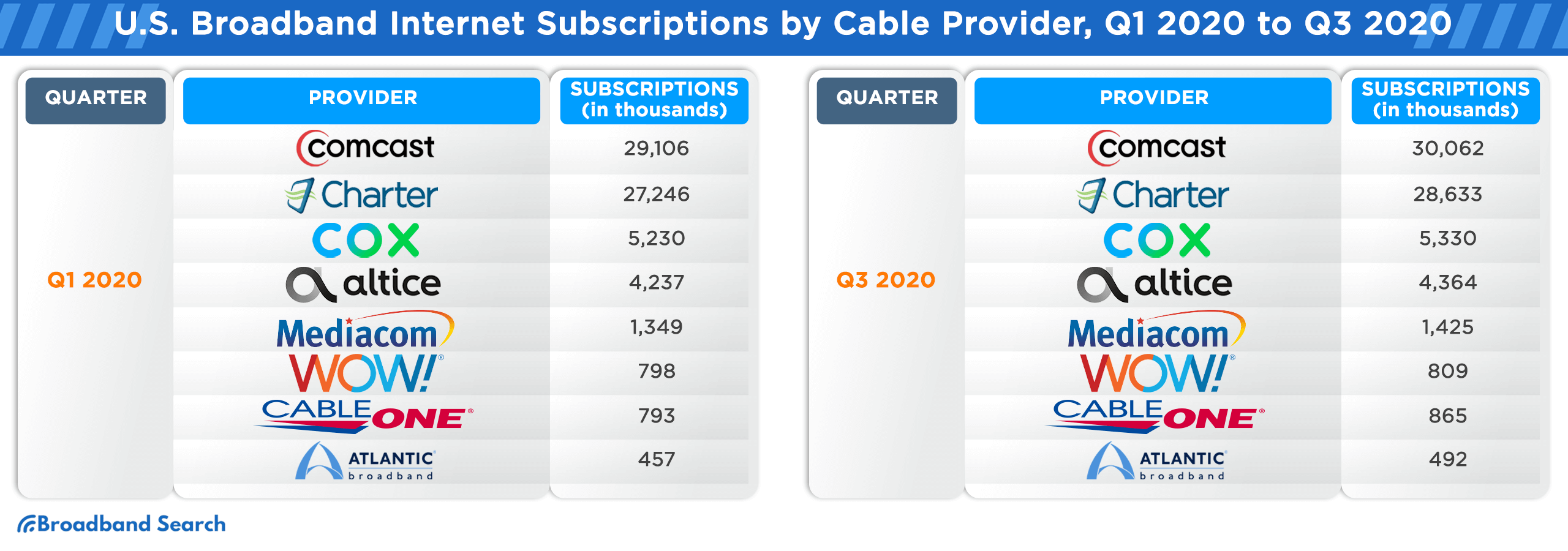
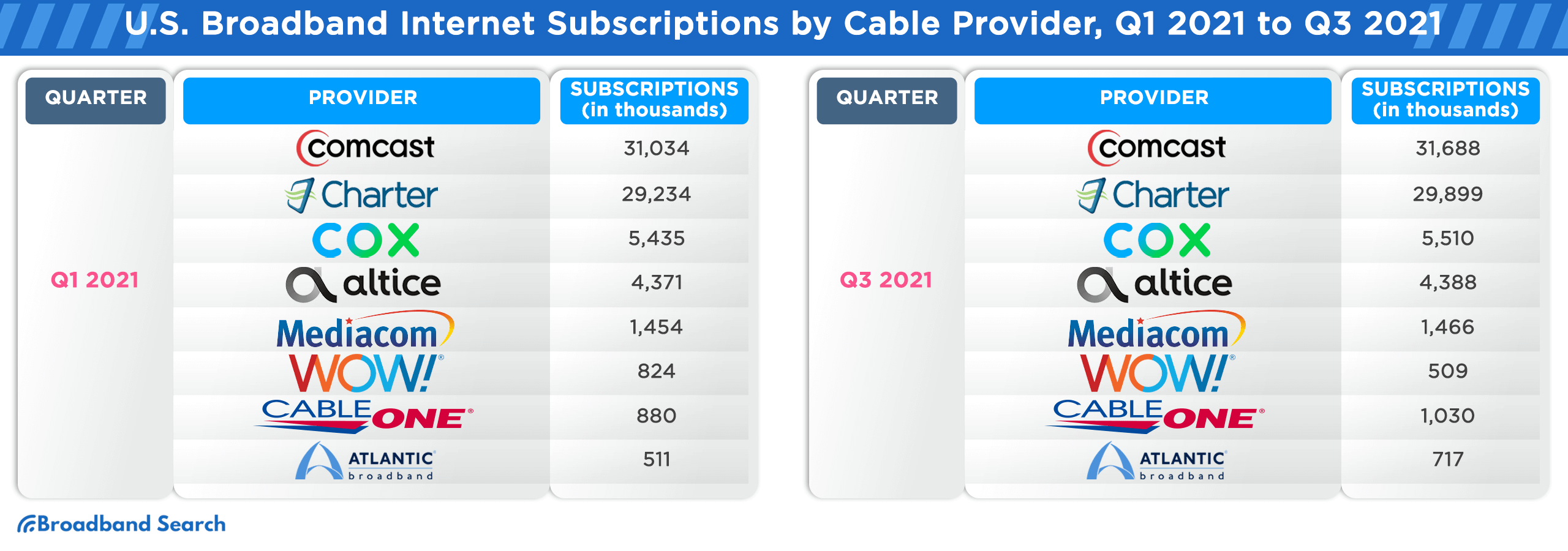
Broadband Internet Subscription Counts in the U.S. from Q1 2016 to Q3 2021, Sorted by Cable Provider
The U.S. broadband landscape has witnessed significant shifts from Q1 2016 to Q3 2021. As technology evolved and consumer demands grew, cable providers vied for market dominance, adapting to trends and expanding their services. The following table provides a comprehensive breakdown of subscription counts for major cable providers during this period, offering insights into their market trajectories and the changing preferences of U.S. consumers.
Top Internet Service Providers/Brands Utilized in the U.S.
In a recent survey querying U.S. consumers about their most utilized internet service providers, "AT&T" was revealed as the leading choice, while "Kinetic by Windstream" was found at the opposite end of the spectrum. These insights were derived from an extensive online survey conducted in 2023 with 5,620 participants from the U.S. Moreover, Statista Consumer Insights provides exclusive market research data from over 50 countries and territories around the world.
- A&T - 22%
- Spectrum - 20%
- Xfinity - 19%
- Verizon - 6%
- Cox - 5%
- T-Mobile - 5%
- CenturyLink - 4%
- Fios - 2%
- Frontier - 2%
- Optimum - 2%
- Cable One - 1%
- Dish - 1%
- Kinetic by Windstream - 1%
- Other - 9%
- Don't know - 1%
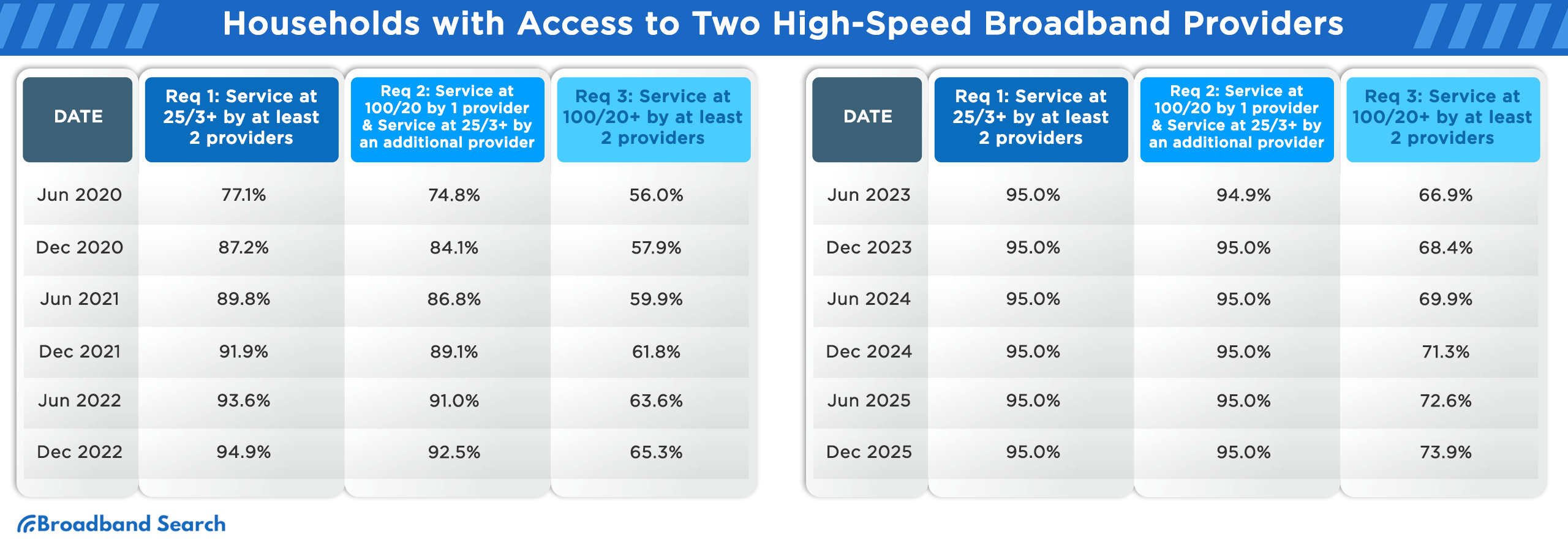
Percentage of Households with Access to a Minimum of Two Broadband Providers Meeting Specific Speed Criteria
Broadband internet access has increasingly become a crucial utility for households worldwide. As technology progresses and user needs evolve, speed and reliability are at the forefront of consumer demands. As of December 2023, about 66% of U.S. households had access to at least two broadband providers delivering speeds of 100/20 Mbps. Only about ~7% had access to two providers offering speeds of 940/500 Mbps.
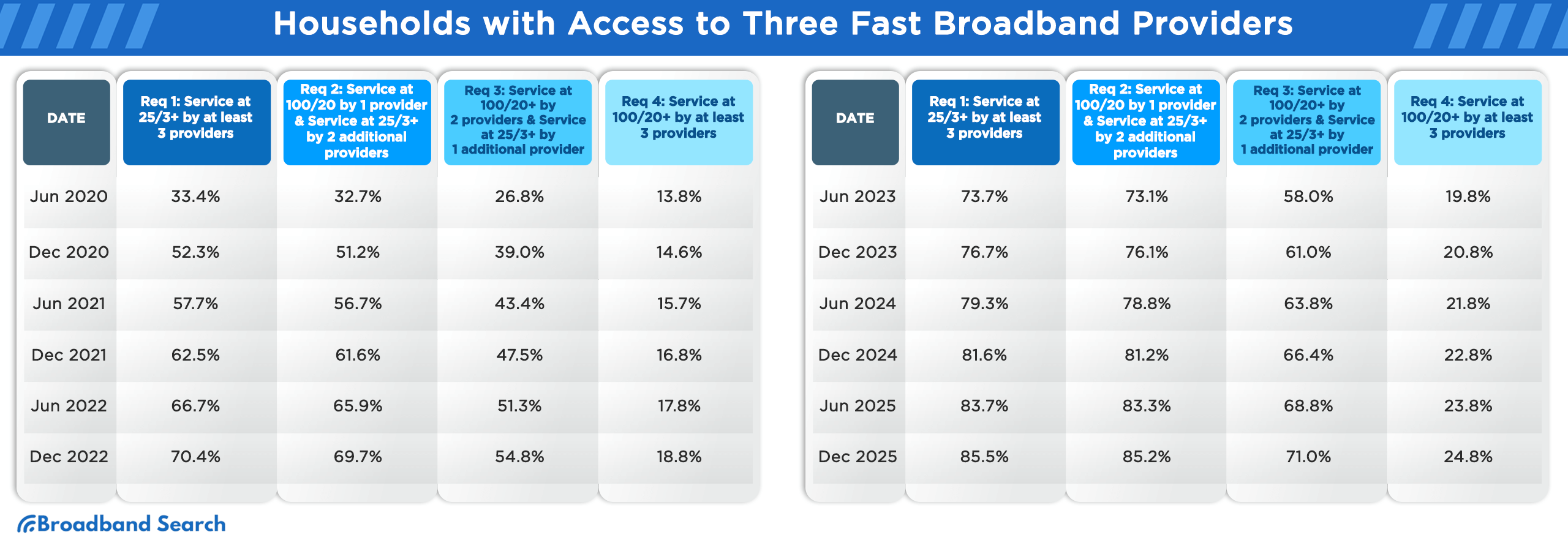
Percentage of Households with Access to at Least Three Broadband Providers Fulfilling Certain Speed Requirements
The competitive landscape of broadband providers is evident in the choices available to consumers. The richness in options not only offers users more freedom but also pushes providers to enhance their offerings continually. Delve into the data below to understand the accessibility percentages of U.S. households to at least three broadband providers, each catering to various speed requirements, spanning from June 2020 to December 2024.
The Role of Competition in the Industry
Competition is not always a straightforward concept, especially in an industry as dynamic as Internet Service Providers. While it drives innovation and pushes companies to elevate their standards, it can also create challenges that shape the contours of the market. In the U.S., where the digital landscape is ever-evolving, the role of competition becomes even more pronounced, influencing service quality, pricing, branding, and promotional strategies.
Factors Influencing Competition in Internet Provider in US
In the competitive landscape of U.S. Internet Service Providers, several key factors play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics. These elements not only drive the strategies of providers but also directly correlate with enhanced customer satisfaction.
Service Quality: The backbone of any ISP, service quality determines connection reliability, speed, and overall customer experience. Providers strive for excellence in this arena to retain and attract consumers.
Price: In a budget-conscious market, competitive pricing can significantly sway decisions. Providers constantly balance between offering value and maintaining profitability.
Brand Image: Beyond just services, the perception and reputation of a brand play a pivotal role. A positive brand image can set providers apart, ensuring customer loyalty and trust.
Promotion: Strategic marketing campaigns and customer-centric offers can be game-changers. Effective promotions not only attract new users but also ensure the retention of existing ones, cementing a provider's position in the market.
Benefits of Increased Competition
Improved Service Quality and Speed: With multiple providers vying for market dominance, there is an inherent push to offer better, faster, and more reliable internet connectivity. This ensures consumers enjoy top-notch service quality and faster internet speeds.
Innovation in Service Offerings and Packages: A saturated market fosters innovation. Providers are constantly brainstorming to introduce unique packages and services that cater to the diverse and evolving needs of the consumer base.
Lower Prices for Consumers: Intense competition often results in providers slashing their prices or offering value-added services at the same price point. This ensures that consumers get more value for their money.
Challenges and Barriers to Entry
Infrastructure Investment Requirements: Building a robust and extensive network infrastructure requires significant capital. This can be a major deterrent for new entrants lacking the necessary financial backing.
Regulatory Hurdles for New Entrants: The ISP market is heavily regulated. Navigating these regulatory waters can be complex and time-consuming, often acting as a barrier for newcomers.
Established Brand Loyalty and Consumer Trust: Penetrating a market where established brands have already built significant trust and loyalty can be daunting. New entrants need more than just quality service; they need strategies to build trust and win over consumers from established brands.
The Role of 5G and Future Trends
The dawn of 5G technology marks a significant leap in the world of communication. As we transition from the constraints of earlier networks to the expansive potential of 5G, the implications for the ISP market and the broader technological landscape are profound.
Introduction to 5G Technology: The Fifth Generation Communication System, popularly known as 5G, is more than just an upgrade from its predecessor. It embodies a transformative change in how data - be it voice, text, or hybrid - is transmitted and received. Leveraging advanced communication protocols and sophisticated technologies, 5G not only promises faster speeds but also seamless integration capabilities with other cutting-edge technologies.
How 5G May Reshape the ISP Market: With unparalleled speeds and lower latency, 5G has the potential to redefine user expectations. ISPs will need to adapt, enhancing their infrastructures and service offerings. The advent of 5G also paves the way for more immersive experiences, from augmented reality to real-time online gaming, reshaping the demands on ISPs.
The Potential for New Entrants and Increased Competition: The 5G revolution also presents an opportunity for new players to enter the ISP market. With its promise of high-speed connectivity even in remote areas, and the ability to support a vast number of connected devices simultaneously, 5G can level the playing field. This could lead to increased competition as new entrants vie for a slice of the market, challenging established players and potentially leading to more innovative offerings and better service for consumers.
The Future of Internet Provider Competition
Internet service providers serve as the backbone of our increasingly digital world. As daily tasks, professional responsibilities, and leisure activities continue to migrate online, the importance of reliable internet connectivity has never been clearer. Our modern lifestyle, characterized by streaming services, online shopping, virtual meetings, and digital collaborations, demonstrates how deeply the internet is woven into our routines. This growing dependence on technology not only elevates the role of ISPs but also influences consumer choices, pushing them to prioritize speed, reliability, and overall service quality.
Looking ahead, the ISP landscape is poised for significant evolution. As technologies like 5G become more mainstream and the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, demands on ISPs will only intensify. New market entrants, spurred by technological advancements, might challenge the status quo, leading to heightened competition and innovation. The future of ISPs is likely to be marked by rapid change, with providers continuously adapting to meet the ever-evolving needs of a technology-driven society.
FAQ
How do data caps and overage fees factor into the ISP competition scenario?
Data caps and overage fees have been contentious points in the ISP industry. Providers with strict caps or high overage fees might find themselves at a competitive disadvantage, especially if rivals offer unlimited plans or more generous data allowances. As consumers become more data-hungry, ISPs that offer flexibility in this regard often have a competitive edge.
How does the rollout of 5G impact the competition among ISPs?
The 5G rollout intensifies competition among ISPs. With its promise of lightning-fast speeds and lower latency, 5G sets a new benchmark for connectivity. ISPs need to adapt and enhance their infrastructure to leverage 5G fully. Moreover, 5G opens up opportunities for new market entrants, potentially shaking up the current ISP hierarchy.
How do rural areas compare with urban areas in terms of ISP competition?
Typically, urban areas enjoy more intense ISP competition due to higher population densities and existing infrastructure. Rural areas, on the other hand, often have fewer options due to the high costs associated with extending infrastructure to less populated regions. However, technologies like satellite internet and the push for broadband expansion are slowly bridging this gap.
Does more competition always mean better service for consumers?
More competition usually drives ISPs to elevate their service standards, innovate, and offer competitive pricing. However, it's not a strict rule. In areas with many ISPs but limited infrastructure, service might suffer. It's essential to consider the balance between competition and the actual service quality delivered.
Are there any new technologies or trends impacting ISP competition?
Beyond 5G, technologies like edge computing, the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), and advances in satellite internet are impacting ISP competition. These technologies demand more from ISPs, pushing them to innovate and adapt. Additionally, consumer trends like remote work and online gaming also influence ISPs' service offerings and competitive strategies.