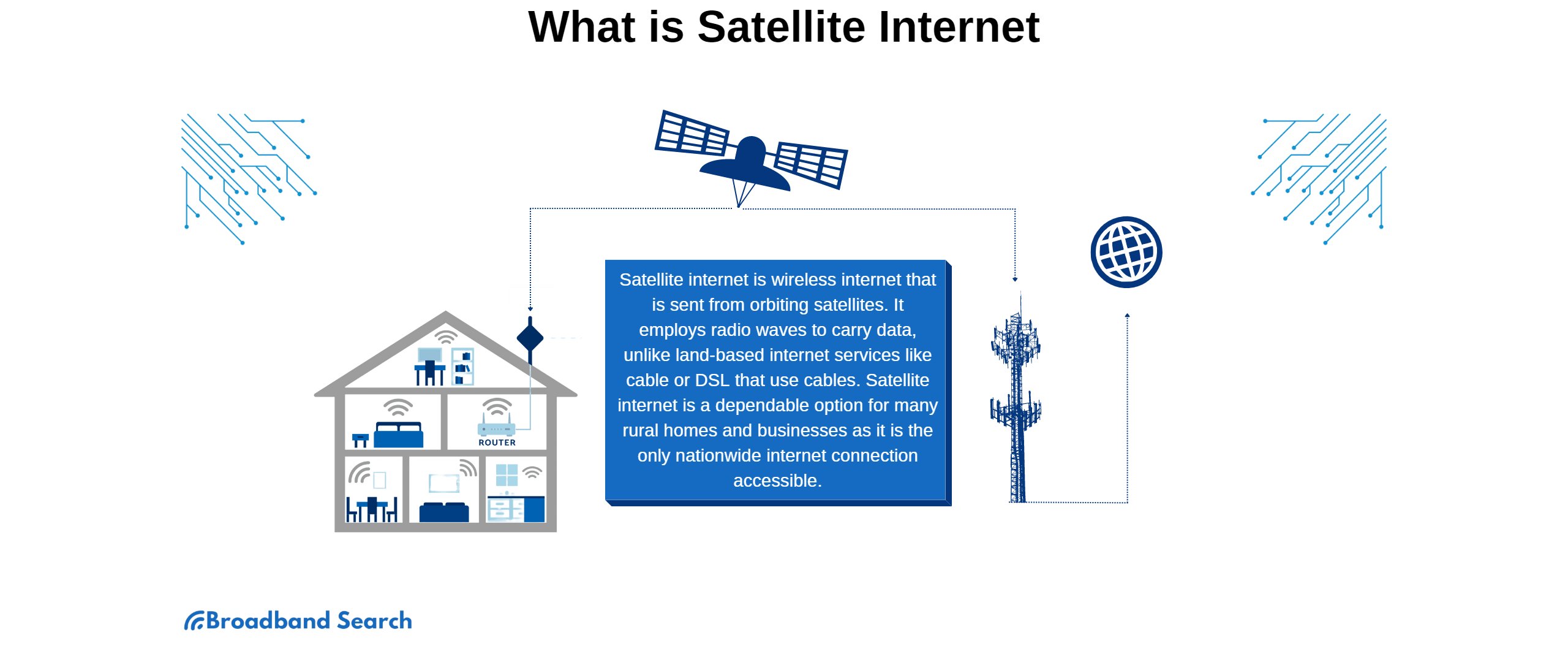
Satellite internet provides a fast-enough alternative to land-based internet service, but the provider and satellite type you use will greatly impact the speed of your connection. When choosing your provider, you'll need to consider the differences between LEO (low earth orbit) and GEO (geostationary earth orbit) satellites, download speeds, data policies, and available plans.
These factors are often address-specific, with block-by-block differences in some areas, so you'll need to compare exactly what's available at your specific address.
Analyzing all the factors that contribute to satellite internet speed can be confusing. Let's break them down to make understanding your options easier as you search for a plan.
Key Takeaways About Satellite Internet Speed and Data
Satellite internet can be fast enough for everyday use, with real-world downloads ranging from 25–200 Mbps depending on the provider and satellite type (LEO vs GEO).
Satellite internet speeds often lag land-based speeds and may not even meet current FCC minimums of 100 Mbps download and 20 Mbps upload. Analysis from Ookla shows that 17.4% of Starlink users tested at or above 100/20.
Data policies also vary. Most plans have a high-speed data limit, then offer “unlimited” standard internet after a customer reaches that cap, at which point speeds will be throttled.
Latency is another factor that impacts responsiveness. The delay between the signal leaving the satellite and reaching your device affects real-time activities, like online gaming or video calls.
Two types of satellite internet: GEO and LEO. GEO (Geosynchronous Equatorial Orbit) satellites orbit at a much higher altitude and therefore have a higher latency (500 ms or more) and a max download speed of 150 Mbps. LEO (Low Earth Orbit) satellites orbit at lower altitudes and offer lower latency (20-50 ms) and faster speeds (up to 200 Mbps).
Always check your exact address: availability, speeds, latency, and promos vary by location; use BroadBandSearch to see what’s available in your area.
How Fast Is Satellite Internet?
The fastest satellite internet download speed is 200 Mbps, but speed and performance depend on the type of satellite. There are two types of satellites used for the internet, GEO and LEO. While they both deliver internet service, their differences affect performance and capabilities.
GEO vs LEO Satellite Internet
GEO (Geostationary Equatorial Orbit) satellites orbit around 22,000 miles above Earth. The distance between your house, the satellite, and the provider’s hub makes for slower speeds and higher latency. One positive of GEO satellite internet is that it’s typically less expensive for a monthly plan.
LEO (Low Earth Orbit) satellites orbiting 200-300 miles above Earth. The closer orbit decreases latency and increases speed. But better performance comes at a higher monthly cost.
Realistic Satellite Speeds
Realistic satellite download speeds are between 25 and 200 Mbps, but that’s a huge range that affects your user experience and the provider you choose to meet your internet needs. Here are the three residential satellite internet providers available as of December 2025 and their performance numbers:
- Starlink (LEO): Capable of download speeds up to 200 Mbps and about 15 Mbps upload speed. Latency averages between 20-50 ms, but performance varies by address and time of day.
- Viasat (GEO): Offers download speeds up to 150 Mbps and 4-5 Mbps upload, depending on area and plan. The Essentials plan features 150 GB of high-speed data and unlimited standard data, while the Unleashed plan has unlimited high-speed data.
- HughesNet (GEO & hybrid): Residential tiers feature download speeds up to 100 Mbps; the HughesNet Fusion plan blends satellite and wireless to reduce perceived latency vs satellite-only (availability varies).
Satellite Internet and Latency
Latency is a measurement of how long it takes for data to travel from your device to the internet provider’s hub and back again in milliseconds (ms). It is also referred to as ping, lag, or delay.
LEO has an average latency of 20-50 ms, while GEO is much higher at 600-700 ms. Thus, most people feel like GEO internet lags when they’re doing interactive tasks, like video calls or live gaming.
Here are some popular activities and the recommended latency for each:
- Video calls: You’ll need 150 ms or less latency, which means LEO works best. If you have GEO internet, you’ll likely notice audio-visual sync issues or delays.
- Online games: Anything over 100 ms will feel laggy. Most online games will work on LEO, but highly competitive games are not recommended. GEO isn’t ideal for online gaming due to its limitations.
- Remote work and cloud-based apps: LEO works for most WFH tasks. You’ll notice significant delays with GEO.
Satellite Internet Data Policies
Satellite internet providers offer both high-speed and standard data speeds. Most will offer a data plan with a specific quantity of high-speed data, after which you’ll switch to slower, standard data for your unlimited plan.
When you reach that data cap, your provider may throttle, or deprioritize, your connection, which means it will slow down your download and upload speeds. You’ll still have unlimited data for the billing period, but it’ll be at slower speeds.
Two providers have unique takes on data use. Starlink’s Fair Use policy aims to manage the network by slowing heavy users or certain types of traffic when the network gets congested.
In contrast, HughesNet’s Priority Data + Unlimited Standard plan has a data cap on its Priority Data but allows you to buy tokens to get your high speeds back when you switch to Standard.
These data plans can vary not only based on the provider, but also on your location. Always read the fine print and make sure the plan you’re considering is available at your specific address.
The Best Satellite Internet Providers (2025)
The best satellite internet providers for 2025 are: Starlink, Viasat, and HughesNet. These three provide service over LEO, GEO, and GEO + Fusion hybrid networks, respectively. Here’s a closer look at what they offer.
Starlink (LEO)
BroadbandSearch has found Starlink’s low Earth orbit satellite internet offers lower latency and higher real-world speeds than GEO providers. It works well for rural customers who need responsive internet and can view the sky clearly from their homes.
Here are some of its features:
- Speeds and Latency: Up to 200 Mbps download and 15 Mbps upload, with latency between 20-50 ms. Speeds vary by location.
- Data policy: No data caps but uses a Fair Use Policy to manage the network during times of heavy usage.
- Pros: Lowest latency among satellite internet providers; speeds are suitable for HD streaming, cloud-based apps, and video calling.
- Cons: Upload speed doesn’t meet FCC requirements; performance varies based on network conditions and location; limited availability compared to GEO plans.
Viasat (GEO)
With a higher geostationary orbit, Viasat has slower speeds and higher latency, but it reaches more communities than LEO. It’s best for areas that don’t have LEO access but need basic internet for email and web browsing.
Here are some of its features:
- Speeds and Latency: Up to 150 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload, with latency typically between 600 and 700 ms, depending on plan and location.
- Data policy: The Essentials plan offers 150 GB high-speed data with unlimited standard data with deprioritization, and Unleashed features an unlimited high-speed data plan.
- Pros: This service has wide availability and offers unlimited high-speed data with some plans.
- Cons: High latency can make real-time tasks, like video conferencing and gaming, quite difficult.
HughesNet (GEO + Fusion Hybrid)
HughesNet offers a unique option that blends GEO satellite internet with some wireless capabilities to improve latency. This makes it ideal for people who need better responsiveness but can’t get LEO service.
Here are some of its features:
- Speeds & Latency: Up to 100 Mbps download and 5 Mbps upload speeds, with latency around 680 ms with Fusion that improves latency where available
- Data policy: A high-speed allotment with unlimited standard internet after reaching that cap, but customers can buy tokens to restore high speed if needed
- Pros: Available in many areas and offers the Fusion option to make it better for responsive tasks
- Cons: High latency can impact competitive gaming, and Fusion isn’t available everywhere
| Provider | Typical Download / Upload Speeds | Typical Latency | Data Policy | Price Range | Contract |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starlink (LEO) | 105 / 15 Mbps | 20-50 ms | Unlimited data with Fair Use Policy that manages traffic by plan. | Up to $120/mo depending on plan and area | Month-to-month |
| Viasat (GEO) | Up to 150 / Up to 4 Mbps | Average 600 ms | Essentials: 150 GB high-speed and unlimited standard (deprioritized). Unleashed: unlimited high-speed. | Up to $130/mo depending on plan and location. | Essentials:12-mo minimum; Unleashed: no annual commitment. |
| HughesNet (GEO + Fusion) | Up to 100 / Up to 5 Mbps | Average 600 ms | Unlimited data (speeds reduced after plan’s Priority/High-Speed data); Fusion blends satellite & wireless for better performance. | Up to $100/mo | 24-mo commitment. |
When to Choose: Starlink vs. Viasat vs. HughesNet
The right choice between Starlink, Viasat, and HughesNet will depend on your internet needs and your location. Always check your address to see which specific plans are available in your area, as this may dictate which plan is most practical for you.
Choose Starlink (LEO) if:
- You need the most responsive satellite option for video calls, light gaming, and cloud apps.
- You can manage with upload speeds between 10–20 Mbps and variable. performance by location and time of day.
- Your property has a clear view of the sky.
- You’re okay with equipment costs and periodic policy and price changes.
Choose Viasat (GEO) if
- LEO isn’t available or capacity-limited at your address.
- You want higher advertised download tiers (up to 150 Mbps).
- You prefer plan options like Essentials (150 GB high-speed + unlimited standard) or Unleashed (unlimited high-speed).
- You mostly browse and stream and can tolerate high latency, and upload speed is less critical.
Choose HughesNet (GEO / Fusion where offered) if:
- You want simple, widely available service with up to 100 Mbps download speed.
- Your use the internet primarily for email, browsing, SD/HD streaming and don’t frequently upload large files.
- Fusion is available in your area and want a GEO plan that feels more responsive for everyday tasks.
Quick tie-breakers
- Lowest latency: Starlink; pick if real-time responsiveness matters most.
- No LEO coverage: Viasat or HughesNet: confirm promos, contracts, and data policies.
- Data behavior: Need “unlimited high-speed”? Viasat Unleashed (where available). Need predictable basics? HughesNet.
- Always verify at your address: Plans, pricing, and performance vary block-by-block
Comparing Satellite Internet Performance with Other Types of Internet
| Connection Type | Download | Upload | Latency | Availability (U.S.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEO Satellite | Up to 200 Mbps | 10–20 Mbps | 20–50 ms | Growing; address-specific coverage |
| GEO Satellite | Up to 150 Mbps | 1–5 Mbps | 600–700 ms | Near-universal line-of-sight; weather/trees matter |
| Fiber | 300–5,000 Mbps | 300–5,000 Mbps (symmetrical) | 8–14 ms | Expanding, strongest in metro and suburban areas |
| Cable | 300–1,200+ Mbps | 10–35 Mbps (higher in some markets) | 13–22 ms | Widespread in urban and suburban areas |
| DSL | 1–100 Mbps | 0.5–10 Mbps | 20–61 ms | Shrinking legacy footprint; varies by telco plant |
| 5G Home Internet | 130–400+ Mbps | 12–55 Mbps | 16–28 ms | Address-specific; strongest in 5G-covered areas |
Bottom Line
Choosing the right satellite internet plan starts with matching the tech to your needs. Determine what you use the internet for and find a plan that fits.
Remember that the new FCC benchmark is 100 Mbps download and 20 Mbps upload, which only LEO comes close to matching. GEO sometimes don’t meet this benchmark.
Data policies are another factor to consider, as these directly impact your experience. Remember, “unlimited” means unlimited standard data on many plans after you use your high-speed internet bucket, and your speeds may slow down during heavy usage times.
Your address also matters. These plans can vary from one block to the next. Always check your specific address before choosing one.
Finally, when making your choice, consider the full cost. In addition to the monthly cost, consider the cost of the equipment, line-of-sight requirements, installation factors, and contract length.
If you’re ready to start comparing plans, use the ZIP code search tool on BroadbandSearch to compare available options side-by-side. If you find that LEO satellite internet isn’t available in your area, remember that GEO can cover basics like email and browsing. You may even be able to stream with a little patience.
FAQ
Do any satellite plans meet 100/20?
Starlink can reach download speeds up to 200 Mbps, depending on location and network conditions, but upload speeds top out at 15 Mbps, which is below the FCC benchmark.
Do satellite internet providers offer unlimited data?
Yes, but the unlimited data is not always high-speed data. Most plans, with the exception of Viasat Unlimited, have a data cap. Once you reach that cap, your speed slows down until the billing period ends.
How fast is HughesNet now?
HughesNet is now offering 100 Mbps download speed, but it still has a slow upload speed of up to 5 Mbps.
Can I game over satellite internet?
GEO satellite internet is not ideal for gaming due to high latency, but Starlink, which is LEO, has a lower latency and faster speeds. Since the recommended latency is 50 ms or less, LEO will work. However, highly competitive and demanding games will struggle over any satellite internet connection.
Which satellite internet provider is the cheapest?
HughesNet offers the lowest price point among Starlink, HughesNet, and Viasat, the three satellite internet providers recommended by BroadbandSearch. Cost varies by plan but starts around $50/month.
What latency should I expect? (LEO vs GEO)
LEO satellite internet (Starlink) has an average latency of 20-50 ms, while GEO (Viasat and HughesNet) has an average that falls between 600-700 ms.